FINASTERIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
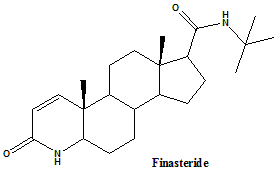
Finasteride
IUPAC nomenclature
(1S,3aS,3bS,5aR,9aR,9bS,11aS)-N-tert-butyl-9a,11a-dimethyl-7-oxo-1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,9b,10,11-dodecahydroindeno[5,4-f]quinoline-1-carboxamide.
Classification
Finasteride is a 5-α reductase inhibitor. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 372.5g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Fine white to off white crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 252-254°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in chloroform |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.03 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Quinoline ring present |
| 7 | Number of Chiral centers | 7 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Competitive and specific inhibition of Type II 5α-reductase.
ii. This leads to the inhibition of the conversion of androgens into 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This results in decrease in the level of DHT in the serum and increase in the level of testosterone concentration in serum.
iii. DHT is the principle androgen for the prostate growth, and thus, the decrease in the level of DHT leads in the decrease in the volume of prostate.
iv. Finasteride also decreases the DHT level in the scalp and thus, help in hair regrowth and slow hair loss. [2]
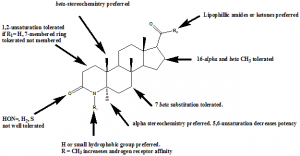
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity relationship of 5α- inhibitors can be better understood by the following representation:
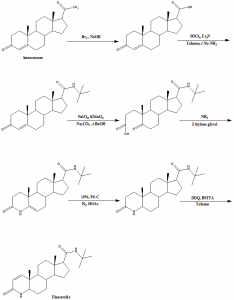
Method of synthesis
Finasteride can be synthesized from the inexpensive luteosterone through six step synthetic reactions. The following six compounds are generated during the synthesis of finasteride:
i. 3- carbonyl-4- androstene-17beta-carboxylic acid
ii. N-tertiary-butyl-3- carbonyl-4- androstene-17beta-formamide
iii. N-tertiary-butyl-5- carbonyl-17beta- carbamoyl-A-lost carbon-3,5-cracking- androstane-3-acid
iv. N-tertiary-butyl-3-carbonyl-4- aza-5- androstene-17beta-formamide
v. N-tertiary-butyl-3- carbonyl-4- aza-5alpha- androstane-17beta- formamide
vi. Finasteride [3]
Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- Benign prostate hyperplasia (enlarged prostate)
- Scalp hair loss
- Prostate cancer
- Hirsutism
- Transgender hormone therapy
Side Effects
Men who is medicated with finasteride may experience sexual dysfunctions like erectile dysfunction, decreased libido and reduced ejaculate.
MCQs
Q.1The terms ‘Proscar’ and ‘Eucoprost’ are associated with which drug?
a) Letrozole
b) Finasteride
c) Nafarelin
d) Anastrozole
Q.2 Molecular weight of Finasteride is?
a) 300.1 gm/mol
b) 285.25 gm/mol
c) 372.5 gm/mol
d) 70 gm/mol
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct side effects of the drug Finasteride?
I. Erectile dysfunction in men
II. Decreased ejaculate
III. Increased libido
a) I & II
b) I & III
c) I, II & III
d) III only
Q.4 The starting chemical required for the synthesis of drug Finasteride is?
a) Luteosterone
b) Boc-Gly-O-Resin
c) N-benzoyldihydrodutasteride
d) None of these
Q.5 Which pairs of drug and its classification are CORRECT?
| I. | Finasteride | GnRH inhibitor |
| II. | Dacarbazine | Triazine |
| III. | Prednisolone | Glucocorticoids |
| IV. | Dactinomycin | Antibiotics |
a) I, II, III & IV
b) I, II & IV
c) I, II & IV
d) II, III & IV
Q.6 Correct physical form in which the drug Finasteride is found?
a) Fine white to off white crystalline solid
b) Red crystals
c) Yellowish crystalline solid
d) Red crystals from methanol
Q.7 Type of ring present in Finasteride structure
a) Quinoline
b) Oxazophosphorine
c) No ring structure present
d) None of these
ANSWERS
1-b
2-c
3-a
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 6thEdn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008: 820. [2] Peters DH, Sorkin EM. Finasteride. Drugs. 1993 Jul 1;46(1):177-208. [3] Dolling UH, McCauley JA, Varsolona RJ, inventors; Merck and Co Inc, assignee. Finasteride processes. United States patent US 5,886,184. 1999 Mar 23.