METHSUXIMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
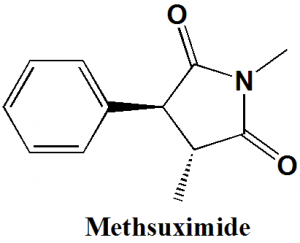
Methsuximide
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-1,3-dimethyl-3-phenyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
Classification
Methsuximide is a succinimide anticonvulsant.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 203.24g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to grayish white crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 52.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | log Kow = 1.45 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrrolidine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 2 |
Mechanism of Action
Methsuximide binds with T-type voltage sensitive calcium channels. The latter involves in mediating the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involves in variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone release, neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell division and cell death.
T-type voltage sensitive calcium channel are also involved in the modulation of firing patterns or neurons which is necessary for the information processing and also in cell growth processes.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of succinimides can be discussed as follows:
- Phenyl substitution makes them active against electrically induced convulsion.
- N-methylation decreases activity against electroshock seizures.
- N-methylation also increases the activity against chemically induced convulsions.
Method of synthesis
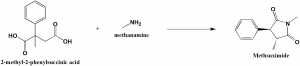
Methsuximide can be synthesized by the reaction of 2-methyl-2-phenylsuccinic acid or its anhydride with methylamine. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Methsuximide is used for:
- The control and prevention of absence or petit mal seizure
Side Effects
Side effects of Methsuximide are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Mood changes
- Signs of infections
- Swollen joints and pain
- Rashes
- Tiredness
- Rapid breathing
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of methsuximide?
a) (RS)-1-methyl-3-phenyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
b) (RS)-1,3-dimethyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
c) (RS)-1,3-dimethyl-3-phenyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
d) (RS)-1,3-dimethyl-3-phenyl-pyrrolidine-2-one
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of succinimides?
I. Phenyl substitution makes them active against electrically induced convulsion.
II. N-methylation increases activity against electroshock seizures.
III. N-methylation increases the activity against chemically induced convulsions.
a) I, II
b) II
c) III
d) II, III
Q.3 Methsuximide can be synthesized by the reaction of 2-methyl-2-phenylsuccinic acid with?
a) Methane
b) Methylamine
c) Ethyl ether
d) Butane
Q.4 Side effects of drug methsuximide is/are?
a) Depression
b) Abdominal pain
c) Diarrhea
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weight.
| i. Methsuximide | A. 203.24 gm/mol |
| ii. Oxazepam | B. 387.9 gm/mol |
| iii. Zaleplon | C. 305.33 gm/mol |
| iv. Flurazepam | D. 286.71gm/mol |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class succinimide anticonvulsant is?
a) Triflupromazine
b) Trimethadione
c) Methsuximide
d) Meprobomate
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of methsuximide is?
a) Pyrrolidine
b) Pyrimidine
c) Cyclohexane
d) Furan
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-b
3-b
4-d
5-a
6-c
7-a