TOLAZOLINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
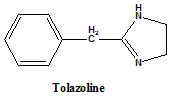
Tolazoline
IUPAC nomenclature
2-Benzyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole.
Classification
Tolazoline is nonselective α-adrenergic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 160.22 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form |
| 3 | Melting point | 174°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 373 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.65 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene and imidazole |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Tolazoline has moderate α-adrenergic antagonist property and also having histamine agonist activity.
- It produces vasodilation through direct effect on peripheral vascular smooth muscles and indirect effects through release of endogenous histamine.
- It reduces pulmonary arterial pressure and vascular resistance.[1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Molecules with 2,6-disubstitutions, which assume an orientation where the phenyl and imidazoline rings are in different plans are having the highest activity.
- Electronic effects have only influence on the actions at H2; action on α-receptors are not influenced.
- Substitutions at 3, 4 or 5 positions of the phenyl ring preclude potent activity at H2-receptor sites while the α-receptor activity is maintained. [2]
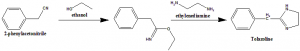
Method of synthesis
Heterecyclation of the ethyl ester of iminophezylacetic acid with the help of ethylenediamine give tolazoline.
Therapeutic Uses
Tolazoline is used for the treatment of:
- Reducing PVR
- Thrombophlebitis
- Thromboangitis obliterans
- Spasm
- Scleroderma
- Raynaud disease
- Persistant fetal circulation syndrome
- Peripheral vascular diseases
- Causalgia
- Arteriosclerosis obliterans
Side Effects
Side effects of Tolazoline are:
- Stomach bleeding
- Intestinal bleeding
- Decreased urine production
- Keidney failure
- Hypotension
- Fall in level of chlorine in blood
- Widening of blood vessels
- Vomiting
- Goose bumps
- Nausea
- Fast heartbeat
- Diarrhea
- Dilated pupils
MCQs
Q.1 “2-Benzyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Metaraminol
b) Tolazoline
c) Prazosin
d) Dihydroergotamine
Q.2 Type of ring structure present in Tolazoline?
a) Imidazole ring
b) Benzene ring
c) Ergoline ring
d) Both a) and b)
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Tolazoline | A. ß1-adrenergic agonist |
| ii. Naphazoline | B. α1-adrenergic agonist |
| iii. Dobutamine | C. α-adrenergic antagonist |
| iv. Phenoxybenzamine | D. Nonselective α-agonist |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-B, iv-A
c) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug…..
I. Effect on peripheral smooth muscles.
II. Reduction in pulmonary and aterial blood pressure
III. Vasodilation
a) II – I – III
b) III – II – I
c) III – I – II
d) I – III – II
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug…..
- Molecules with 2,6-disubstitutions, which assume an orientation where the phenyl and imidazoline rings are in different plans are having the lowest activity.
- Electronic effects have only influence on the actions at H2; action on α-receptors are not influenced.
- Substitutions at 3, 4 or 5 positions of the phenyl ring preclude potent activity at H2-receptor sites while the α-receptor activity is maintained.
a) FTT
b)TFT
c)FFT
d) TTT
Q.6 Tolazoline can be produced through heterocyclation of ethyl ester of?
a) Paraaminophenol
b) Hydroxyphenyl acetone
c) Ethylenediamine
d) Iminophezylacetic acid
Q.7 The drug Tolazoline is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of hypotension
b) During fall in level of chlorine in blood
c) Decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance
d) Treatment of intestinal bleeding
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-a
4-d
5-a
6-d
7-c