TRIAZOLAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
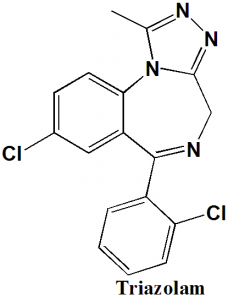
Triazolam
IUPAC nomenclature
8-Chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine.
Classification
Triazolam is a benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 343.2 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to pale yellow crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 233-235°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.42 |
| 5 | Solubility | Poorly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Diazepine, triazole, benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
i. Triazolam binds nonspecifically with benzodiazepine receptors BNZ1.
ii. It coupled with GABAA receptors and increases the GABA affinity for the GABA receptor.
iii. This results in opening of the chloride channel and thus, causes hyperpolarization of the cell membrane which prevents further excitation of the cell.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
- An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A increases the functional anxiolytic activity.
- Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
- When Heterocycles used as ring A, drug shows poor pharmacological activity.
- A proton-accepting group is essential on Ring B for binding with GABAA
- When the proton accepting group is present on the 2-position of the ring B, and is in coplanar spatial orientation with Ring A, maximum activity is observed.
- Replacement of oxygen with sulfur in ring B results in alteration in the selectivity for binding with GABA BZR subpopulations, but anxiolytic properties are maintained.
- There is no effect on agonist activity, but the antagonist activity dereases when methylene 3-position or imine nitrogen of the ring B is substituted.
- Derivatives having the 3-hydroxy moiety are fast excreted.
- Sterically large substituents on ring B, like tert-butyl group reduces the receptor affinity and the in vivo activity.
- 4,5-double bond and 4-position nitrogen is not essential for anxiolystic activity.
- BZR affinity is decreased if C=N bond is replaced with C-N bond.
- 5-phenyl ring C is not necessary for the binding with BZR.
- Substitution at the para position of the ring C decreases the agonist activity of the drug.
- There is no change observed in the agonist property of the drug when there is substitution at ortho position.
- When 1,2-bond f the ring C is annelated with an additional electron rich ring such as imidazole, affinity of the BZR increases. [1]
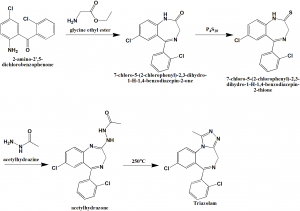
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 2-amino-2′,5-dichlorobenzophenone with glycine ethyl ester gives 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1-H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one..
ii. On reaction with phosphorous pentasulfide, carbonyl groups converts into thiocarbonyl group to produce 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1-H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-thione.
iii. On reaction with acetylhydrazine, acetylhydrazone is produced.
iv. On heating the formed acetylhydrazone, triazolam is produced. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Triazolam is used for:
- Treatment of insomnia
Side Effects
Side effects of Triazolam are:
- Dizziness
- Memory loss
- Hallucinations
- Confusion
- Mood changes
- Anxiety
MCQ
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Triazolam?
a) 8-Chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
b) 8-Chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazine
c) 5-ethyl-5-(3-methylbutyl)-1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione
d) 3-ethyl-5-(5-methylbutyl)-1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Triazolam?
I. Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
II. An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A increases the functional anxiolytic activity.
III. Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
a) III
b) I, II
c) I, III
d) All statements are correct
Q.3 The correct order for the synthesis of drug Triazolam from 2-amino-2’5-dichlorobenzophenone can be?
I. Reaction with phosphorous pentasulfide
II. Reaction with glycine ethyl ester
III. Heating
IV. Reaction with acetylhydrazine
a) II – IV- III – I
b) II – I – IV – III
c) IV- II – I – III
d) III – II – I – IV
Q.4 Side effects of drug Triazolam is/are?
a) Dizziness
b) Hallucinations
c) Confusion
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct octanol/water partition coefficient-
| i. Estazolam | A. 0.9 |
| ii.Nitrazepam | B. 2.25 |
| iii. Triazolam | C. 4.7 |
| iv. Zaleplon | D. 2.42 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
d) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
Q.6 An example of drug from class benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic?
a) Clozapine
b) Amobarbital
c) Triazolam
d) Lurasidone
Q.7 The type of ring system found in structure of Triazolam?
a) Diazepine
b) Benzene
c) Triazole
d) All of the above
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-b
4-d
5-d
6-c
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 473-474. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.