ASPIRIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
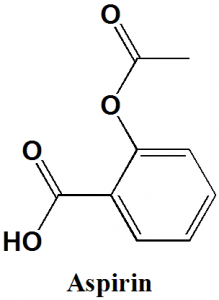
Aspirin
IUPAC nomenclature
2-Acetoxybenzoic acid
Classification
- Non-selective COX inhibitors (traditional NSAIDs)
- Salicylates
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 180.16 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 140°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 1 g soluble in 300 ml of water. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.18 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- The acetyl group of actetylsalicyclic acid binds irreversibly with serine residue of COX-1 (cyclooxygenase-1) enzyme which leads to its irreversible inhibition. Due to this, the pain producing prostaglandins production is prevented.
- The conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane is also prevented which checks the platelet aggregation and thus, clotting and venous and arterial thromboembolism is also prevented.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for salicylates can be summarized as follows:
- Active moiety responsible for the action is salicylate anion.
- Side effects of the drug are associated with carboxylic acid function.
- Reducing the acidity of carboxylic acid by converting into amide maintains the analgesic action but eliminates the anti-inflammatory properties.
- Substitution on the carboxyl or phenyl hydroxyl groups results in changes in the toxicity and potency of the drug.
- Activity is abolished when the phenolic hydroxyl group is placed on meta or para position to the carboxyl group.
- Introduction of the halogen atom on the phenolic ring increases the potency and the toxicity of the drug.
- Substitution on the 5th-position on the phenolic ring increases the anti-inflammatory property of the drug. [1]
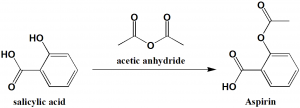
Method of synthesis
Aspirin can be synthesised by the acetylation of the salicylic acid by acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Aspirin is used for:
- Reducing fever
- Relieve mild to moderate pain
- Prevention of blood clotting
- Reducing the risk of stroke
- Reducing the risk of heart attack
- As a blood thinner
Side Effects
Side effects Aspirin are:
- Heartburn
- Stomach upset
- Easy bleeding
- Difficulty in hearing
- Kidney problems
- Ringing in ears
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Pale skin
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
MCQs
Q.1 “2-acetoxybenzoic acid” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Aspirin
b) Paracetamol
c) Loperamide
d) Zolpidem
Q.2 Correct melting point of the drug Aspirin is?
a) 124°C
b) 321°C
c) 140°C
d) 26°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Loperamide | A. Antidiarrheal agent |
| ii. Aspirin | B. ß-blockers |
| iii. Methoxyflurane | C. NSAID |
| iv. Metoprolol | D. Anticonvulsant drug |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
Q.4 Mechanism of action of drug Aspirin includes?
I. Binding irreversibly with COX-2 enzyme.
II. Binding with COX-1 enzyme.
III. Prevention of conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane
IV. Prevention of Thromboembolism
a) II, III, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of Salicylates drugs?
- Active moiety responsible for the action is salicylate anion.
- Side effects of the drug are associated with carboxylic acid function.
- Reducing the acidity of carboxylic acid by converting into amide eliminates the analgesic action but maintain the anti-inflammatory properties.
- Substitution on the carboxyl or phenyl hydroxyl groups results in changes in the toxicity and potency of the drug.
a) FFTT
b) TFTF
c) TFFT
d) TTFT
Q.6 Acetylation of salicylic acid leads to formation of which drug?
a) Tolazoline
b) Aspirin
c) Isoflurane
d) Orphenadrine
Q.7 The drug Aspirin is used for?
a) Reducing fever
b) Prevention of blood clot
c) Blood thinner
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-a
4-a
5-d
6-b
7-d