Notes: Anti-Cancer Drug Mechanisms of Alkylating and Antimetabolite Agents
1. Alkylating Agents
-
Mechanism of Action:
-
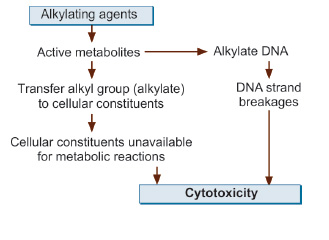
Alkylating agents add alkyl groups (e.g., methyl, ethyl) to DNA, primarily at the N7 position of guanine.
-
This causes:
-
DNA cross-linking (intra- and inter-strand).
-
Mispairing of bases.
-
DNA strand breakage.
-
Inhibition of DNA replication and transcription → cell death.
-
-
Cell cycle non-specific (but most toxic to rapidly dividing cells).
-
-
Examples:
-
Cyclophosphamide
-
Melphalan
-
Chlorambucil
-
Busulfan
-
Nitrosoureas (Carmustine, Lomustine)
-
-
Participate in GPAT MOCK TEST: Click Here
2. Antimetabolites
-
Mechanism of Action:
-
Structural analogs of normal cellular metabolites (purines, pyrimidines, folic acid).
-
They interfere with DNA/RNA synthesis by:
-
Inhibiting enzymes involved in nucleotide synthesis.
-
Being incorporated into DNA/RNA, leading to chain termination or faulty nucleic acids.
-
-
S-phase specific (active during DNA synthesis phase).
-
-
Subclasses and Examples:
-
Folic Acid Antagonists:
-
Methotrexate → Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) → ↓ thymidylate/purine synthesis.
-
-
Pyrimidine Analogues:
-
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) → Inhibits thymidylate synthase.
-
Cytarabine → Inhibits DNA polymerase.
-
-
Purine Analogues:
-
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) → Inhibits IMP conversion to AMP/GMP.
-
Fludarabine, Cladribine → DNA incorporation and polymerase inhibition.
-
-
📝 MCQs: Mechanism of Anti-Cancer Drugs
GET MORE MCQ: Click Here
1. Which of the following is the primary target of alkylating agents?
A. Topoisomerase
B. DNA polymerase
C. N7 position of guanine in DNA
D. RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: C
2. What is the main mechanism of action of methotrexate?
A. Inhibits DNA polymerase
B. Inhibits thymidylate synthase
C. Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase
D. Causes DNA alkylation
✅ Answer: C
3. Which phase of the cell cycle do antimetabolites primarily act on?
A. G1 phase
B. S phase
C. G2 phase
D. M phase
✅ Answer: B
4. 5-Fluorouracil inhibits which enzyme?
A. Ribonucleotide reductase
B. Dihydrofolate reductase
C. DNA polymerase
D. Thymidylate synthase
✅ Answer: D
5. DNA cross-linking caused by alkylating agents leads to:
A. Increased transcription
B. Enhanced protein synthesis
C. Inhibition of DNA replication
D. Increased RNA stability
✅ Answer: C