Notes on Sulfonamide Pharmacology, Classification, Mechanism of Action, Adverse drug reactions, Spectrum on Bacteria and MCQ for NEETPG, GPAT
Sulfonamide Pharmacology, Classification, Mechanism of Action, and Spectrum on Bacteria
Pharmacology and Classification
Sulfonamides are a class of synthetic antimicrobial agents, the first effective antibacterial drugs, introduced in the 1930s. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit bacterial growth by interfering with folate synthesis. Sulfonamides are classified based on their chemical structure, duration of action, and clinical use:
- Short-acting: Sulfadiazine, Sulfisoxazole (half-life <12 hours).
- Intermediate-acting: Sulfamethoxazole (half-life 10-12 hours).
- Long-acting: Sulfadoxine (half-life >100 hours).
- Topical: Silver sulfadiazine (used for burns).
- Special purpose: Sulfasalazine (for inflammatory bowel disease).
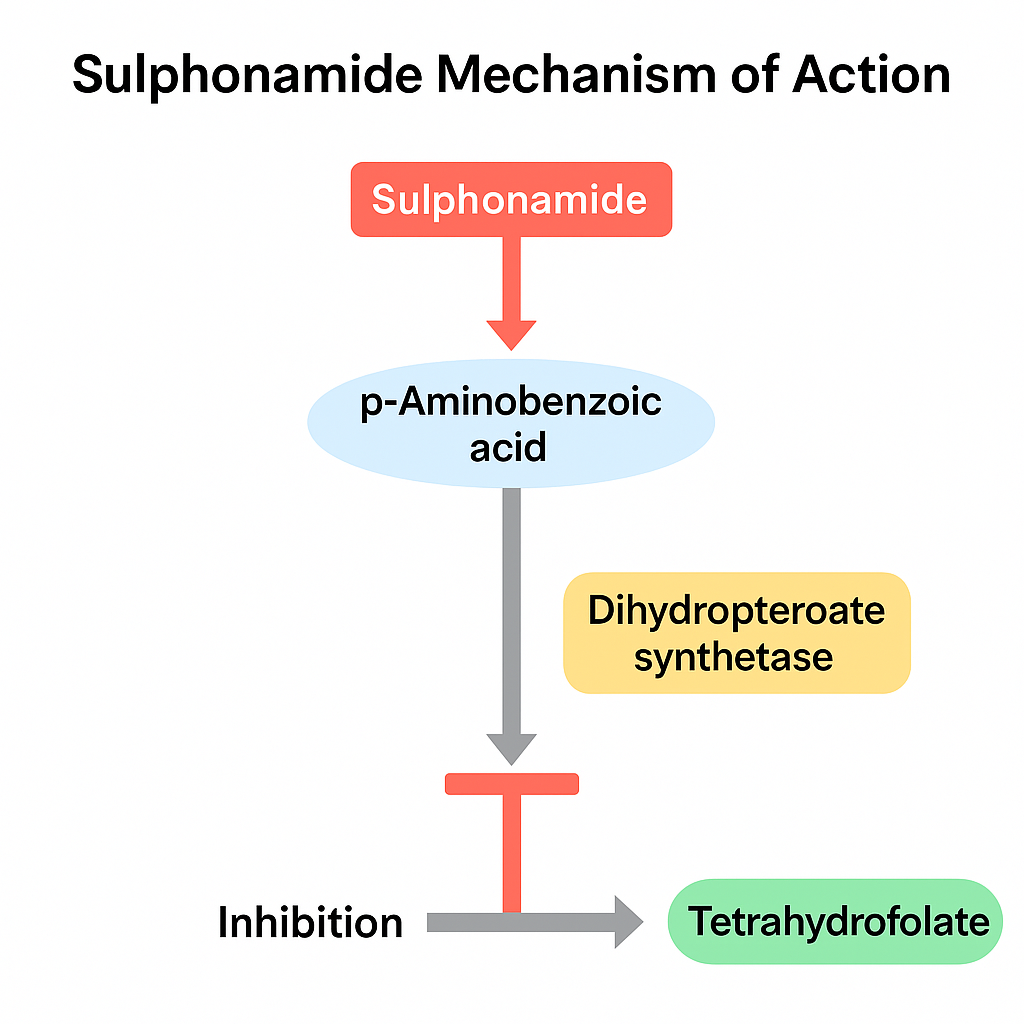
Mechanism of Action
Sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) in the folic acid synthesis pathway. Bacteria synthesize folate de novo, a precursor for DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. Sulfonamides mimic para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate for DHPS, binding to the enzyme’s active site and blocking the incorporation of PABA into dihydropteroate. This inhibits tetrahydrofolic acid production, halting bacterial growth. Human cells, which acquire folate from the diet, are unaffected.
Diagram (Text-based representation):
PABA → [Dihydropteroate Synthase] → Dihydropteroate → Tetrahydrofolic Acid → DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis
↓ (Sulfonamide competes with PABA)
Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
Spectrum on Bacteria
Sulfonamides are broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against:
- Gram-positive bacteria: Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Shigella spp.
- Other: Chlamydia, Nocardia, some protozoa (e.g., Toxoplasma gondii). Resistance is common due to altered DHPS or increased PABA production, limiting efficacy against many modern pathogens like Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Chart on Various Sulfonamides with Uses, Adverse Drug Reactions, and Drug-Drug Interactions
| Sulfonamide | Uses | Adverse Drug Reactions | Drug-Drug Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfadiazine | Urinary tract infections, toxoplasmosis | Rash, fever, Stevens-Johnson syndrome | Warfarin (increases bleeding risk) |
| Sulfisoxazole | Otitis media, urinary tract infections | Nausea, hematuria, photosensitivity | Phenytoin (increased toxicity) |
| Sulfamethoxazole | (Combined with trimethoprim as Bactrim) for Pneumocystis pneumonia, UTIs | Allergic reactions, bone marrow suppression | Methotrexate (enhanced toxicity) |
| Sulfadoxine | Malaria (with pyrimethamine) | Severe skin reactions, hepatotoxicity | Anticoagulants (altered efficacy) |
| Silver Sulfadiazine | Topical treatment for burns | Local irritation, argyria (rare) | Topical anesthetics (reduced efficacy) |
| Sulfasalazine | Ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis | Gastrointestinal upset, leukopenia | Digoxin (reduced absorption) |
Notes:
- Adverse Reactions: Sulfonamides can cause hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., rash, anaphylaxis) and rare but serious conditions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome. They are contraindicated in patients with sulfa allergies or G6PD deficiency due to hemolysis risk.
- Drug Interactions: Sulfonamides can displace other drugs from plasma proteins (e.g., warfarin, phenytoin), increasing their effects, and may enhance methotrexate toxicity by competing for renal excretion.
For more MCQ based on Sulphonamide Join GPAT TEST Series
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) on Sulfonamides
- What is the primary mechanism of action of sulfonamides?
a) Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
b) Competitive inhibition of dihydropteroate synthase
c) Disruption of bacterial cell membranes
d) Inhibition of protein synthesis
Answer: b) - Which of the following is a long-acting sulfonamide?
a) Sulfadiazine
b) Sulfadoxine
c) Sulfisoxazole
d) Sulfamethoxazole
Answer: b) - Sulfonamides are effective against which bacterial group?
a) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
b) Streptococcus pneumoniae
c) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
d) All of the above
Answer: b) - What is a common adverse drug reaction of sulfonamides?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Stevens-Johnson syndrome
c) Increased blood clotting
d) Hyperkalemia
Answer: b) - Which sulfonamide is used topically for burn wounds?
a) Sulfasalazine
b) Silver sulfadiazine
c) Sulfamethoxazole
d) Sulfadoxine
Answer: b)