CHLORPHENIRAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
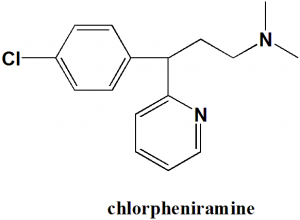
Chlorpheniramine
IUPAC nomenclature
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-yl-propan-1-amine
Classification
- H1-receptor antihistamine
- Alkylamine antihistamine
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 274.79 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 130-135oC |
| 4 | Solubility | 160 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.38 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Pyridine , phenyl |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Chlorpheniramine binds to histamine H1 receptors and blocks the action of endogenous histamine.
ii. Due to this, there is relief in the negative symptoms produced by histamine.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity of alkyl amines antihistamines can be summarized as:
- E- and Z- isomers in alkenes shows large difference in activity, where, E-isomers are more potent than Z-
- The two aromatic rings have different binding environments at the receptors.
- 5-6 angstrom distance is required between aromatic ring and tertiary aliphatic amine for biding at the receptor.
- S-enantiomers have greater affinity for H1 histamine receptors [1]
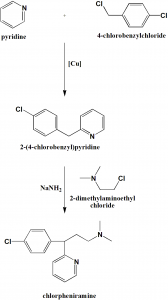
Method of synthesis
i. Pyridine undergoes alkylation by 4-chlorobenzylcloride to give 2-(4-chlorobenzyl)pyridine.
ii. Alkylation of the last with 2-dimethylaminoethylchloride in presence of sodium amide gives chlorpheniramine. [2]
Medicinal Uses
Chlorpheniramine is used for treatment of:
- Allergies
- Hay fever
- Common cold
- Watery eyes
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Cold symptoms
- Itchy
Side Effects
Side effects of Chlorpheniramine are:
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
- Hallucinations
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 Which of the following statements related with the physical properties of drug Chlorpheniramine?
I. Molecular weight: 343.9 gm/mol
II. Physical appearance: White crystalline solid
III. Melting point: 178oC
IV. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.38
a) I, II, IV
b) II, IV
c) III, IV
d) I, V
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Chlorpheniramine | A. 3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-yl-propan-1-amine |
| ii. Loxapine | B. 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine |
| iii. Cevimeline | C. (N-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate |
| iv. Homatropin | D. (2R,2R)-2′-Methylspiro[4-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2,5′-[1,3]oxathiolane]. |
a. i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
b. i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
c. i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
d. i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
Q.3 Mechanism of action of Chlorpheniramine includes?
I. It binds with Histamine H1 receptor and produces antagonistic effects.
II. Permanent relief in negative symptoms produced due to histamine
III. Binding with alpha-adrenergic receptors
a) I
b) II, III
c) I, III
d) III
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Chlorpheniramine: Alkylamine antihistamine drug
- Naproxen: Alylating agent
- Diclofenac: DMARDs
- Sevoflurane: Inhalational anesthetics
a) TFFT
b) FTTF
c) FTTF
d) TTFF
Q.5 Which of the following statement is true related with the SAR of alkyl amine antihistamine drugs?
a) E- and Z- isomers in alkenes have no difference in activity
b) Z-isomers are less potent than E-isomers
c) E- and Z- isomers are inactive
d) S-enantiomers are inactive
Q.6 The correct sequence for the steps for synthesis of drug Chlorpheniramine from pyridine can be?
I. Alkylation by 4-chlorobenzylchloride
II. Alkylation with 2-dimethylaminoethylchloride
III. Oxidation
a) I – II
b) I – III
c) III – II – I
d) II – I – III
Q.7 Side effect of drug Chlorpheniramine?
a) Drowsiness
b) Seizures
c) Blurred vision
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-a
4-a
5-b
6-a
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.