Classification and Characteristics of Bacteria, Lectures on Bacteria Cell for BSc, MSc, B.Pharma
CLASSIFICATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA
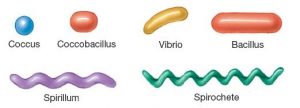
Classification of bacteria on basis of their basic cell shapes
Cocci: Unicellular, spherical or elliptical shape.
- Monococcus: A single discrete round shape. Eg: Micrococcus flavus
- Diplococcus: Two spherical shaped bacteria attached with each other. Eg: Diplococcus pneumonia.
- Streptococcus: A chain of spherical bacteria attached with each other. Eg: Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Tetracoccus: Four round cells right angle to each other. Eg: Staphylococcus aureus.
- Sarcina: Eight or sixteen cells attached with each other in a cubic shape. Eg: Sarcina lutea
Bacilli: Rod shaped or cylindrical shaped bacteria may be present single or in pairs. Eg: Bacillus cereus.
Vibrio: Curved comma shaped bacteria. Eg: Vibrio cholera.
Spirilla: Bacteria present in spiral or spring like shape with multiple curvatures. Eg: Spirillum volutans.
(The image is taken from Black JG. Microbiology: principles and explorations for education purpose only)
On the basis of growth characteristics
- On the basis of the requirement of oxygen for growth by microorganism [click here]
- On the basis of optimum temperature required by bacteria for proper growth [click here]
- On the basis of pH required for bacteria to grow properly [click here]
- On the basis of hydrostatic pressure required by bacteria for growth [click here]
- On the basis of osmotic pressure required by bacteria for its growth [click here]
On the basis of mode of nutrition
- Phototrophs: These bacteria gain energy from sunlight. They may get electrons from inorganic compounds (photolithotrophs), for eg.: Chromatium okenii, or may get electrons from organic compound (Photoorganotrophs).
- Chemotroph: These bacteria cannot carry photosynthesis and gains energy from chemical compounds. They can be further classified as chemolithotrophs (Nitrosomonas) and chemoorganotrophs (Pseudomonas pseudoflava)
- Autotrophs: These bacteria uses carbon dioxide as the source of carbon. They can be photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs.
- Heterotrophs: Bacteria which cannot fix carbon dioxide and thus, uses other organic sources for food. Most of the human pathogens falls under this category.
On the basis of cell wall
- Gram-positive bacteria: Bacteria having thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall.
- Gram-negative bacteria: Bacteria having thin layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall.
- Acid fast bacteria: They have high lipid contains in their cell wall.
General characteristic of bacteria
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms. Most of the species of bacteria are highly pathogenic in nature and causes human and animal diseases. They have a rigid cell wall, a cell membrane, nuclear region and 70S type of ribosomes. (click here for detailed information)
Structure of Bacterial Ribosome
Bacterial Cell Nuceloid Structure & Function
Bacterial Cell Capsule Structure & Function
Bacterial Cell Flagella Structure & Function
Bacterial Cell Pili Structure
MCQs
Q.1. Micrococcus flavus is an example of?
a) Monococcus bacteria
b) Diplococcus bacteria
c) Streptococcus bacteria
d) Tetracoccus bacteria
Q.2. Rod shaped bacteria are known as?
a) Vibrio
b) Spirilla
c) Bacilli
d) Cocci
Q.3. Bacteria which gain energy from sunlight and get electrons from inorganic compounds are known as?
a) Photoorganotrophs
b) Photolithotrophs
c) Chemoorganotraphs
d) Chemolithotrophs
Q.4. Gram negative bacteria have?
a) Thick layer of peptidoglycan in cell wall
b) Thin layer of peptidoglycan in cell wall
c) High lipid contain in the cell wall
d) None of the above
Q.5. Bacteria have which type of ribosomes in their nuclear region?
a) 80S
b) 70S
c) 94S
d) 43S
Q.6. Which of the following bacteria are the phototrophs?
I. Chromatium okenii
II. Nitrosomonas
III. Pseudomonas pseudoflava
a) I, III
b) I, II
c) I
d) II, III
Q.7. Match the following bacteria with their correct classification:
| i. Staphylococcus aureus | A. Monococcus |
| ii. Spirillum volutans | B. Tetracoccus |
| iii. Micrococcus flavus | C. Vibrio |
| iv. Vibrio cholera | D. Spirilla |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-b
4-b
5-b
6-c
7-d
REFERENCE
Black JG. Microbiology: principles and explorations.