Anticancer Drug Classification – Notes for GPAT, Pharmacist, Drug Inspector, NEETPG, NORCET and Nursing Exams
Anticancer Drug Classification – Notes
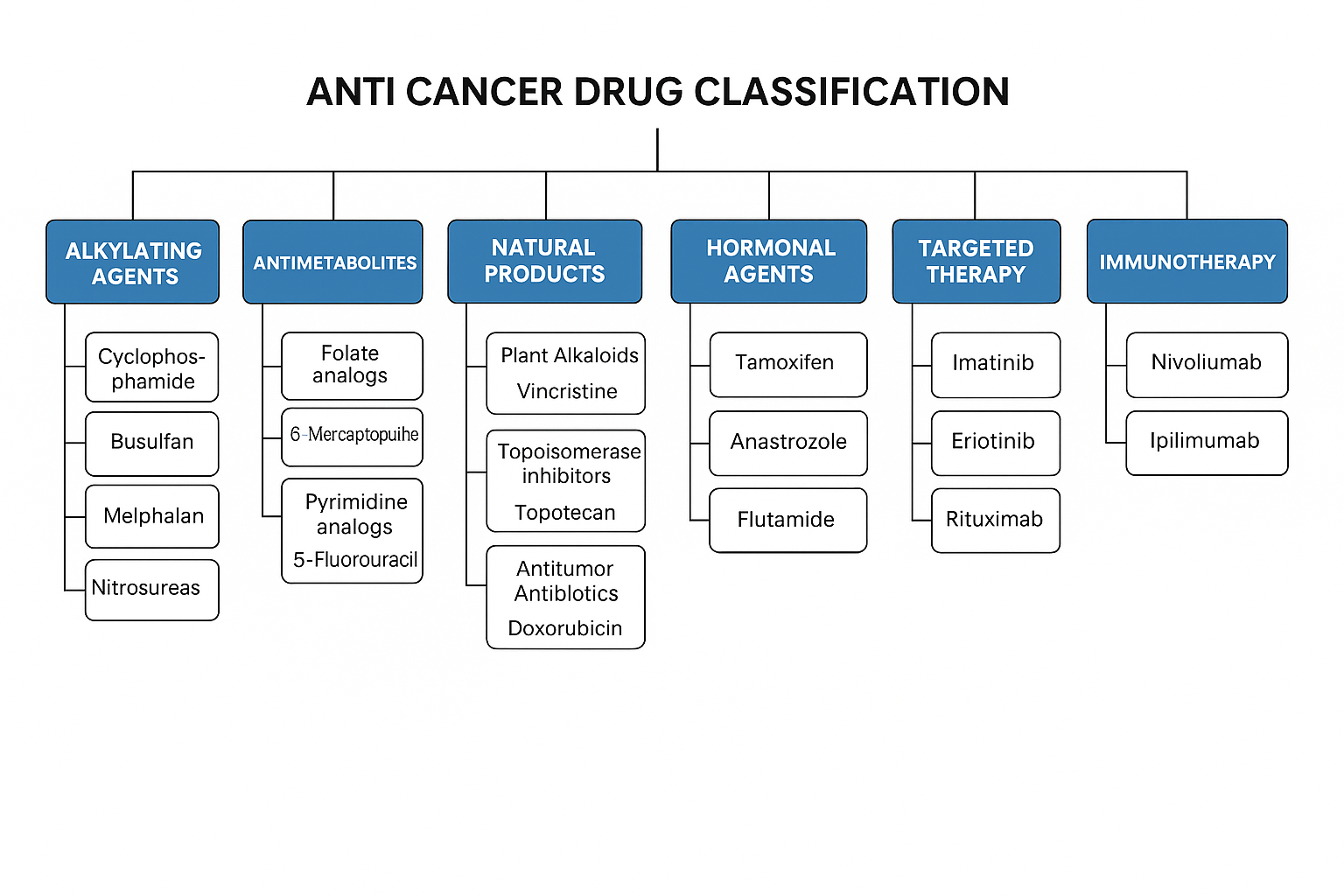
Anticancer drugs (antineoplastic agents) are used to treat malignancies by inhibiting cell growth and proliferation. They are classified based on their mechanism of action:
1. Alkylating Agents
-
Mechanism: Add alkyl groups to DNA → DNA cross-linking → inhibition of replication & transcription
-
Examples:
-
Cyclophosphamide
-
Busulfan
-
Melphalan
-
Nitrosoureas (e.g. Carmustine)
-
2. Antimetabolites
-
Mechanism: Mimic natural metabolites → interfere with DNA/RNA synthesis
-
Subtypes:
-
Folate analogs – Methotrexate
-
Purine analogs – 6-Mercaptopurine, Fludarabine
-
Pyrimidine analogs – 5-Fluorouracil, Cytarabine
-
3. Natural Products
a. Plant Alkaloids
-
Vinca Alkaloids (Vincristine, Vinblastine) – inhibit microtubule polymerization
-
Taxanes (Paclitaxel, Docetaxel) – stabilize microtubules
b. Topoisomerase Inhibitors
-
Topoisomerase I inhibitors: Topotecan, Irinotecan
-
Topoisomerase II inhibitors: Etoposide, Teniposide
c. Antitumor Antibiotics
-
Bind DNA → inhibit RNA synthesis, strand breakage
-
Examples: Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, Bleomycin, Mitomycin
4. Hormonal Agents
Used in hormone-sensitive cancers (breast, prostate)
-
Anti-estrogens – Tamoxifen, Fulvestrant
-
Aromatase Inhibitors – Anastrozole, Letrozole
-
Anti-androgens – Flutamide, Bicalutamide
-
GnRH agonists/antagonists – Leuprolide, Degarelix
5. Targeted Therapy
-
Target specific molecular pathways/proteins in cancer cells
-
Examples:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors – Imatinib, Erlotinib
-
Monoclonal antibodies – Rituximab, Trastuzumab, Bevacizumab
-
6. Immunotherapy
-
Enhance immune system to fight cancer
-
Checkpoint inhibitors: Nivolumab (PD-1), Ipilimumab (CTLA-4)
-
CAR-T cell therapy
7. Miscellaneous
-
Hydroxyurea
-
Procarbazine
-
Asparaginase
8. Supportive Agents
-
Used to manage chemotherapy side effects:
-
Filgrastim (G-CSF) – neutropenia
-
Mesna – protects bladder from cyclophosphamide toxicity
-
Leucovorin – rescue for methotrexate
-
❓ MCQs on Anticancer Drugs
Q1. Which of the following is a purine analog?
A. Methotrexate
B. 6-Mercaptopurine
C. 5-Fluorouracil
D. Cyclophosphamide
✅ Answer: B
Q2. Paclitaxel acts by:
A. Inhibiting DNA synthesis
B. Stabilizing microtubules
C. Inhibiting thymidylate synthase
D. Alkylating DNA
✅ Answer: B
Q3. Which drug is a monoclonal antibody targeting HER2/neu?
A. Bevacizumab
B. Rituximab
C. Trastuzumab
D. Cetuximab
✅ Answer: C
Q4. Leucovorin is used as a rescue agent with:
A. Cyclophosphamide
B. Methotrexate
C. 5-Fluorouracil
D. Bleomycin
✅ Answer: B
Q5. Bleomycin’s dose-limiting toxicity is:
A. Myelosuppression
B. Nephrotoxicity
C. Pulmonary fibrosis
D. Cardiotoxicity
✅ Answer: C
Q6. Which of the following is a topoisomerase II inhibitor?
A. Irinotecan
B. Topotecan
C. Etoposide
D. Vinblastine
✅ Answer: C