Classification of Viruses and Characteristics of Viruses, MCQ of Viruses For GPAT, CSIR NET, NEET PG & Pharmacist Exam
CLASSIFICATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUS
Classification of virus
On the basis of genetic material:
- DNA viruses: DNA viruses have DNA as their genetic material. They cause a large range of benign symptoms in humans and animals causing serious health issues. Examples are parvovirus, papillomavirus and herpesvirus.
- RNA virus: RNA viruses have RNA as their genetic material. Examples are Ebiola virus, Rabies virus, Measles virus, Rotavirus, Dengue virus, Hepatitis C virus, yellow fever virus and polio virus.
- DNA-RNA viruses: Leukoviruses and Rous’s viruses which are the RNA tumor viruses have both DNA and RNA as their genetic material.
On the basis of number of strands of genetic material:
| Double-stranded DNA | Adenovirus, herpes virus, lamda virus, bacteriophages T2, T4, T6, T7, T3, pox viruses |
| Single-stranded DNA | Bateriophages φ, 74, X |
| Double-stranded RNA | Reoviruses, wound tumor virus, rice dwarf viruses |
| Single-stranded RNA | Avian Leukemia virus, tobacco mosaic virus, influenza virus, poliomyelitis, bacteriophage MS-2. |
On the basis of type of host:
| Type of virus | Description | Examples |
| Animal viruses | These infect live humans and animals.
They have either DNA or RNA as their genetic material. |
Influenza virus, polio virus, mumps virus, rabies virus, etc. |
| Plant viruses | These viruses infect plants.
They have RNA as their genetic material. |
Turnip yellow virus, beet yellow virus, potato virus, tobacco mosaic virus |
| Bacteriophages | These viruses infect bacterial cells.
They contain DNA as their genetic material. |
Bacteriophages T2, T4, T6, T7, T3 |
Baltimore classification:
|
Group number |
Description |
| Group I | · ds-DNA as their genome.
· mRNA is produced by transcription. |
| Group II | · ss-DNA as their genome.
· ss genome is converted into dsDNA and then transcripted to mRNA. |
| Group III | · dsRNA as their genome.
· Strands are separated and one of the strands can be used as a template for mRNA synthesis using RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme. |
| Group IV | · ssRNA as their genome with positive polarity.
· Full-kength RNA strands of negative polarity are formed form dsRNA intermediates. |
| Group V | · ssRNA with negative polarity.
· Negative strands can be directly converted to mRNA |
| Group VI | · Two copies of ssRNA genomes.
· ssRNA converts into dsDNA using reverse transcriptase enzyme. |
| Group VII | · Partial dsDNA as their genome.
· dsDNA makes ssRNA intermediates which acts as mRNA and can be converted into dsDNA through reverse transcription. |
General characteristics of viruses
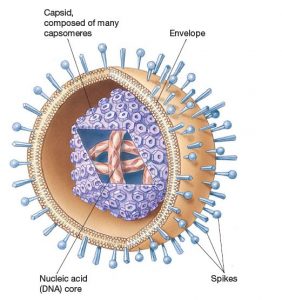
Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites. They are too small to be seen with a light microscope. All the cell organelles along with nucleus and cytoplasm are absent in viruses. They appear to be as a borderline between living and non-living.
Fig: structure of virus
The above image is taken only for educational purpose from [1]
Virus have nucleic acid core. These nucleic acids are the genomic material of viruses and are used for the replication purposes in the host cells. These nucleic acid can be present in the form of DNA or RNA. Nucleic acid of most of the viruses are covered with capsids. Capsids are made of protein subunit called capsomeres. Outside capsid, there may be a bilayer membrane present which is allied envelopes. Viruses which have the presence of envelopes are called enveloped viruses, while others are called naked viruses. There may be projection made up of glycoprotiens are present on the envelope, for example, in the form of spikes. Envelopes helps the viruses to be remain hidden from the host’s immunity cells. On contrast, enveloped viruses can be destroyed easily with change in surrounding physical conditions, such as temperature, while, naked viruses more resistant to the changing surrounding environments.
Size of viruses can range between 30nm to 300nm. Shape of viruses can be determined by the shape of capsids and envelopes. Based on this, shape of viruses can be helical, polyhedral. Icosaedral, bullet shaped, spherical or complex shaped.
MCQs
1. Size of viruses range between?
a. 100 mm to 150 mm
b. 30 nm to 300 nm
c. 300 nm to 3000 nm
d. 3 nm to 30 nm
2. Viruses without nuclear envelop is called as?
a. Icosahedral virus
b. Naked virus
c. Enveloped virus
d. Bilayered virus
3. In viruses, nucleic acid can be present in the form of?
a. DNA virus
b. RNA virus
c. Both a. and b.
d, None of the above
4. Capsids are made of subunits known as?
a. Capsomeres
b. Flagella
c. Hyphae
d. Septa
5. Leukoviruses have?
a. DNA as their genetic material
b. RNA as their genetic materia
c. Both DNA and RNA as their genetic material
d. Have no genetic material
6. According to Baltimore classification, viruses having ss-DNA as their genome can be put in which group number?
a. Group I
b. Group II
c. Group III
d. Group IV
7. Match the following viruses with the type of genetic material they have-
| Double-stranded DNA | Adenovirus |
| Single-stranded DNA | Bateriophages φ |
| Double-stranded RNA | Reoviruses |
| Single-stranded RNA | Tobacco mosaic virus |
a. i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
b. i-A, ii-D, iii-D, iv-D
c. i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d. i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-b
2-b
3-c
4-a
5-c
6-b
7-a