Diabetes Mellitus : Definition, Classification, Pathogenesis, Treatment And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
” Diabetes mellitus represents a group of metabolic disorders in which there is impaired glucose utilization, including hyperglycemia.”
1.] In diabetes mellitus fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism is commonly affected.
2.] People with diabetes are very much prone to infection.
3.] In this metabolic syndrome some of the major features are – central obesity, hypertriglyceridaemia, low LDL cholesterol, hyperglycemia and the hypertension.
4.] Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of morbidity ( refers to having a disease or a symptoms of disease, or to the amount of disease in population, it also refers to medical problems caused by treatment) and mortality all over the world.
5.] The rise in prevalence is more for – Type 2 diabetes than for Type 1.
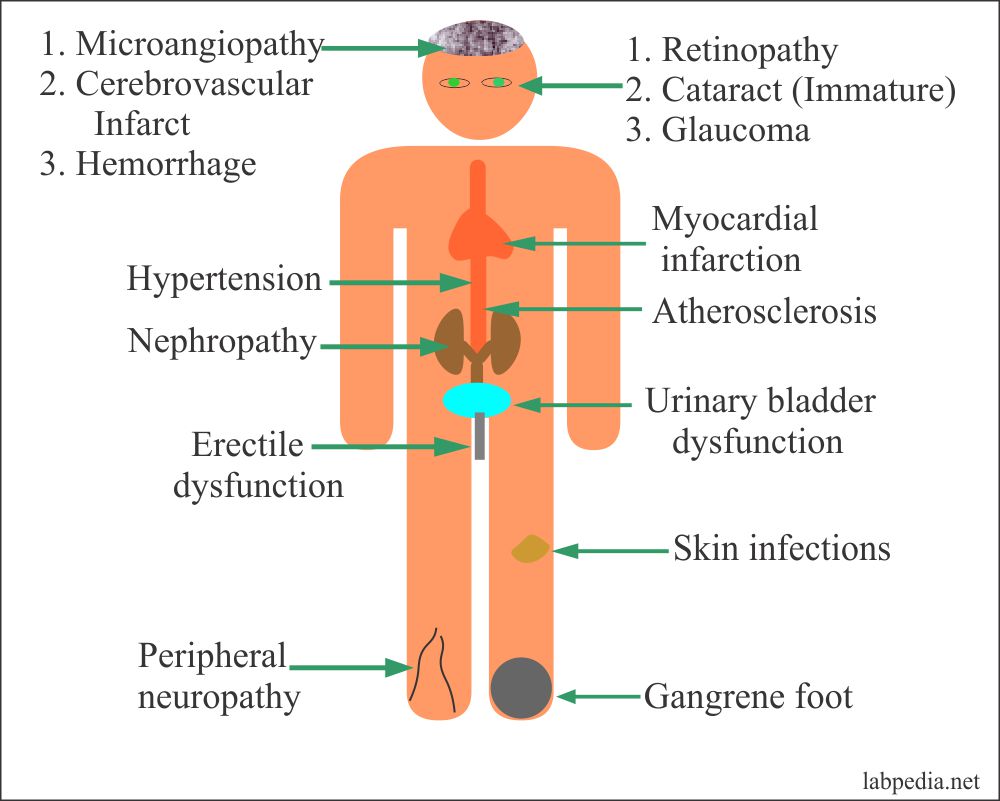
The above image is taken for education purpose only from labpedia.com
CLASSIFICATION :-
There are basically two types of diabetes :
A.] Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus : It is also called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. In this type 1 diabetes about 10% cases of diabetes mellitus were constituted. Previously, it is termed as juvenile – onset diabetes (JOD) due to its occurrence in younger age and was called insulin dependent for insulin replacement as treatment.
Based on underlying etiology, type 1 diabetes mellitus is further divided into 2 types :-
- Subtype 1A (immune – mediated) DM : characterized by auto – immune destruction of beta cells which usually leads to insulin deficiency.
- Subtype 1B (idiopathic) DM : characterized by insulin deficiency with tendency to develop ketosis but these patients are negative for autoimmune markers.
B.] Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus : This type comprises about 80% cases of DM. Previously, this type 2 diabetes is termed as non – insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or maturity – onset diabetes. Type 2 DM mainly affect older individuals. Many Type 2 DM patients require insulin therapy to control hyperglycemia or to prevent ketosis.
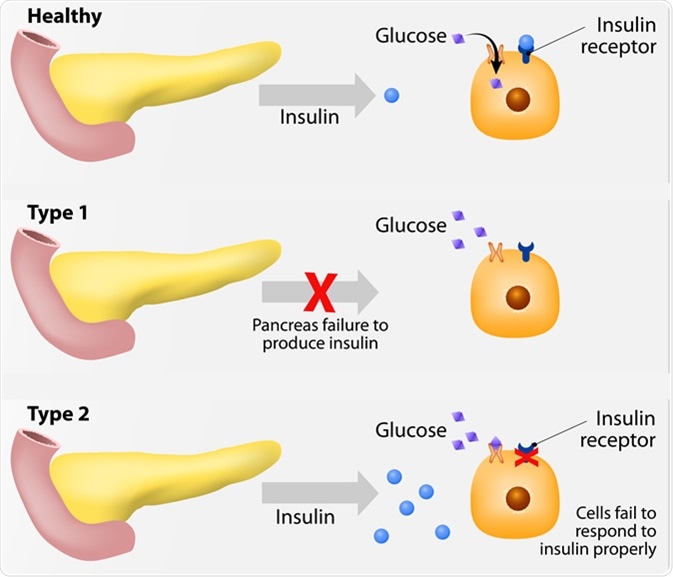
The above image is taken for education purpose only from news – medical.net
PATHOGENESIS :-
Depending upon the etiology discussed above of DM; hyperglycemia may result from the following :
- Reduced insulin secretion
- Decreased glucose use by the body
- Increased glucose production
A.] Pathogenesis of Type 1 DM : Basically, in type 1 diabetes mellitus there is a destruction of beta – cells mass, which leads to absolute deficiency of insulin.
Pathogenesis of type 1 ADM are as follows :
- At birth, individuals with genetic susceptibility to this disorder have normal beta – cell mass.
- Also beta – cells act as an auto antigens and activate CD4+ T lymphocytes, bringing about immune destruction of pancreatic beta – cells by autoimmune phenomena and take months to years.
- Trigger of autoimmune process appears to be some infectious or environmental factor which specifically targets beta – cells.
B.] Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM : In type 2 DM either a delayed insulin secretion relative to glucose load (impaired insulin secretion), or the peripheral tissue are unable to respond to insulin (insulin resistance).
Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM are as follows :
- Type 2 DM is a more complex multi factorial disease.
- There is a greater role of genetic defect and heredity.
- Two main mechanism for hyperglycemia in type 2 DM – insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, are interlinked.
- Obesity also plays a very important role.
- Increased hepatic synthesis of glucose also contribute to hyperglycemia.
TREATMENT :-
Medication given to the TYPE-I Diabetic patients are as follows :-
Short-acting insulin
- regular insulin (Humulin and Novolin)
Rapid-acting insulins
- insulin aspart
- insulin glulisine
- insulin lispro
Intermediate-acting insulin
- insulin isophane
Long-acting insulins
- insulin degludec
- insulin detemir
- insulin glargine
- insulin glargine
Combination insulins
- insulin aspart protamine-insulin aspart
- insulin lispro protamine-insulin lispro
- insulin lispro protamine-insulin lispro
- human insulin NPH-human insulin regular
- human insulin NPH-human insulin regular
- insulin degludec-insulin aspart
Amylinomimetic drug
- Pramlintide is an amylinomimetic drug. It’s an injectable drug given before meals.
Medications for type 2 diabetes
Sulfonylureas
- glimepiride
- gliclazide
- glipizide
- glyburide
- chlorpropamide
- tolazamide
- tolbutamide
Biguanides
- The most common biguanide is metformin
- Metformin can also be combined with other drugs for type 2 diabetes.
Thiazolidinediones
- Rosiglitazone
- Pioglitazone (Banned now)
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Acarbose
- Miglitol
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors help the body continue to make insulin.
These drugs can also help the pancreas make more insulin. These drugs include:
- Alogliptin
- Linagliptin
- Saxagliptin
- Sitagliptin
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 receptor agonists)
These drugs are similar to the natural hormone called incretin.
- Albiglutide
- Dulaglutide
- Exenatide
- Liraglutide
- Semaglutide
Meglitinides
- Nateglinide
- Repaglinide
Sodium-glucose transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors
- Dapagliflozin
- Canagliflozin
- Empagliflozin
- Ertugliflozin
Dopamine agonist
- Bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist.

The above image is taken for education purpose only from cell.com
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :-
1.] Diabetes is beat defined as ?
a. A metabolic disease characterized by low blood sugar
b. A metabolic disease characterized by high blood sugar
c. A family of blood infection
d. None of the above
2.] diabetes can be cured with diet, exercise and medication ?
a. True
b. False
3.] Which is not an symptom of diabetes ?
a. Itchy skin
b. Thirst
c. Frequent urination
d. Muscle Pain
4.] Insulin is a natural hormone secreted by which organ or gland ?
a. The kidney
b. The liver
c. The pancreas
d. The spleen
5.] Type – 2 diabetes can cause long term damage in the ?
a. Kidneys
b. Eyes
c. Nerves
d. All of the above
6.] Gestational diabetes occurs ?
a. During pregnancy
b. After a bout with shingles
c. At birth
d. After menopause
7.] People with diabetes are prone to ?
a. Acne (pimples)
b. Shingles
c. Infection
d. Migraine
8.] When the body does not respond to the insulin it makes this is called ?
a. Type 1 diabetes
b. Type 2 diabetes
c. Both
d. None of the above
9.] With Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin ?
a. True
b. False
10.] Prediabetes is considered as a reversible condition ?
a. True
b. False
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (b) A metabolic disease characterized by high blood sugar
2.] (b)
3.] (d) Muscle pain
4.] (c) The pancreas
5.] (d)
6.] (a) During pregnancy
7.] (c) Infection
8.] (b) Type 2 diabetes
9.] (a)
10.] (a)
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 808 – 818.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 909 – 922.