Protein Synthesis and MCQs For NEET, GPAT, SSC, Pharmacist and Staff Nurse Exam
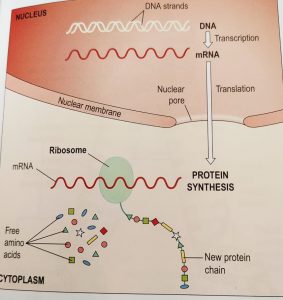
The DNA holds the biological information of a cell; which lies within the base code in the center of double helix. The product of these information is always proteins. proteins are very essential for all the aspects of life; it forms the major structural elements of the body as well as enzymes; essential for the biochemical process. The fundamental building blocks of proteins are 20 amino acids. Since the DNA is a very big molecule to leave the nucleus through the nuclear membrane; so an intermediary molecule known as mRNA carry the info from nucleus to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis takes place.
Messenger Ribonucleic Acid(mRNA)
mRNA is a single strand chain of nucleotide which undergoes synthesis in the nucleus from an appropriate gene. mRNA is formed according the requirement of a particular protein by the cell. Characteristics of RNA includes:-
- it has only 1 strand
- it contains sugar ribose
- it has four bases- adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil.
The process through which mRNA is formed by using DNA as a template, is known as transcription.
Transcription:- since the info lies within the bases of the DNA, so the first step is to open the helix arrangement to find the bases. Only the particular gene which is to be transcribed is opened; and the rest of the chromosome part remains coiled. When the helix arrangement is opened, it exposes both the base strands; but the enzymes which make the mRNA uses only 1 strand. That’s why the mRNA is single stranded.
As the enzymes move along the open DNA, it reads the info and adds the complementary base to the mRNA. For example, if the DNA base is cytosine, guanine is added to the mRNA and vice versa. and if if the DNA base is thymine, adenine is added to mRNA; but if adenine is the base, uracil is added instead of thymine. When the enzyme gets a stop signal, it ends the synthesis of mRNA and it is released. The DNA is again packed in double helix by other enzymes. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores.
Translation:- It is the process of final synthesis of the protein using the info carried on the mRNA. It takes place on the free ribosomes and also the ribosomes present on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Firstly, the mRNA attaches to the ribosomes, and the ribosomes reads the base sequence of the mRNA.
Since proteins are made of 20 amino acids, so it is not possible to use the four bases individually in a simple one to one code. to make it easier and provide enough options, the code is read in triplets; which five 64 combinations. Each of these specific triplet sequence is known as codon. For example, the base sequence is ACA (adenine, cytosine, adenine)codes for amino acid cysteine.
The first codon is a start codon, which initiate the synthesis process. The ribosomes slides along the mRNA and reads appropriate code and makes new protein molecule by adding appropriate amino acids. The ribosome continues this process until it reaches the stop codon. At this point, it terminate the synthesis of protein and makes a new protein. Some of the new proteins stays in the cell itself while others releases elsewhere.
Gene expression:- Although all the cell having nucleus have an identical copy of genes; but each cell type uses only those genes which are related to its function. for example: only RBCs contain hemoglobin molecules but all the body cells contain the hemoglobin gene. The control for selective gene expression is done by various regulatory substances; and those genes which are of no need by a cell are kept switch off.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1 . Which part of DNA stores the biological info of a cell?
A. sugar B. phosphate group
C. bases D. all of the above
2. What are the fundamental building blocks of a protein?
A. lipids B. carbohydrates
C. amino acids D. fatty acids
3. What is the function of proteins?
A. makes structural element of body B. biochemical process
C. makes structural element of enzymes D. all of the above
4. What is the full form of mRNA?
A. making ribonucleic acid B. messenger ribose acid
C. messenger ribonucleic acid D. marking ribonucleic acid
5. Match the following-
a. DNA 1. This process occurs on ribosomes
b. RNA 2. Process for the synthesis of mRNA
c. transcription 3. It contains ribose sugar
d. translation 4. It contains deoxyribose
6. Synthesis of RNA is done through which process?
A. transcription B. hemostasis
C. homeostasis D. translation
7. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. DNA has 2 strands
B. translation occurs in cytoplasm
C. gene expression is specific for each type of cell
D. RNA contains adenine, guanine, uracil and thymine
8. Which base is not the part of RNA?
A. adenine B. cytosine
C. guanine D. none of the above
9. Where the synthesis of protein takes place?
A. mitochondria B. ribosomes
C. cytosol D. nucleus
10. A protein is made up of how many amino acids?
A. 20 B. 22
c. 25 D. 30
ANSWERS:-
- bases
- amino acids
- messenger ribonucleic acid
- all of the above
- a – 4 b – 3 c – 2 d – 1
- transcription
- RNA contains adenine, guanine, uracil and thymine
- none of the above
- ribosomes
- 20
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:- Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-: 440442.