RIBAVIRIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
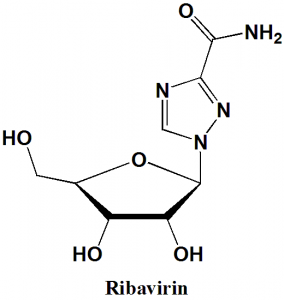
Ribavirin
IUPAC nomenclature
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide.
Classification
Ribavirin is a synthetic guanosin nucleoside and antiviral agent.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 244.2 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 174-176°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | -1.85 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Triazole, furane |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 4 |
Mechanism of Action
- Ribavirin activates by adenosine kinase and converts into its active metabolites, mono-, di- and tri-phosphate metabolites.
- Ribavirin triphosphate (RTP) is the predominant metabolite which binds to the neucleotide binding site and inhibits the viral mRNA polymerase. Due to this, binding of correct neucleotides is prevented and there is decrease in viral replication and production of defective virions.
- RTP also inhibits viral mRNA 2’-O-methyltransferase and mRNA guanyltransferase of dengue virus. This inhibition disturbs the posttranslational capping of the 5’ end of viral mRNA through prevention of the cap methylation step.
- Ribavirin monophosphate mimics inosin 5’- monophosphate and competitively inhibits the IMPDH. This decreases the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides and hence, decreases the GTP pool which results in the decrease in the viral protein synthesis and replication rate.
- Ribavirin induces mutation in the target virus. RTP pairs with CTP and UTP to block HCV RNA elongation. This results in premature termination of the nascent HCV RNA and production of defective virions due to mutations.
- Ribavirin enhanced induction of interferon-related genes, including the interferon-α receptor, and down-regulation of genes involved in interferon inhibition, apoptosis, and hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro
Structure Activity Relationship
- 1,2,4-triazole ring, carboxamide group and ß-D-ribofuranosyl moiety are important for antiviral activity.
- 3-carboxamide derivatives and thiocarboxamide derivatives are only active against DNA viruses.
- 5’ imidazole riboside derivatives show antiviral activity with hydrogen or halide. Larger substitutions shows lesser activity.
- Substitution of the 5’ carbon with hydroxyl group results in a compound with antibacterial as well as antiviral properties, but is having unacceptable toxicity.
- Replacement of the 5’ carbon with amino group results in activity only against viruses. [1]
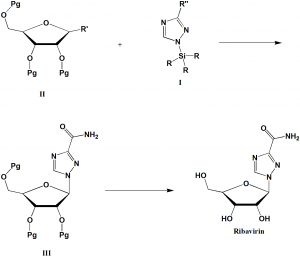
Method of synthesis
During the synthesis of ribavirin, there is coupling of preformed triazole nucleus with protected derivatives of sugar. There is activation of the triazole nucleus with silylating agents followed by reaction with the appropriate protected ribofuranose.
R’ is an O-acetyl group or a halogen.
Pg is a group protecting the hydroxyl function
R’’ is a carbon methoxy group.
R is methyl group.
In the final step, the deprotection of the sugar and conversion of the ester group into amide produces Ribavirin. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Ribavirin is used for:
- Treatment of chronic Hepatitis C infection
- Investigation drug in Clinical Stages for SARS-CoV-2 Treatment
Side Effects
Side effects of ribavirin are:
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Headache
- Stomach upset
- Cough
- Trouble sleeping
- Blurred vision
- Joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Pale skin and eyes
- Dark urine
- Weakness
MCQ
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug ribavirin-
| i. 1,2,4-triazole ring | A. Important for antiviral activity |
| ii. 3-carboxamide derivative | B. Shows antiviral activity with halide |
| iii. 5’ imidazole riboside derivatives | C. only active against DNA viruses |
| iv. Substitution of 5’ carbon with hydroxyl group | D. compound having antibacterial and antiviral properties |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
d) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Ribavirin: 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide.
- Quazepam: 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione
- Lopinavir: 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a + 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1b
- Benztropin: (RS)-2-[{4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino]ethanol
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFTF
d) TFTT
Q.3 Physical appearance of ribavirin drug is?
a) White powder
b) Red powder
c) Yellow liquid
d) Transparent oil
Q.4 Ribavirin acts as a/an?
a) Alkylating agent
b) Mutagen
c) Enzyme inhibitor
d) Agonist
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug ribavirin?
a) Treatment of hepatitis C
b) Treatment of anxiety
c) Treatment of influenza
d) Treatment of HIV
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Ezpiclone: Nonbezodiazepine sedative-hypnotic
II, Ribavirin: Synthetic guanosin neucleoside
III. Oxazepam: ß-inhibitor
IV. Homatropin: Acetylcholine nicotinic antagonist
a) II, III
b) III, I
c) II, IV
d) I, II
Q.7 Octanol/water partition coefficient of ribavirin is?
a) 0.2
b) 2.6
c) -1.85
d) -2.0
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-a
4-b
5-a
6-d
7-c