TRIFLUPROMAZINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
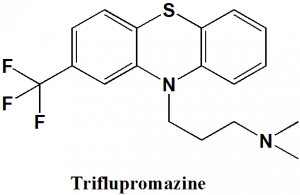
Triflupromazine
IUPAC nomenclature
N,N-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine
Classification
Triflupromazine is phenothiazine antipsychotic drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 352.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Viscous, light amber colored liquid; large irregular crystals on prolonged standing. |
| 3 | Melting point | 170-178°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 5.54 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenothiazine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Triflupromazine inhibits e activity of dopamine D1and dopamine D2 receptors through binding with them.
- The anti-emetic mechanism is due to the blockage of dopamine D2 neurotransmitter receptor in the CTZ and vomiting center.
- Drug blocks dopamine and the vagus nerve in the GIT tract.
- It also binds with muscarinic M1 and M2 and tryptamine D receptors.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity relationship of phenothiazine can be described as follows:
- Tilting of side chain towards ring A grants favorable Vander Waal’s interaction of the side chain. This interaction decides the potency of the drug towards the dopamine receptors.
- Optimal neuroleptic activity occurs when the ring A substituent is in the 2nd-position.
- A trifluoromethyl substituent provides a greater number of favorable Van der Waal’s contacts with the side chain than the chlorine substituent. Thus, phenothiazne with trifluoromethyl substituents are more potent than those with chlorine substituent.
- A piperazine side chain provides more Van der Waal’s contacts with 2-substituent than the alkylamino side chain. Thus, piperizine phenothiazine are more potent in antischizophrenic effects than alkylamino phenothiazines.
- Hydroxyethylpiperazine side chain phenothiazines displays more favorable Van der Waal’s interactions with ring A than simple piperazines.
- In the thioxanthene and xanthenes containing ring systems, the cis forms are more potent neuroleptics than the trans isomers.
- Phenothiazine analogues having the presence of exolytic double bond are more potent than the corresponding compounds lacking the exolytic double bonds. [1]
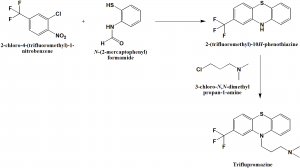
Method of synthesis
i. 2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1-nitrobenzene is reacted with N-(2-mercaptophenyl)formamide to produce a series of intermediates compounds, finaly producing 2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazine.
ii. 2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazine so formed undergoes alkylation with the help of 3-chloro-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine to form triflupromazine.
Therapeutic Uses
Triflupromazine is used for:
- Severe emetics
- Severe hiccups
Side Effects
Side effects of triflupromazine are:
- Akathesia
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
MCQs
Q.1 Complete the following sentence related with the SAR of drug triflupromazine
“A trifluoromethyl substituent provides a ……….. number of favorable Van der Waal’s contacts with the side chain than the chlorine substituent. Thus, phenothiazne with trifluoromethyl substituents are …………. potent than those with chlorine substituent.”
a) Greater; more
b) Greater; less
c) Lesser; more
d) Lesser; less
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Triflupromazine: N,N-dimethyl-3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl]propan-1-amine
- Thioridazine: 10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-2-methylsulfanylphenothiazine
- Thiopental: 5,5-diethyl-2-thioxodihydropyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-dione
- Thiobarbital: 5-ethyl-5-pentan-2-yl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione
a) FFTF
b) TTFF
c) FTTF
d) FFFT
Q.3 Correct statement related with the solubility of Triflupromazine is?
a) Practically insoluble in water
b) Slightly soluble in water
c) Soluble in water
d) Freely soluble in water
Q.4 Triflupromazine has no effect on?
a) Dopamine D1 receptors
b) Dopamine D2 receptors
c) Muscarinic receptors
d) Nicotinic receptors
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Triflupromazine?
a) Treatment of severe emetics
b) Treatment of psychotic disorders
c) Reducing halucinations
d) Treatment of dry mouth symptoms
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Triflupromazine: phenothiazine antipsychotic drug
II. Haloperidol: Buterophenone antipsychotic drug
III. Amprenavir: Nitrogen mustard
IV. Thiopental: barbiturate sedative hypnotic
a) I, II, IV
b) I, IV
c) III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.7 Triflupromazine can be synthesized from 2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazine by alkylation with?
a) 3-chloro-N,N-dimethylbutan-1-amine
b) 3-chloro-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine
c) 1,2-dichloro-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine
d) 3-chloro-N,N-dimethylpropanol
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-a
4-d
5-a
6-d
7-b