Suspending agents, Properties of Suspending agents and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Suspending Agents: Suspending agents are similar to viscosifiers in a formulation. They function by keeping small particles of active, and possibly other excipients, suspended during the shelf life of the product.
Examples – Acacia, Agar, Carbomer, Carboxymethyl cellulose sodium (CMC), Carrageenan, Microcrystalline cellulose and Sodium Carboxymethyl cellulose Co-processed, Colloidal silicon dioxide, Dextrin, Guar gum, Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), Hypromellose (HPMC), Kaolin, Methylcellulose, Pectin, Polyvinyl Alcohol, Povidone, Tragacanth.
1.Acacia:
INN: Acacia
Synonyms: Gum Arabic
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Acacia (9000-01-5)
Molecular Formula: A complex containing principally calcium, magnesium, and potassium salts of the polysaccharide arabic acid, which on acid hydrolysis yields L-arabinose, Lrhamnose, D-galactose, and an aldobionic acid containing Dglucuronic acid and D-galactose.
Structure: A very complex gum, which has no specific structural formula.
Description: White to yellowish white, angular microscopic fragments, spheroidal tears or powder.
Properties: Soluble 1 in 20 of glycerin and propylene glycol, Insoluble in alcohol (ethanol 95%) and 1 in approximately 2.7 of water at room temperature; 5% aqueous solution pH 4.5–5.0; moisture content 8–13%; specific gravity 1.35-1.49; Solution viscosity varies, depending upon the source of the material, presence of salts (calcium, sodium, etc.), the pH of the solution, and storage conditions of the acacia prior to use.
Incompatibilities: Alcohol or alcoholic solutions precipitate acacia as a stringy mass, when the alcohol amounts to more than about 35% of the total volume. Solution is affected by dilution with water. The mucilage is destroyed through precipitation of the acacia by heavy metals. Borax also causes a precipitation that is prevented by glycerin. It contains calcium and, therefore, possesses the incompatibilities of this ion.
Uses: As a suspending agent for insoluble substances in water, in the preparation of emulsions.
2.Agar:
INN: Agar-Agar
Synonyms: Agar, Vegetable Gelatin; Gelosa; Chinese or Japanese Gelatin
Molecular Formula: Varies, but the commonality is a 1–3 linked β-D-galactopyranosyl unit joined by a 1–4 linkage to a 3,6-anhydro α-D-galactopyranosyl unit.
Structure: Varies greatly, depending on the source of the material.
Description: A white to off-white hydroscopic powder.
Properties: Insoluble in cold water and alcohol; slowly solubilizes in hot water to approximately 1–1.5% w/w. When cooled, the solution produces a stiff gel that can melt at 60–100°C, depending on composition.
Incompatibilities: Salt solutions can impact the gel formation of the polymer.
Use: Substitute for gelatin, gelling agent.
3.Carboxy Methyl cellulose sodium:
INN: Carmellose sodium
Synonyms: Cellulose gum, CMC sodium
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose, carboxymethyl ether, sodium salt [9004-32-4]
Structure:
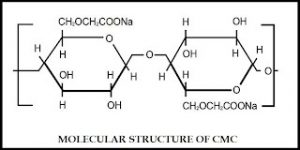
Description: Depending on the grade, CMC is a white to offwhite odorless powder of varying particle size.
Properties: This hygroscopic material should contain less than 10% water, density of 0.7 g/cc (tapped), viscosities of a 1%w/w aqueous solution can range from 10 to 8000 mPa.s, depending on the grade being evaluated.
Incompatibilities: Strongly acidic solutions and soluble salts of iron, aluminum, zinc, and mercury. Complexes can be formed with gelatin and pectin.
Uses: As a suspending agent for liquid formulations, as a binder for tablets or capsules (in solution) and as a coating agent on tablets.
4.Microcrystalline cellulose And sodium carboxymethyl cellulose co-processed:
Synonyms: Cellulose gel
Description: Tasteless, odorless, white to off-white, coarse to fine powder.
Properties: pH (dispersion) 6–8; swells in water, producing, when dispersed, a white, opaque dispersion; at concentrations above 2%, can form a thixotropic gel; insoluble in water, organic solvents, and dilute acids; soluble in strong acids. Temperature of liquid at time of dispersion will affect viscosity.
Incompatibilities: High concentrations of dissolved salts.
Uses: As a thixotropic suspending agent.
5.Colloidal silicon dioxide:
INN: Colloidal anhydrous silica; Silica colloidalis anhydrica;
Colloidal silicon dioxide
Synonyms: Colloidal silica; fumed silica; light anhydrous silicic acid; silicic anhydride
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Silica (7631-86-9)
Structure: SiO2 (60.08)
Description: Light, white, non-gritty powder.
Properties: Insoluble in water or acids (except hydrofluoric); dissolved by hot solutions of alkali hydroxides; particle size approximately 15 nm; 4% solution pH 3.5-4.4.
Incompatibilities: Diethylstilbestrol (DES).
Uses: As a moisture scavenger, glidant, or anti-caking agent in tablets and powders; as a suspending and thickening agent in liquid and semi-solid preparations.
6.Guar gum:
INN: Guar Gum, Guar galactomannan
Synonyms: Guar flour, jaguar gum
Chemical Name & CAS Number Galactomannan polysaccharide (9000-30-0)
Molecular Formula: (C6H12O6)n
Structure:
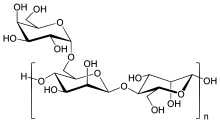
Description: Odorless, white to off-white, bland tasting powder.
Properties: 1% dispersion pH 5.0–7.0; density 1.492 g/cc; insoluble in hot or cold water, but will swell to form a thixotropic gel.
Incompatibilities: Aalcohol, acetone, tannins, strong acid, or alkalis will cause the gel to break up; guar interferes with the absorption of penicillins.
Uses: As a binder or disintegrant in tablets and capsules; suspending and thickening agent for liquids.
7.Hydroxy Propyl cellulose:
INN: Hydroxypropylcellulose; hydroxypropyl cellulose
Synonyms: Cellulose, hydroxypropyl ether; HPC; hyprolose; hydoxypropylated cellulose
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose, 2-hydroxypropyl ether (9004-64-2)
Description: Off-white, odorless, tasteless powder; softens at 130°C; burns completely at about 475°C in N2 or O2; refractive index (2% solution) about 1.337; pH (aqueous solution) 5–8.5; solutions are nonionic.
Structure:
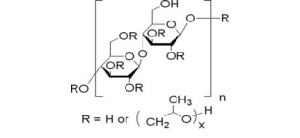
Properties: Soluble in water below 38°C (insoluble above 45°C); soluble in many polar organic solvents; pH 5.0–8.5 for 1% aqueous solution; density 0.5g/cc.
Uses: As a binder, granulating agent, and film-coating agent in the manufacture of tablets; an alcohol-soluble thickener and suspending agent for elixirs and lotions; and a stabilizer for emulsions.
8.Hydroxy Propyl Methylcellulose (hypromellose):
INN: Hypromellose; Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose
Synonyms: HPMC; MHPC
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose, 2-hydroxypropyl methyl ether (9004-65-3)
Structure:
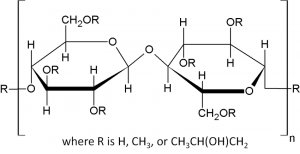
Description: White to slightly off-white, fibrous or granular, free-flowing powder.
Properties: Swells in water and produces a clear to opalescent, viscous, colloidal mixture; undergoes reversible transformation from sol to gel on heating and cooling, respectively. 1% aqueous solution pH 5.5–8.0; density 1.326g/cc; particle size and viscosity will vary, depending upon the grade.
Uses: As a protective colloid that is useful as a dispersing and thickening agent, also used in the preparation of sustained release matrix tablets and as a film coating material.
9.Methylcellulose:
INN: Methylcellulose; Methylcellulosum
Synonyms: Benecel; MC; Methocel
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Cellulose methyl ether (9004-67-5)
Molecular Formula: Long chain substituted cellulose, where 27–32% of the hydroxyl groups are in the form of methyl ether.
Structure:
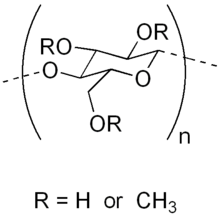
Description: White to off-white, odorless, tasteless granule or powder.
Prosperities: pH of 1% solution 5.5–8.0; density 1.341 g/cc; insoluble in hot water (disperses), in cold water disperses to form a colloidal dispersion that is clear.
Incompatibilities: High concentrations of electrolytes increase viscosity; incompatible with aminacrine hydrochloride, chlorocresol, mercuric chloride, phenol, tannic acid, and paraben preservatives.
Uses: As a protective colloid for many types of dispersed substances; an effective stabilizer for oil-in-water emulsions; a granulating solution for tablets and capsules. It has been formulated into many coating systems.
10.Polyvinyl Alcohol:
INN: Polyvinyl alcohol
Synonyms: PVA; vinyl alcohol polymer
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Ethenol, homopolymer (9002-89-5)
Molecular Formula: (C2H4O)n
Structure:
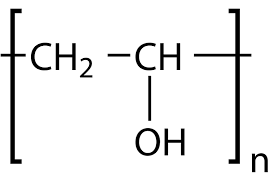
Description: White to cream-colored powder or granules; odorless.
Properties: Freely soluble in water; insoluble in organic solvents; solution effected more rapidly at somewhat elevated temperatures; viscosity is grade dependent.
Use: As a suspending agent; a lubricant and protectant in ophthalmic and nasal preparations, such as artificial tears, contact-lens cleaners, and nasal sprays.
11.Povidone:
INN: Povidone; Polyvidonum
Synonyms: poly[1-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethylene]; polyvidone; ployvinvypyrrolidone; PVP; 1 vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone polymer
Chemical Name & CAS Number: 1-ethenyl-2-Pyrrolidinone homopolymer (9003-39-8)
Molecular Formula: (C6H9NO)n
Structure:
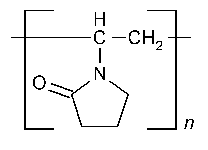
Description: White to creamy white, odorless powder, hygroscopic powder.
Properties: Soluble in water, alcohol, or chloroform; insoluble in ether; pH (1 in 20 solution) 3 7; density 1.18 g/cc; melting point 150°C; particle size is grade dependent.
Uses: As a suspending agent in liquid products and a binder in wet granulation processes.
12.Tragacanth:
INN: Tragacanth; Tragacantha
Synonyms: Gum Tragacanth; Gum Dragon; Goat’s Thorn; Persian tragacanth
Chemical Name & CAS Number: Tragacanth gum (9000-65-1)
Molecular Formula: A mixture of water soluble and insoluble polysaccharides derived from dried gum of Astragalus gummifer. It’s comprised of 60–70% bassorin and 30–40% soluble gum (tragacanthin).
Description: Flattened, lamellated, frequently curved fragments or straight or spirally twisted linear pieces 0.5-2.5 mm in thickness; white to weak-yellow in color; translucent; horny in texture; odorless; insipid, mucilaginous taste. When powdered, it is white to yellowish white.
Properties: 1% dispersion pH 5–6; practically insoluble in water and alcohol; when mixed with water, it does swell to 10 times its original volume creating a viscous dispersion.
Incompatibilities: Above pH of 7 tragacanth, reduces activity of benzalkonium chloride.
Use: As a suspending agent; granulating agent.
Multiple choice questions:
1.They function by keeping small particles of active, and possibly other excipients, suspended during the shelf life of the product. Identify such agents.
a)emulsifying agents
b)suspending agents
c)wetting agents
d)all of these
2.Which of the following are advantages of suspending agents?
a)Acacia
b)Agar
c)Carbomer
d)All of these
3.Hypromellose is
a)HPC
b)HPMC
c)CMC
d)All of these
4.Gum Arabic is synonym of
a)Acacia
b)Agar
c)Tragacanth
d)All of these
5.Synonym of Agar is/are
a)Vegetable Gelatin
b)Gelosa
c)Chinese or Japanese Gelatin
d)All of these
6.Carboxy Methyl cellulose sodium is used as
a)suspending agent for liquid formulations
b)a binder for tablets or capsules (in solution)
c)a coating agent on tablets
d)all of these
7.Microcrystalline cellulose And sodium carboxymethyl cellulose co-processed have which of the following physical characteristics?
a)Tasteless
b)Odorless
c)White to off-white
d)All of these
8.Colloidal silicon dioxide is incompatible with
a)Diethylstilbestrol
b)High concentrations of dissolved salts
c)Strongly acidic solutions
d)Soluble salts of iron
9.(C6H12O6)n is molecular formula of
a)Acacia
b)Carrageenan
c)Guar gum
d)Tragacanth
10.Hydroxy Propyl cellulose is used as
a)binder
b)granulating agent
c)film-coating agent
d)all of these
11.Hydroxy Propyl Methylcellulose have which of the following physical properties?
a)White to slightly off-white
b)Fibrous or granular
c)Free-flowing powder
d)All of these
12.Cellulose methyl ether is the chemical name of
a)Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC)
b)Hypromellose (HPMC)
c)Methylcellulose
d)Polyvinyl Alcohol
13.(C2H4O)n is molecular formula of
a)Pectin
b)Polyvinyl Alcohol
c)Povidone
d)Kaolin
14.(C6H9NO)n is molecular formula of
a)Pectin
b)Polyvinyl Alcohol
c)Povidone
d)Kaolin
15.Tragacanth is obtained from
a)dried gum of Astragalus gummifer
b)dried leaves of Astragalus gummifer
c)dried bark of Astragalus gummifer
d)shoot of Astragalus gummifer
Solutions:
- b)suspending agents
- d)All of these
- b)HPMC
- a)Acacia
- d)All of these
- d)all of these
- d)All of these
- a)Diethylstilbestrol
- c)Guar gum
- d)all of these
- d)All of these
- c)Methylcellulose
- b)Polyvinyl Alcohol
- c)Povidone
- a)dried gum of Astragalus gummifer
References:
- Remington Essential of Pharmaceutics, 1st edition 2013, page no. 686, 699, 690, 693, 694, 696, 699, 702.
- Raymond C Rowe handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition, page no. 1-3, 13-14, 118-121, 185-188, 298-300, 317-322, 326-329, 438-441, 564, 565, 581-585, 744-746.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE