INDOMETHACIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
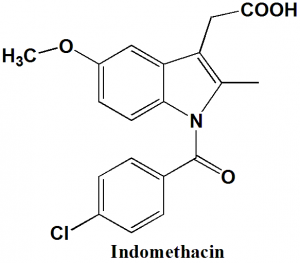
Indomethacin
IUPAC nomenclature
2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetic acid
Classification
- Non-selective COX inhibitors (traditional NSAIDs)
- Indole derivatives
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 357.8 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Pale yellow to yellow-tan crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 158°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Practically insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether, castor oil |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.27 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Indole, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Indomethacin is a nonspecific and reversible inhibitor of the cyclooxygenase(COX) enzyme.
- Indomethacin inhibits both the isoforms of COX: COX-1 and COX-2; but the drug has higher selectivity for the COX-1 receptors which is responsible for the increased adverse gastric effects of drug.
- The drug binds with the active site of the enzyme and its substrate, arachidonic acid.
- It also inhibits phospholipase A2 which reduces the release of enzyme responsible for the release of Arachidonic acid.
- Due to inhibition of synthesis f prostaglandins, indomethacin also promotes the closure of ductus arteriosus.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of indomethacin can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of the carboxyl group with other acidic functionalities decreases the activity.
- As the acidity of the carboxyl group increases, the anti-inflammatory activity of drug also increases and vice-versa.
- Amide analogues are inactive.
- Acylation of indole nitrogen decreases the activity.
- N-benzoyl derivatives substituted in the para-position with fluoro chloro, trifluoromethyl or hiomethyl group are most active.
- Substitution on the indole ring with groups like methoxy, fluoro, dimethylamino, methyl,, allyloxy or acetyl increases the activity of drug.
- Nitrogen atom on the indole ring is not important for the activity of the drug.
- Alkyl substitution at the α-position is more active than the aryl substitutions.
- Only S-(+)-enantiomers shows the anti-inflammatory activity.[1]
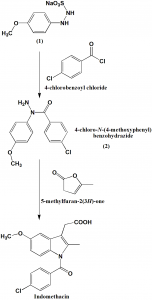
Method of synthesis
i. Acylation of the ß-modified arylhadrazine (1) using chlorobenzoic acid by pyridine-catalyzed acylation to give α-acyl-arylhydrazine (2).
ii. Indole ring is formed by reaction of the (2) with α-Angelica lactone nder acidic conditions. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Indomethacin is used for:
- Treatment of osteoarthritis
- Treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis
- Treatment of Gouty arthritis
- Treatment of Ankylosing spondylitis
- Treatment of shoulder pain caused by bursitis or tendinitis
Side Effects
Side effects of indomethacin are:
- Allergic reactions
- Fever
- Sore Throat
- Rash
- Chest pain
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Slurred speech
- Leg swelling
- Vision changes
- Heart problems
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Ark urine
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Stomach bleeding
- No urination
- Swelling of feet and ankles
- Anemia
- Indigestions
- Headaches
- dizziness
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Indomethacin?
a) 2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetic acid
b) 2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl} propanoic acid
c) 2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}butanoic acid
d) 2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}pentanoic acid
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Indomethacin?
I. Replacement of the carboxyl group with other acidic functionalities increases the activity.
II. As the acidity of the carboxyl group increases, the anti-inflammatory activity of drug also increases and vice-versa.
III. Amide analogues are inactive.
a) I, II
b) I, II, III
c) III
d) I
Q.3 Number of chiral centers present in the structure of indomethacin is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Side effects of drug Indomethacin is/are?
a) Abdominal pain
b) Heart problems
c) Allergic reactions
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weight.
| i. Indomethacin | A. 357.8gm/mol |
| ii. Bitolterol | B.225.28 gm/mol |
| iii. Xylometazoline | C. 461.5gm/mol |
| iv. Terbutaline | D.244.37 gm/mol |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class NSAIDs is?
a) Indomethacin
b) Methyldopa
c) Prazosin
d) Methysergide
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of Indomethacin is?
a) Indole
b) Pyrrole
c) Furan
d) No ring structure present
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-a
4-d
5-c
6-a
7-a