METHOXYFLURANE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
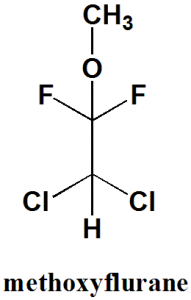
Methoxyflurane
IUPAC nomenclature
2,2-dichloro-1,1-difluoro-1-methoxyethane
Classification
Methoxyflurane is an inhalational anesthetic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 169.96 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Clear colorless liquid |
| 3 | Boiling point | 105°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 28,300 mg/L in water at room temperature. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.21 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Methoxyflurane decreases the gap junction channel opening times and increases gap junction channel closing time which induces reduction in junctional conductance.
- The drug also increases the fluidity of the lipid membrane and thus, activates calcium dependent ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Methoxyflurane also binds with D subunit of ATP synthase, GABA receptors, glutamate receptors , glycine receptors, the large conductance Calcium ion activated potassium channel and NADH dehydrogenase.
Structure Activity Relationship
The SAR for inhaled anesthetics can be summarized as follows:
- Halogenations of the hydrocarbons and ether increase the anesthetic potency.
- Halogenations of the hydrocarbons tends to induce arrhythmia in the following order F<Cl<Br<I.
- Due to presence of asymmetric halogenated carbon in ether, they are better anesthetics.
- Halogenated methyl ethyl ethers are more stable, more potent and have better clinical profile than halogenated diethyl ether.
- Fluorination increases the stability and decreases the flammability.
- Compete halogenations of the alkane or ether decreases the anesthetic potency and increases the convulsant potency
- Presence of double bond increases chemical reactivity and toxicity.
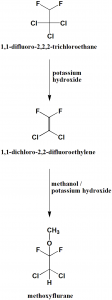
Method of synthesis
i. 1,1-difluoro-2,2,2-trichloroethane undergoes dehydrochlorination by help of potassium hydroxide to produce 1,1-dichloro-2,2-difluoroethylene.
ii. Methanol is added to the above formed compound in the presence of potassium hydroxide. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Methoxyflurane is used for:
- Relieving moderate to severe pains
Side Effects
Side effects of Methoxyflurane are:
- Nephrotoxicity
- Severe to fatal hepatotoxicity
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of methoxyflurane?
a) 2,2-dichloro-1,1-difluoro-1-methoxyethane
b) 5-Ethyl-5-phenyl-1,3-diazinane-4,6-dione
c) (RS)-1,3-dimethyl-3-phenyl-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione
d) 2-chloro-1,1-difluoro-1-methoxyethane
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Inhaled anesthetics?
I. Due to presence of asymmetric halogenated carbon in ether, they are better anesthetics.
II. Halogenated methyl ethyl ethers are less stable, more potent and have better clinical profile than halogenated diethyl ether.
III. Fluorination increases the stability and increases the flammability.
a) I, II
b) I
c) III
d) II, III
Q.3 Methoxyflurane can be synthesized by reaction of 1,1-dichlroo-2,2-difluoroethylene with ?
a) Methanol
b) Ethyl alcohol
c) Propanol
d) Ethanoic acid
Q.4 Side effects of drug Methoxyflurane is/are?
a) Shallow breathing
b) Decreased libido
c) Nephrotoxicity
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weight.
| i. Methoxyflurane | A. 373.9 gm/mol |
| ii. Prochlorperazine | B. 169.96 gm/mol |
| iii. Phenytoin | C. 407.5 gm/mol |
| iv. Trifluperazine | D. 296.5 gm/mol |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class Inhalational Anesthetics is?
a) Primidone
b) Methoxyflurane
c) Ephedrine
d) Amphetamine
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of Methoxyflurane is?
a) Pyridine
b) Pyrimidine
c) Cyclohexane
d) None
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-a
4-c
5-b
6-b
7-d