ACETYLCHOLINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
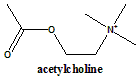
Acetylcholine
IUPAC nomenclature
2-Acetoxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium
Classification
Acetylcholine is a cholinergic agonist. It is a choline ester.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 146.21 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form. |
| 3 | Melting point | 148°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | 600gm/L in water |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of acetylcholine is as a cholinergic agonist.
Structure Activity Relationship
- When the nitrogen of the quaternary ammonium group is replaced with arsenic, phosphorous, sulfur or selenium, their activity decreases.
- It is necessary for the atom present at the nitrogen position to have a positive charge to have muscarinic activity.
- When all three methyl groups are replaced by larger alkyl groups at the quaternary nitrogen, drug become inactive as agonist.
- When all the methyl groups associated with the quaternary nitrogen atom are replaced by ethyl groups, the compound becomes cholinergic antagonist.
- Replacement of just one methyl grup associated with quaternary nitrogen with an ethyl or a propyl group gives the compound which is having lesser activity than acetylcholine.
- Substitution of the methyl groups associated with quaternary nitrogen with hydrogen atoms also leads to diminishing of the muscarinic activity.
- At the ethylene bridge, synthesis of acetic acid esters of quaternary ammonium alcohols of greater length than choline led to a series of compounds which are having lesser activity as the length of the chain increases.
- There should be no more than 5 atoms between nitrogen and terminal hydrogen to have the maximum muscarinic activity.
- Replacement of the ethylene bridge by the alkyl groups larger than methyl groups decreases the activity.
- The R-(-) isomer is 20 time less potent.
- For the maximum potency, the alkyl groups at the nitrogen atoms should not be larger than methyl groups.
- Presence of oxygen in an ester form increases the activity.
- For maximum activity, there should be two- carbon atoms between the nitrogen and oxygen atom. [1]
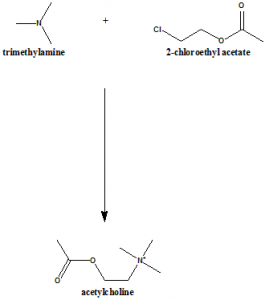
Method of synthesis
Trimethylamine and 2-chloroethyl acetate reacts together to give acetylcholine.
Therapeutic Uses
Acetylcholine is used for treatment of:
- Myasthenia gravis
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Reverse the action of muscle relaxants
Side Effects
Side effects of acetylcholine are:
Ocular side effects:
- Corneal swelling
- Corneal clouding
- Corneal decomposition
Systemic side effects:
- sweating
- difficulty in breathing
- hypotension
- flushing
- slow heart rate
MCQs
Q.1 “2-Acetoxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Acetylcholine
b) Cevimeline
c) Trospium chloride
d) Carvedilol
Q.2 Molecular weight of Acetylcholine is?
a) 146.21 gm/mol
b) 199.32 gm/mol
c) 428 gm/mol
d) 406.5 gm/mol
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Cavedilol | A. Antispasmodic agent |
| ii. Trospium chloride | B. Cholinergic agonist. Choline ester. |
| iii. Acetylcholine | C. Mixed α/ß blocker |
| iv. Metocurine | D. Nicotinic antagonist |
a) i-,B ii-,C iii-A, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-A
Q.4 Mechanism of action of Acetylcholine can be due to?
a) Antagonism of cholinergic receptors
b) Agonism of cholinergic receptors
c) Anticholinestrase inhibition
d) Anticholinestrase Stimulation
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug acetylcholine.
When the nitrogen of the quaternary ammonium group is replaced with arsenic, phosphorous, sulfur or selenium, their activity Increases.
It is necessary for the atom present at the nitrogen position to have a Negative charge to have muscarinic activity.
When all three methyl groups are replaced by larger alkyl groups at the quaternary nitrogen, drug becomes inactive as agonist.
When all the methyl groups associated with the quaternary nitrogen atom are replaced by ethyl groups, the compound becomes cholinergic antagonist.
a) TTFF
b) FTFT
c) TFFT
d) FFTF
Q.6 Trimethylamine and 2-chloroethylacetate reacts together to give?
a) Cevimeline
b) Acetylcholine
c) Zolpidem
d) Trospium chloride
Q.7 The drug Acetylcholine is mainly used for?
a) Alzhiemer’s disease
b) Myasthenia gravis
c) Reversing action of muscle relaxants
d) All of the above
FREE GPAT online Test: Participate: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-c
4-b
5-a
6-b
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Foye WO. Principles of medicinal chemistry. Williams & Wilkins; 2017, 320.