Phospholipid Metabolism: Synthesis of Phospholipid and MCQs for GPAT, NEET, CSIR NET, UPSC, SSC
Phospholipids are major types of membrane lipids. The two types of phospholipids are
- Those who have glycerol as the alcohol and are known as glycerophospholipids or phospho-glycerides, examples include:
- Phosphatidylserine
- Phosphatidylinositol
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Phosphatidylethanolamine
- Cardiolipin
- Those who contain sphingosine as an alcohol and are known as sphingolipids
- Sphingomyelin
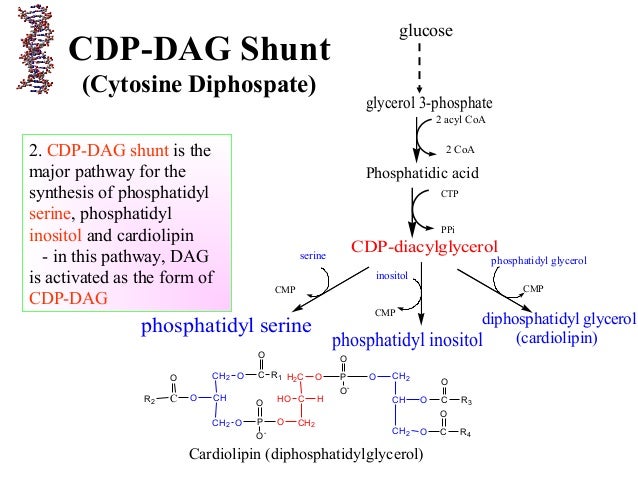
Synthesis of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol
The initial steps for the synthesis of glycerophospholipids are similar to that of the synthesis of triacylglycerol. Phosphatidic acid is the common intermediate for both synthesis of glycerophospholipids and synthesis of triacylglycerol.
- Synthesis of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol starts with the formation of CDP-diacylglycerol, an active phosphatidyl unit.
- The activated phosphatidyl unit reacts with the hydroxyl group of the alcohol if the alcohol is serine, it forms phosphatidylserine; and if the alcohol is inositol, it forms phosphatidylinositol.
Synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine
- Phosphatidylcholine or lecithin is synthesized by using the choline from the diet. The choline is first converted into its active form. For this, phosphorylation of choline with ATP to form phosphocholine. The phosphocholine than reacts with CTP to form CDP-choline(active form).
- The phosphatidylcholine unit of CDP-choline is transferred to the diacylglycerol to form phosphatidylcholine.
- Similarly, phosphatidylethanolamine is synthesized by the ethanolamine by forming CDP-ethanolamine

Synthesis of cardiolipin
Cardiolipin or diphosphatidyl glycerol is present in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and is used for the functioning of cytochrome oxidase activity and phosphate transfer.
In its synthesis process, CDP-diacylglycerol combines with glycerol-3-phosphate to form phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerol than reacts with one molecule of CDP-diacylglycerol with then form cardiolipin.

Synthesis of sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin is a sphingosine phospholipid; and its backbone is sphingosine
- The synthesis of all sphingolipids begin with the formation of ceramide witch is synthesized in endoplasmic reticulum. Palmitoyl-CoA and serine condense to form 3-ketosphingasine.
- In all sphingolipids, amino group of sphingosine is acylated to form ceramide. Ceramide then reacts with phosphatidylcholine to form sphingomyelin. This mainly occurs in Golgi apparatus.

Multiple choice questions (MCQs)
1. What type of lipids are phospholipids?
A. Membrane lipid
B. Prosthetic lipids
C. Both
D. None
2. In how many class are phospholipids classified?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
3. Which of the following is an example of glycerophospholipids?
A. Phosphatidylserine
B. Phosphatidylinositol
C. Phosphatidylethanolamine
D. All of the above
4. Which compound is termed as backbone in case of sphingolipids?
A. Esters
B. Fatty acids
C. Sphingosine
D. Both B and C
5. Cytidine diacylglycerol can also be written as?
A. CDP-diacylglycerol
B. CTP-diacylglycerol
C. CDG
D. None of the above
6. Match the following-
a. Phosphatidylcholine 1. lecithin
b. Phosphatidylethanolamine 2. cephalin
c. Cardiolipin 3. diphosphatidylglycerol
d. Plasmalogens 4. Glycerol ether phospholipid
7. Phosphatidic acid is the common intermediate for which two pathways?
A. Synthesis of triacylglycerol and glycerophospholipid
B. Synthesis of fatty acids and glycerophospholipid
C. Synthesis of ketone bodies and glycerophospholipid
D. None of the above
8. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. Choline is not required to convert into its active form
B. Synthesis of phosphatidylserine starts with CDP-diacylglycerol
C. Cardiolipin is used for phosphate transferase
D. Cephaline is also synthesized by 2 pathways
9. What is the other name of lecithin?
A. Phosphatidylcholine
B. Phosphatidylserine
C. Cardiolipin
D. Sphingomyelins
10. In all glycerophospholipids, is the glycerol always bound to ester linkage?
A. Yes
B. Exception is plasmalogens
C. Exception is cardiolipin
D. All of the above
11. What is the starting compound for the synthesis of sphingolipids?
A. Pyruvate
B. Lactate
C. Ceramide
D. Glucose
12. Where is ceramide synthesized?
A. Nucleus
B. Endoplasmic reticulum
C. Mitochondria
D. Cytosol
13. Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of plamitoyl-CoA and serine to 3-ketosphinganine requires which compound?
A. Lactate
B. Acetyl-CoA
C. Pyridoxal phosphate
D. Lipoprotein
14.Where is sphingomyelin formed?
A. Cytosol
B. Mitochondria
C. Golgi apparatus
D. Nucleus
ANSWERS:-
1. Membrane lipids
2. 2
3. All of the above
4. Sphingosine
5. CDP-diacylglycerol
6. a – 1 b – 2 c – 3 d – 4
7. Synthesis of triacylglycerol and glycerophospholipid
8. Choline is not required to convert into its active form
9. Phosphatidylcholine
10. Exception is plasmalogens
11. Ceramide
12. Endoplasmic reticulum
13. Pyridoxal phosphate
14. Golgi apparatus
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCE:- Pankaja Naik- Biochemistry; 4th edition; page no:- 232-235.