PRAZOSIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Prazosin
IUPAC nomenclature
[4-(4-Amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl](2-furyl)methanone.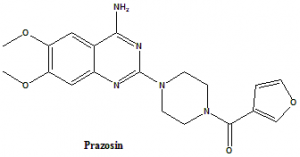
Classification
Prazosin belongs to class α1-antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 383.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form. |
| 3 | Melting point | 277-280°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 1.4 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.3 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Quinazoline, piperazine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
i. The drug inhibits postsynaptic α1-adrenoceptors.
ii. This results in inhibition of vasoconstricting effect of catecholamines.
iii. This further leads to blood vessel dilation. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Cyclohexanediamine derivatives are having no potency and selectivity
- Dialkylpiperizine compounds are having high affinity and selectivity for α1-adrenoceptors.
- Cis Derivatives are most potent. [2]
Method of synthesis
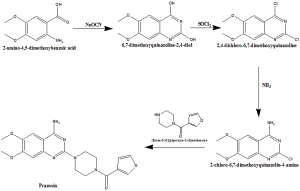
i. 2-amino-4,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid reacts with sodium cyanate to give 6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline-2,4-diol.
ii. Later compound undergoes chlorination to give 2,4-dichloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline.
iii. It than reacts with ammonia to produce 2-chloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine.
iv. Latter compound reacts with (furan-3-l)(piperazin-1-yl) methanone to give prazosin.
Therapeutic Uses
Prazosin is used for:
- Treatment of high blood pressure
- Prevention of strokes
- Prevention of heart attacks
- During kidney problems
Side Effects
Side effects of Prazosin are:
- Nausea
- Palpitations
- Weakness
- Lack of energy
- Headache
- Lightheadedness
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
MCQs
Q.1 Correct statements related with the physicochemical properties of drug Prazosin?
I. Molecular weight is 383.4 gm/mol
II. Melting point is approx. 150°C
III. Octanol/water partition coefficient is 5.4
a) I
b) I, II
c) II, III
d) I, II, III
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Prazosin | A. (RS)-4-(2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-yl]amino}ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol |
| ii. Metaraminol | B. 2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole |
| iii. Naphazoline | C. 3-[(1R,2S)-2-amino-1-hydroxypropyl]phenol |
| iv. Dobutamine | D. [4-(4-Amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-1-piperazinyl](2-furyl)methanone |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-D, ii-C, iii-B, iv-A
Q.3 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug……
I. Inhibition of postsynaptic α1-adrenoceptors.
II. Inhibition of vasoconstricting effect of catecholamines.
III. Stimulation of vasoconstricing effect of catecholamines
IV. Blood vessels dilation
a) I – III – IV
b) I – II – IV
c) II – III – IV
d) I – II – III – IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Prazosin: selective α2-adrenergic antagonist
- Clodine: Selective α2-adrenergic agonist
- Tolazoline: nonselective α-adrenergic antagnist
- Methoxamine: selective α2-adrenergic agonist
a) FTTT
b) FTTF
c) TTTT
d) FTFT
Q.5 Cis derivatives of prazosin will have?
a)Most potency
b) Most selectivity
c) Least potency
d) Least selectivity
Q.6 The correct sequence for the steps for synthesis of drug prazosin from 2-amino-4,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid?
I. Reaction with (furan-3-l)(piperazin-1-yl)mehanone
II. Chlorination
III. Reaction with sodium cyanate
IV. Reaction with ammonia
a) III – II – IV – I
b) III – II – I – IV
c) I – III – II – IV
d) II – IV – I – III
Q.7 Side effect of drug prazosin include?
a) Lack of energy
b) Palpitations
c) Light headedness
d) All of the above
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-b
4-c
5-a
6-a
7-d