PYRROBUTAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
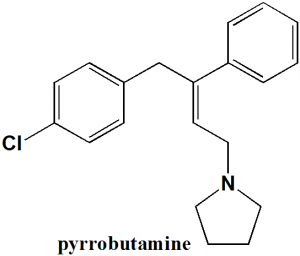
Pyrrobutamine
IUPAC nomenclature
1-[(2E)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylbut-2-en-1-yl]pyrrolidine
Classification
- H1-receptor antihistamine
- Alkylamine antihistamine
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 311.8 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | N/A |
| 3 | Melting point | N/A |
| 4 | Solubility | N/A |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Pyrrolidine, phenyl |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
Pyrrobutamine do competition for H1 receptor with histamine and after bounding with receptor, it acts as inverse agonist.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity of alkyl amines antihistamines can be summarized as:
- E- and Z- isomers in alkenes shows large difference in activity, where, E-isomers are more potent than Z-
- The two aromatic rings have different binding environment at the receptors.
- 5-6 angstrom distance is required between aromatic ring and tertiary aliphatic amine for biding at the receptor.
- S-enantiomers have greater affinity for H1 histamine receptors [1]
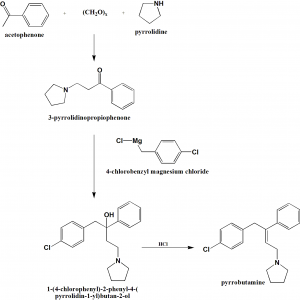
Method of synthesis
i. Acetophenone, paraformaldehyde and pyrrolidine are reacted together to form 3-pyrrolidinopropiophenone.
ii. Last reacts with 4-chlorobenzyl magnesium chloride to give 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-phenyl-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)butan-2-ol.
iii. Above formed compound is treated with hydrochloric acid to produce pyrrobutamine. [2]
Medicinal Uses
Pyrrobutamine is used for treatment of:
- Allergies
- Hay fever
- Common cold
- Itchy
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Uticaria
Side Effects
Side effects of pyrrobutamine are:
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
- Hallucinations
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the Alkylamine antihistamine drugs-
| i. E-isomers in alkenes are | A. More potent than Z-isomers |
| ii. S-enantiomers have | B. Less potent than Z-isomers |
| C. Greater affinity for H1 histamine receptors | |
| D. Lesser affinity for H1 histamine receptors |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-D
d) i-B, ii-C
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Pyrrubutamine:1-[(2E)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenylbut-2-en-1-yl]pyrrolidine
- Tolazoline: N,N-Dimethyl-2-[3-(1-pyridin-2-ylethyl)-1H-inden-2-yl]ethan-1-amine
- Amphetamine: 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
- Molindone: 2-[(2,6-dichloro-3-methylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid
a) TFFF
b) FFTT
c) FTFT
d) TTTT
Q.3 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of pyrrobutamine is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Pyrrobutamine acts as reverse agonist for?
a) H1 receptors
b) H2 receptors
c) Muscarinic receptors
d) Nicotinic receptors
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Pyrrobutamine?
a) Treatment of arrhythmias
b) Treatment of Allergic symptoms
c) Treatment of hay fever
d) Treatment of Runny nose
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Pyrrobutamine: Ethanolamine ether antihistamine drug
II. Enflurane: Inhalational anesthetics
III. Diazepam: Alpha adrenergic blockers
IV. Sulpieride: Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotics
a) I, IV
b) I, II
c) II, III
d) III, IV
Q.7 Type of ring structure present in the structure of pyrrobutamine?
a) Pyridine
b) Purine
c) Pyrrolidine
d) Pyran
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-a
4-a
5-a
6-b
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] US 2 655 509 (Eli Lily,1953; prior. 1951).