STAINING Principle, Reagents, Procedure, Steps, Results Interpretation of gram staining and acid fast staining
STAINING
Introduction
- A stain is a chemical which can bind with the cellular components and give them color. Different dyes which can be used for staining are basic/cationic dyes (methylene blue, crystal violet, malachite green, safranin) and anioninc/acidic dyes (eosin and picric acid).
- Cationic dyes bids with the negatively charged cellular components such as those are present in cell membrane, whereas, anionic dye binds with positively charged cellular components. [1]
Simple staining
Simple staining is the use of single dye which helps in revealing the basic cell shapes and cell arrangements. Stains which can be used in the simple staining are crystal violet, carbolfuchsin, safranin and methylene blue.
Differential staining
It is the use of two or more dyes to differentiate between two different kinds of organisms or two different parts of organisms. Two common methods for differential staining are:
- The gram staining
- The acid fast staining
The gram staining
Gram staining is based on the amount of peptidoglycan present in the cell wall of bacteria.
- Those bacteria which have thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall are can retain the primary stain and are known as gram-positive bacteria.
- Those bacteria which have thin layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall cannot retain the primary stain and are called gram-negative bacteria.
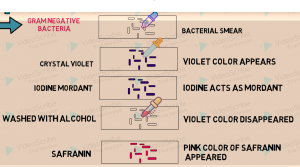
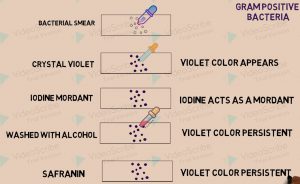
Steps for gram staining:
i. Bacterial smear is prepared on a slide.
ii. Crystal violet stain is added on the smear.
iii. After 1 min. stain is drains and rinsed with water and iodine mordant is added on the smear.
iv. After 1 min. iodine is drained and slide is rinsed with water.
v. Decolorizing with the help of alcohol and rinsing immediately
vi. Safranin is added, remains there for 1 min. and then drained and rinsed.
vii. Slide is looked under compound microscope.
Result interpretations:
Gram positive bacteria appear purple in color, whereas, gram negative bacteria retains the color red(pink) color of safranin dye.
The Ziehl-Neelsen acid fast staining
Tuberculosis and leprosy causing pathogens can be stained with the help of this technique. Organisms of genus Mycobacterium can be stained by acid-fast staining method. The lipid component in the acid fast bacteria is responsible for this property.
Steps:
i. Bacterial smear is prepared on a slide.
ii. Carbolfuchsin is added on the smear and heated
iii. After draining and rinsing, it is decolorized using 3% HCl in 95% ethanol and rinsed again.
iv. It is then stained with methyene blue dye.
Result interpretation:
Those bacteria belonging to the genus Mycobacterim will only retain the bright red color. Others will lose the red carbolfuchisin color.
MCQs
1. An example of cationic dye is?
a. Malachite green
b. Eosin
c. Picric acid
d. All of the above
2. Simple staining is used for?
a. Studying cellular organelles
b. Revealing basic cell shapes
c. Differentiating two different types of cell
d. Understanding the working of mitochondria
3. Gram staining is the type of?
a. Simple staining
b. Differential staining
c. Acid-fast staining
d. Special staining
4. Gram staining is based on?
a. Amount of lipid present in cell wall
b. Porosity of cell membrane
c. Amount of peptidoglycan present in cell wall
d. Type of flagella bacteria has
5. Correct steps for gram staining can be?
I. Addition of iodine mordant
II. Addition of crystal violet
III. Addition of safranin
IV. Decolorization with alcohol
II – I – IV – III
III – I – IV – II
II – IV – I – III
III – IV- I – II
6. Type of dyes used in the Ziehl-Neelsen acid fast staining?
I. Crystal violet
II. Carbolfuchsin
III. Safranin
IV. Methylene blue
a. I, II
b. I, III
c. II, III
d. II, IV
7. Match the following types of staining with their correct applications-
| i. Gram staining | A. Revealing basic cell shape |
| ii. Acid fast staining | B. Differentiating between gram positive and gram negative bacteria |
| iii. Simple staining | C. Identification of mycobacterium |
a. i-C, ii-B, iii-A
b. i-B, ii-C, iii-A
c. i-B, ii-A, iii-C
d. i-A, ii-B, iii-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-b
4-c
5-a
6-d
7-b