SODIUM SALICYLATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
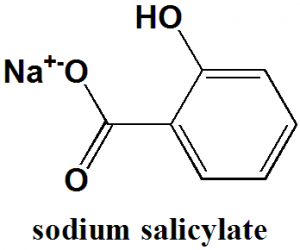
Sodium salicylate
IUPAC nomenclature
Sodium;2-hydroxybenzoate
Classification
- Non-selective COX inhibitors (traditional NSAIDs)
- Salicylates
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 160.1g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Dry powder or liquid |
| 3 | Melting point | 200°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 0.78 M |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | logP = -1.43 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Sodium salicylate inhibits release of prostaglandin E2 when added together with interlukin 1ß
- It also causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 activity. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for salicylates can be summarized as follows:
- Active moiety responsible for the action is salicylate anion.
- Side effects of the drug are associated with carboxylic acid function.
- Reducing the acidity of carboxylic acid by converting into amide maintains the analgesic action but eliminates the anti-inflammatory properties.
- Substitution on the carboxyl or phenyl hydroxyl groups results in changes in the toxicity and potency of the drug.
- Activity is abolished when the phenolic hydroxyl group is placed on meta or para position to the carboxyl group.
- Introduction of the halogen atom on the phenolic ring increases the potency and the toxicity of the drug.
- Substitution on the 5th-position on the phenolic ring increases the anti-inflammatory property of the drug. [2]
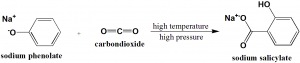
Method of synthesis
Sodium salicylate is prepared from sodium phenolate and carbon dioxide under higher temperature and pressure.
Therapeutic Uses
Sodium salicylate is used for:
- Treatment of acne vulgaris
- Treatment of psoriases
- Treatment of warts
- Treatment of scalp dermatoses
- Treatment of dermatitis seborreic
Side Effects
Side effects Sodium salicylate are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Excess stomach acid secretion
- Heartburn
- Stomach cramps
- Irritation in stomach and intestines
- Rupture of wall of stomach or intestine
- Allergic reaction
- Rash
- Hemolytic anemia
- Anemia
- Bleeding in stomach
- Bronchospasm,
- Itching
- Wheezing
- Trouble breathing
- Stomach or intestinal ulcers
- Hives
- Skin redness
MCQs
Q.1 Choose the correct option related with the mechanism of action of drug Sodium salicylate?
a) Inhibits release of Prostaglandin E2
b) It stimulates the activity of COX-2
c) It stimulates the activity of COX-1
d) All of the above
Q.2 Medicinal use of drug Sodium salicylate is/are?
a) Treatment of acne ulgaris
b) Treatment of psoriases
c) Treatment of warts
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Sodium salicylate?
I. Active moiety responsible for the action is salicylate anion.
II. Side effects of the drug is associated with carboxylic acid function.
III. Reducing the acidity of carboxylic acid by converting into amide maintain the analgesic action but increase the anti-inflammatory properties.
IV. Substitution on the carboxyl or phenyl hydroxyl groups results in changes in the toxicity and potency of the drug.
a) I, IV
b) II, III
c) III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.4 Sodium salicylate can be prepared by reaction of sodium phenolate with?
a) Carbondioxide
b) Sodium hypophosphate
c) Salicylic acid
d) None of the above
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug sodium salicylate is?
I. Molecular weight = 160.1 gm/mol
II. Melting point = 100oC
III. Available in gaseous form only
IV. Ring structure present
a) FFTF
b) TFFT
c) FTTF
d) TFFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Sodium salicylate: Sodium;2-hydroxybenzoate
II. Carmustine: 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
III. Lomustine: N,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amide 2-oxide
IV. Cisplatin: (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
a) I, IV
b) I, II, III, IV
c) II, III
d) III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Sodium salicylate | A. Inhalational anesthetics |
| ii. Propranolol | B. ß-adrenergic blocker |
| iii. Promazine | C. Non-selective COX inhibitor |
| iv. Halothane | D. Phenothiazine antipsychotic drug |
a) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-d
4-a
5-b
6-a
7-c