HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
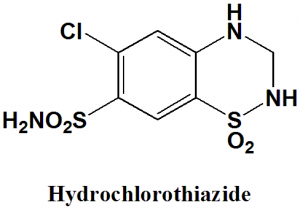
Hydrochlorothiazide
IUPAC nomenclature
6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
Classification
- Thiazide diuretic
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 297.7 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 274oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in DMF, NaOH solution; soluble in ethanol; insoluble in ether |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | -0.07 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Benzothiazine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Hydrochlorothiazide inhibits reabsorption by the Na-Cl symportor by acting on the proximal region of the DCT.
- Inhibition of this reduces the concentration gradient magnitude between the DCT and epithelial cell which results in the reduction in reabsorption of water.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of thiazide diuretics can be summarized as:
- Chlorothiazide is the simplest member of the series.
- Hydrogen atom at the 2-N is most acidic due to presence of electron-withdrawing group.
- Sulfonamide group at C-7 position provides additional acidity to the drug.
- Electron withdrawing group is essential at position 6 for diuretic activity of the drug.
- Substitution oh hydrogen at 6 position gives little diuretic activity, whereas, substitution with chloro and trifluoromethyl groups gives highly active compounds.
- Substitution of electron donating group at position 6 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Replacement or removal of sulfonamide groups from position 7 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Saturation of the double bond to give 2,4-dihydro derivative are 10-folds more active than the unsaturated compounds.
- Substitution of a lipophillic group at 3 position increases the potency.
- Substitution with the entities such as haloalkyl, aralkyl or thioether gives compounds with longer duration of action due to increased lipid solubility.
- Alkyl substitution at the 2-N position can increase the action duration. [1]
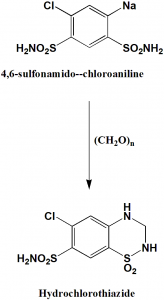
Method of synthesis
Cyclization of 4,6-sulfonamido-3-chloroaniline by using paraformaldehyde and simultaneous reduction of double bond at C3-C4 to get the drug hydrochlorothiazide.[2]
Medicinal Uses
Hydrochlorothiazide is used for:
- Management of hypertension
- Management of edema related to CHF, chronic renal failure, glomerulonephritis, nephritic syndrome and hepatic cirrhosis.
Side Effects
Side effects of hydrochlorothiazide are:
- Lightheadedness
- Blurred vision
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Sneezing
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Swelling of face
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Muscle spasm
- Dizziness
- Headache
MCQs
Q.1 Which of the following statements are correct related with the physicochemical properties of drug Hydrochlorothiazide?
I. Molecular weight: 297.7 gm/mol
II. Physical appearance: White crystalline powder
III. Melting point: 45 oC
a) I, II, III
b) I, II
c) II, III
d) I, III
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Hydrochlorothiazide | A. 4-(5H-Dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-1-methylpiperidine |
| ii. Naproxen | B. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide |
| iii. Hydroxyzene | C. (+)-(S)-2-(6-Methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoic acid
|
| iv. Cyproheptidine | D. (±)-2-(2-{4-[(4-chlorophenyl)-phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)ethanol |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-B, iv-A
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.3 Mechanism of action of drug Hydrochlorothiazide includes?
I. Release if NO
II. Inhibition of reabsorption of sodium and chloride
III. Active synthesis of cGMP
IV. Reduction in reabsorption of water
a) I, III, IV
b) II, IV
c)I, II, III
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Sedative hypnotics
- Amyl nitrite: α-adrenergic blocker
- Methoexital: ß-adrenergic blocker
- Naphazoline: Inhalational anesthetics
a) TFFT
b) FFTT
c) FFFF
d) TTTF
Q.5 Which of the following statements related with the SAR of thiazide diuretics is/are correct?
a) Hydrogen atom at the 2-N is most acidic due to presence of electron-withdrawing group.
b) Sulfonamide group at C-7 position provides additional acidity to the drug.
c) Electron withdrawing group is essential at position 6 for diuretic activity of the drug.
d) All of the above
Q.6 Type of rings present in the structure of Hydrochlorothiazide?
I. Dihydropyridine
II. Benzothiazine
III. Dihydrofuran
IV. Cyclobutane
a) II, IV
b) I , II
c) III, IV
d) II
Q.7 Side effect of drug Hydrochlorothiazide is/are?
a) Pale skin
b) Nausea
c) Muscle spasm
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-b
4-c
5-d
6-d
7-d