MEPHENYTOIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
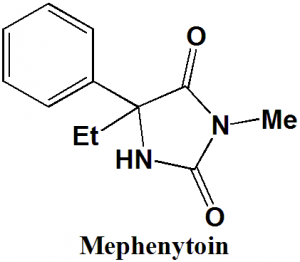
Mephenytoin
IUPAC nomenclature
5-Ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-imidazolidine-2,4-dione
Classification
Mephenytoin belongs to class phenylhydantoins
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 218.25 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid crystalline form |
| 3 | Melting point | 136.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Practically insoluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.69 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Imidazolidine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
Mephenytoin blocks:
- Frequency dependent neuronal sodium channel
- Use-dependent neuronal sodium channel
- Voltage-dependent neuronal sodium channel.
In this way, the drug limits repetitive firing of the action potential.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of hydantoins can be described as follows:
- For the activity of the drug, a phenyl or other aromatic substituent is necessary.
- Substitution with an alkyl group at position 5 will result in the sedative properties of drug.
- Some hydantoins may also exhibit properties against chemically induced convulsions.
- Many hydantoins are ineffective against electroshock induced convulsions.
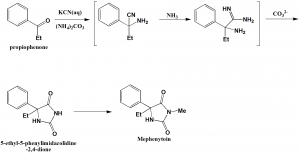
Method of synthesis
Propiophenone, potassium cyanide, ammonium bicarbonate and dimethyl sulfate undergoes Buchere-Bergs methylation reaction to form mephenytoin. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Mephenytoin is used for:
- Prevention and control of seizures
Side Effects
Side effects of Mephenytoin are:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Insomnia
- Drowsiness
- Slow heartbeat
- Unusual eye movements
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Loss of coordination
- Blurred vision
- Increased hair growth
- Allergic reactions.
MCQs
Q.1. Mephenytoin blocks?
a) Frequency dependent neuronal sodium channels
b) Use-dependent neuronal sodium channels
c) Voltage-dependent neuronal sodium channel
d) All of the above
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Mephenytoin is/are?
a) Control of seizures
b) Treatment of nausea and vomiting
c) Treatment of schizophrenia
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of Hydantoins?
I. For the activity of the drug, a phenyl or other aromatic substituent is necessary.
II. Substitution with an alkyl group at position 5 will result in the sedative properties of drug.
III. Some hydantoins may also exhibit properties against chemically induced convulsions.
IV. Many hydantoins are ineffective against electroshock induced convulsions.
a) I, III, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) III, IV
Q.4 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of mephenytoin?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug mephenytoin?
- Molecular weight is 525 gm/mol
- It is present in solid crystalline form
- It is practically insoluble in water
a) FTF
b) FFT
c) FTT
d) TFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Mephenytoin: 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione
II. Thoridazine: 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine
III. Mephobarbital: Phenyl-5-ethyl-1-methylbarbituric acid
IV. Thiopental: 5-ethyl-5-pentan-2-yl-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione
a) I, II
b) I, IV
c) II, III
d) III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Mephenytoin | A. Phenothiazine |
| ii. Promazine | B. Barbiturate |
| iii. Clonazepam | C. Phenylhydantoins |
| iv. Thiamylal | D. Benzodiazepine |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-a
3-c
4-a
5-c
6-d
7-a