LOXAPINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
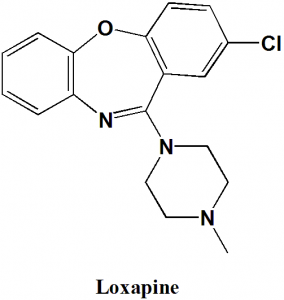
Loxapine
IUPAC nomenclature
8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine.
Classification
Loxapine is an antipsychotic drug.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 327.8 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Pale yellow crystals from petroleum ether. |
| 3 | Melting point | 109-111°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 1.03e-01 g/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.6 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Piperazine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
Loxapine is a dopamine antagonist and serotonin 5-HT2 blocker. Exact mechanism of action is not known. Changes in the level of excitability of subcortical inhibitory areas have been observed, producing calming effects and suppression of aggressive behavior.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity relationship of phenothiazine like compounds can be described as follows:
- Tilting of side chain towards ring A grants favorable Vander Waal’s interaction of the side chain. This interaction decides the potency of the drug towards the dopamine receptors.
- Optimal neuroleptic activity occurs when the ring A substituent is in the 2nd-position.
- A trifluoromethyl substituent provides a greater number of favorable Van der Waal’s contacts with the side chain than the chlorine substituent. Thus, phenothiazne with trifluoromethyl substituents are more potent than those with chlorine substituent.
- A piperazine side chain provides more Van der Waal’s contacts with 2-substituent than the alkylamino side chain. Thus, piperizine phenothiazine are more potent in antischizophrenic effects than alkylamino phenothiazines.
- Hydroxyethylpiperazine side chain phenothiazines displays more favorable Van der Waal’s interactions with ring A than simple piperazines.
- In the thioxanthene and xanthenes containing ring systems, the cis forms are more potent neuroleptics than the trans isomers.
- Phenothiazine analogues having the presence of exolytic double bond are more potent than the corresponding compounds lacking the exolytic double bonds. [1]
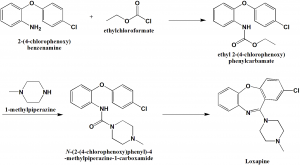
Method of synthesis
i. 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)anyline undergoes acylation using ethylchloroformate to produce N-ethoxycrbonyl-2-(4-chlorophenoxy)aniline.
ii. Treatment of the above formed compound with the mixture of phosphorus oxychloride and phosphorus anhydride yields loxapine.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Loxapine is used for:
- Treatment of schizophrenia
- Reducing nervousness
- Reducing aggression
- Decreasing hallucinations
Side Effects
Side effects of loxapine are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Trouble sleeping
- Stiff muscles
- Muscle spasms
- Twisting neck
- Arching back
- Eyes rolling up
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
MCQs
Q.1 What are the correct statements related with the physicochemical properties of Loxapine drug?
I. Molecular weight = 300 gm/mol
II. It appears as pale yellow crystals
III. No chiral carbon is present in its structure
IV. Phenothiazine ring is present in the structure
a) I, II, III
b) I, II, IV
c) II, III
d) I. II. III. IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Loxapine | A. 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one |
| ii. Quazepam | B. 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine |
| iii. Temazopam | C. 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione |
| iv. Clobazam | D. 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4-dione |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
Q.3 Loxapine is antagonist for which receptors?
I. Dopaminergic receptors
II. Serotonin 5-HT2
III. ß-adrenoceptors
IV. α-adrenoceptors
a) I, III, IV
b) I, II
c) III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Loxapine: antipsychotic drug
- Ritonavir: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
- Ribavirin: Guanosine nucleoside antiviral drug
- Triazolam: Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
a) TFTT
b) TTFF
c) FFTT
d) FFFT
Q.5 Greater potency of phenothiazines with Piperazine side chain substitution is due to?
a) Greater number of favourable Van der Waal’s contacts
b) Bleaching action of chlorine
c) Affinity of fluorine with potassium is higher
d) High molecular weight of fluorine
Q.6 Correct steps for the synthesis of loxapine drug from 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)anyline is?
I. Treatment with Phosphoprus oxychloride
II. Treatment with the mixture of Phosphorus oxychloride and Phosphorus anhydride
III. Acylation with Ethylchloroformate
IV. Alkylation with Ethylchloroformate
a) I – III
b) III – II
c) II – IV
d) III – II
Q.7 Side effect of drug Loxapine are?
a) Depression
b) Muscle spasms
c) Constipation
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-b
4-a
5-a
6-d
7-d