SCOPOLAMINE (HYOSCINE) Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
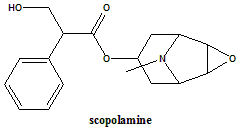
Scopolamine (hyoscine)
IUPAC nomenclature
(–)-(S)-3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropionic acid (1R,2R,4S,5S,7α,9S)-9-methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo[3.3.1.02,4]non-7-yl ester
Classification
Scopolamine is a acetylcholine antagonist-muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 303.35 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in viscous liquid form. |
| 3 | Melting point | 59°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform or acetone. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | Log Kow = 0.98 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 6 |
Mechanism of Action
Scopolamine interfere with the transmission of the nerve impulses by Ach in the parasympathetic nervous system. It particularly acts for the vomiting center. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most protect derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
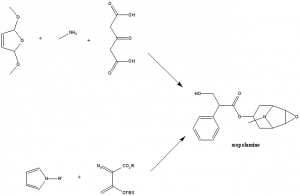
Method of synthesis
A modified Robinson-Schopf reaction or [4+3] cycloaddition can help in synthesizing the scopolamine. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Scopolamine is used for:
- Prevention of nausea
- Prevention vomiting
Side Effects
Side effects of scopolamine are:
- Blurred vision
- Widened pupils
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Decreased sweating
- Constipation
- Itching and redness of skin
MCQ
Q.1 Maximum potency obtained of scopolamine when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is?
a) 1 carbon unit
b) 2 carbon unit
c) 3 carbon unit
d) 4 carbon unit
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Bethanchol: 2-(Carbamoyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylpropan-1-aminium.
- Glycopyrollate: (–)-(S)-3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropionic acid (1R,2R,4S,5S,7α,9S)-9-methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo[3.3.1.02,4]non-7-yl ester
- Scopolamine: (1,1-dimethylpyrrolidin-1-ium-3-yl) 2-cyclopentyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
- Propranolol: (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
a) FTTF
b) FFFT
c) TFFT
d) TTTT
Q.3 Physical appearance of Hyoscine is?
a) White crystalline powder
b) Viscous liquid form
c) Red crystals
d) Granular appearance
Q.4 Scopolamine produces effect on?
a) Nicotinic receptors
b) Muscarinic receptors
c) Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Scopolamine?
a) Treatment of peptic ulcers
b) Treatment of Blurred vision
c) Prevention of nausea and vomitting
d) None of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Bethanchol: Cholinergic agonist
II. Glycopyrollate: Acetylcholine antagonist
III. Scopolamine: Nicotinic receptors antagonist
IV. Propranolol: α-adrenergic antagonist
a) I , III
b) I , IV
c) III
d) I, II
Q.7 Number of chiral carbons scopolamine having?
a) 0
b) 3
c) 6
d) 9
FREE GPAT online Test: Participate: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-b
2-c
3-b
4-b
5-c
6-d
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Renner UD, Oertel R, Kirch W. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in clinical use of scopolamine. Therapeutic drug monitoring. 2005 Oct 1;27(5):655-65. [2] Nocquet PA, Opatz T. Total Synthesis of (±)‐Scopolamine: Challenges of the Tropane Ring. European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2016 Feb;2016(6):1156-64.