Anatomy of Ureters, Urinary Bladder and Urethra and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Pharmacist, and Staff Nurse Exam
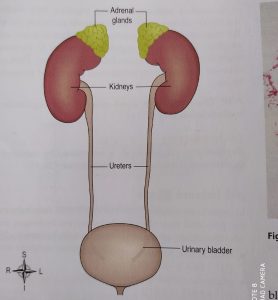
URETERS
The two ureters are about 20-25 cm long with diameter of 3 mm. the ureters are continuous from renal pelvis, it passes down through the abdominal cavity into the pelvic cavity behind the peritoneum, and passes obliquely into the urinary bladder. Because of this arrangement, the urine accumulates, pressure in the bladder rises and ureters’ walls gets compressed which results in opening into the bladder. It prevents back flow of urine back to the ureters because the bladder fills during micturition.
The walls of ureters consist of 3 layers of tissues which are as follows
- The outer layer consist of fibrous tissue as it continues with the fibrous capsule of kidney
- The middle one is the muscular layer consisting of smooth muscle fibers
- The inner layer is mucosa which is composed of transitional epithelium.
The main function of ureter is to carry urine from kidneys to the urinary bladder. Peristaltic contraction of muscular layer of ureters push urine from kidneys to the urinary bladder but hydrostatic pressure and gravity also plays an imp role. The peristaltic waves that passes from renal pelvis to the bladder varies from 1 to 5 per minute, depending on how fast the urine is being formed.
URINARY BLADDER
The urinary bladder acts as a reservoir for urine, it lies in the pelvic cavity and its size and position varies depending on the amount or urine it contains. The bladder rises into the abdominal cavity when it is distended.
The organs associated with the bladder varies in males and females like in males, the organ present posteriorly is rectum and seminal vesicles while that in females is uterus and upper part of vagina. Anteriorly and superiorly present organs are same in males and females that is pubic symphysis and small intestine respectively. Inferiorly females have urethra and muscles forming pelvic floor while in males it is urethra and prostate gland.
The bladder is pear shaped but when filled with urine it becomes like a balloon , the posterior surface is the base and at its lowest point known as the neck it open into urethra.
Like ureters, the bladder wall also consist of 3 layers-
• The outer layer is of loose connective tissue, it contains blood vessels lymphatic vessels and nerves
• The middle layer is of muscle fibers and elastic tissue which is loosely arranged in three layers. This is known as detrusor muscle, its contraction help in emptying the bladder
• The inner layer is of transitional epithelium which permits flow of urine ahead when the bladder fills.
When the bladder is empty, its inner layer contains folds but when it fills with urine the folds starts to disappear. when all the folds disappear, this provides the signal that the urine need to be passed ahead . The max capacity of bladder is about 600-700mL.
At the floor of bladder is a triangular area known as trigone. The two posterior corners are urethral openings while the anterior corneris an opening to the urethra known as internal urethral orifice.
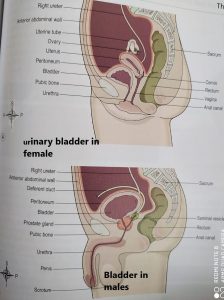
URETHRA
The urethra is like a canal which extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior. It is longer in males than in females.
The male urethra is associated with both urinary system as well as reproductive system because it provides pathway for the flow of both urine and semen. It is about 20cm long and consist of three parts-the prostatic urethra which passes through the prostate gland, the membranous urethra which is the shortest and narrowest and extends from the prostate gland to the penis and lastly the penile urethra which lies within the penis.
The female urethra is about 4cm long and 6mm in diameter. It passes downwards behind the pubic symphysis sand open at the external urethral orifice In front of vagina. The wall has two main layers, the outer muscular layer and the inner layer of mucosa which is continued with that of urinary bladder.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. What is the length and diameter of ureters
A. 22cm and 3mm B. 15cm and 4mm
C. 25cm and 4mm d. 10cm and 2mm
2. Where the urinary bladder lies?
A. in the pelvic cavity B. in the abdominal cavity
C. just below the kidney D. below the urethra
3. What is the approximate length and diameter of female urethra?
A. 4cm and 6mm B. 10cm and 5mm
C. 2cm and 8mm D. 8cm and 6mm
4. What is the approximate length of male urethra?
a. 12cm b. 15cm
c. 5cm d. 20cm
5. which of the following tissue is present in the urinary bladder?
A. elastic tissue B. transitional epithelium
C. muscular tissue D. all of the above
6. Which of the following statement is true?
A. the ureters passes behind the peritoneum and in front of psoas muscle.
B. When the bladder is filled, folds appear in the inner lining
C. the muscular tissue of the bladder stores blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves
D. the outer layer of female urethra is the lining of mucosa
7. Which of the following organ is associated with bladder superiorly?
A. pubic symphysis B. uterus
C. rectum D. none of the above
8. Match the following –
A) Muscular layer of ureter 1. Permits flow of urine
B). loose conn tissue of bladder 2. Forms detrusor muscles
C.) elastic tissue of bladder 3. Stores blood, lymphatic vessels
D) transitional epithelium of bladder 4.form functional unit of urethra
9. which factor is most important in pushing urine from ureter towards the bladder?
a. gravity b. peristaltic contraction
c. hydrostatic pressure d. peristaltic relaxation
10. which of the following organ is associated with the bladder inferiorly in males?
A. small intestine B. prostate gland
C. rectum D. seminal vesicles
ANSWERS:-
- 22cm-3mm
- in the pelvic cavity
- 4cm-6mm
- 20cm
- all of the above
- the ureters passes behind the peritoneum and in front of psoas muscle.
- none of the above
- a – 4 b – 3 c – 2 d – 1
- peristaltic contraction
- prostate gland
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:
1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-: .
2. Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: .