SECOBARBITAL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
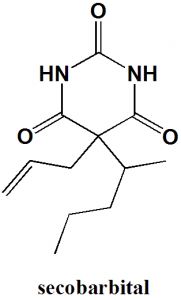
Secobarbital
IUPAC nomenclature
5-(pentan-2-yl)-5-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione
Classification
Secobarbital is a barbiturate sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 238.28g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White amorphous or crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 100°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.97 |
| 5 | Solubility | Very soluble in water |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrimidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 2 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Drug binds with different binding sites associated with chloride ionopore at the GABAA
ii. This results in increase in the duration of time for the opening of the chloride ionopore.
iii. As a result, the post synaptic inhibitory effect of GABA in the thalamus is prolonged.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Tri-keto form is most stable in aqueous solution.
- 4,6-dialcoholic tautomeric forms are least stable in aqueous solution.
- 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid is the prime requirement for the barbiturates to be sedative hypnotics.
- Esterification of either of the 1,3-diazine nitrogens decreases hypnotic activity.
- Substitution of either of the 1,3-diazine nitrogens with aliphatic carbons retains the anticonvulsive properties.
- Esterification of the 5th-position substituents yields agents with analgesic activity but with weak hypnotic properties.
- Introduction of the polar functional group at the 5th– position yields compounds which are fully devoid of sedative-hypnotic or anticonvulsive activity.
- As the number of carbons at R2 carbon increases, the lipophillicity of the drug increases.
- Modification of the 2nd-position oxygen of the barbiturate backbone with sulfur atom yields thiobarbiturate derivatives with increased lipophillicity, shorter duration of action, faster time of onset compared to oxy-derivative. [1]
Method of synthesis
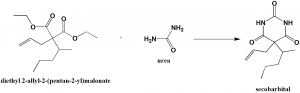
Secobarbital can be synthesized by reaction of α-allyl-α-(1-methylbutyl)-malonic ester with urea.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Secobarbital is used for:
- Treatment of seizures
- For producing sedation during the time of anxiety.
Side Effects
Side effects of Secobarbital are:
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Loss of coordination
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Restlessness
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
- Shallow breathing
MCQ
Q.1 Choose the correct statements related to the physicochemical properties of drug secobarbital-
I. Molecular weight is 238.28 gm/mol
II. White amorphous crystalline powder
III. It is very soluble in water
IV. Melting point is 325K
a) I, II
b) I, II, III
c) III, IV
d) I, III, IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct Trade names.
| i. Secobarbital | A. Mustine |
| ii. Mechlorethamine | B. Ipamide |
| iii. Cyclophosphamide | C. Saconal |
| iv. Ifosfamide | D. Cycloxan |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
Q.3 Effect produced due to binding of secobarbital with GABAA receptor??
a) Increase in GABA affinity for GABA receptor
b) Decrease in GABA affinity for GABA receptor
c) Blocking of GABA receptor for GABA
d) None of the above
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Secobarbital: Neuraminidase inhibitor analogue
- Phenobarbital: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- Ribavirin: Conventional nucleoside analogue
- Tipranavir: HIV protease inhibitor
a) FFTT
b) TTTF
c) FTTT
d) TFTT
Q.5 Esterification of either of the 1,3-diazine nitrogens of secobarbital results in?
a) Decrease in hypnotic activity
b) Increase in hypnotic activity
c) Bioavailability increases
d) Bioavailability decreases
Q.6 Type/s of ring present in the structure of secobarbital?
I. Pyrimidine
II. Indole
III. Benzene
a) II, III
b) I, II
c) I
d) I, II, III
Q.7 Side effect of drug Secobarbital?
a) Insomnia
b) Dizziness
c) Loss of coordination
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-a
4-a
5-a
6-c
7-d