KETOROLAC Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
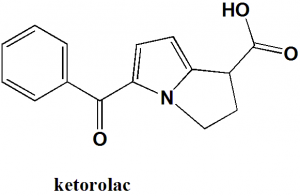
Ketorolac
IUPAC nomenclature
(±)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Propionic acid class
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 255.27 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 162-165°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Trimethamine salt solubility is 200 g/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.1 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrrolizine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Ketorolac non-selectively inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes which are responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins.
- The reduced level of prostaglandins responsible for controlling the inflammation and pain in the body.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of propionic acid derivatives can be summarized as follows:
- Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be increased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- Related side effects of the drug can be decreased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- S- (+)-enantiomer possess greater activity than (-)-enantiomer.[1]
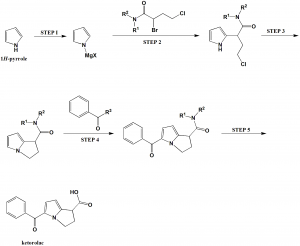
Method of synthesis
i. (STEP I): Pyrrole is converted into pyrrole Grignard reagent by the reaction of pyrrole with methylmagnesium chloride.
ii. (STEP 2): Pyrrole Grignard reagent so formed is contacted with dihalobutanamide to form N-alkyl-N-aryl-4-chloro-2-(2-pyrrolyl)butanamide.
iii. (STEP 3): The pyrrolylbutanamide is cyclized to form N-alkyl-N-aryl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxamide.
iv. (STEP 4): The above formed compound undergoes 5-aroylation method to form N-alkyl-N-aryl-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H pyrrolizine-1-carboxamides.
v. (STEP 5): The ketorolac-amide so formed is converted to ketorolac through hydrolysis using strong base in an alkanol. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Ketorolac is used for:
- Short-term treatment for moderate to severe pain
- Used before or after medical surgery for reducing the pain
Side Effects
Side effects of Ketorolac are:
- Skin rash
- Changes in vision
- Shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Swelling
- Stomach bleeding
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Difficulty in urination
- Anemia
- Skin reactions
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Tremors
- Stomach pain
- Confusion
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Symptoms of meningitis
MCQs
Q.1 “(±)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Ketorolac
b) Pralidoxim
c) Morphine
d) Scopolamine
Q.2 Melting point of ketorolac is?
a) 163oC
b) 163K
c) 163oF
d) None of the above
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Ketorolac | A. Inhalational anesthetics |
| ii. Promazine | B. Carbamate cholinesterase inhibitor |
| iii. Halothane | C. NSAID |
| iv. Pyridostigmine | D. Phenothiazine |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
Q.4 Correct statements from below which are related with the mechanism of action of Ketorolac can be??
I. It is a non-selective COX inhibitor
II. Side effects of drug is due to COX-2 inhibition
III. Therapeutic action is due to COX-1 inhibition
IV. COX inhibition results in reduced production of prostaglandins
a) I ,IV
b) III, II
c) IV , I
d) II , III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of propionic acid derivatives can be?
- Anti-inflammatory activity of the drug can be decreased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- Related side effects of the drug can be decreased by substitution of an α-methyl group on the alkanoic acid portion of acetic acid derivatives.
- S- (+)-enantiomer possess greater activity than (-)-enantiomer
a) TFF
b) FFT
c) FTF
d) FTT
Q.6 Ketorolac-amide can be converted to Ketorolac through?
a) Hydrolysis
b) Alkylation
c) Demethylation
d) Chlorination
Q.7 The drug ketorolac is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of seizures
b) As an anesthetic
c) Reducing mild to severe pain
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-d
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-c