ATROPINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
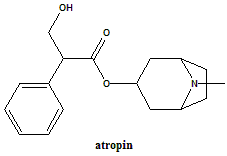
Atropine
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-(8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate.
Classification
Atropine is a acetylcholine antagonist-muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 289.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Rhombic or orthorhombic prisms. |
| 3 | Melting point | 118.5°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | 0.01M in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.83 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Cycloalkane and benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 4 |
Mechanism of Action
Atropine binds with muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and inhibits them. Thus, they produce a wide range of anticholinergic effects. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
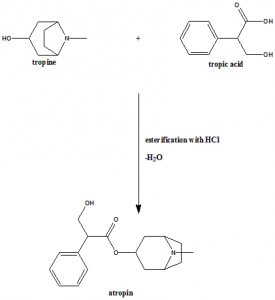
Method of synthesis
Tropine and tropic acid reacts together to give atropine.
Therapeutic Uses
Atropine is used for:
- Reduce salivation
- Reduce mucous secretion
- Reduce other secretions in the air way during a surgery
- Treatment of spasms in stomach, intestines, bladder and other organs.
- As an antidote for treatment of poisons
Side Effects
Side effects of atropine are:
- Dryness in mouth, nose or throat
- Dryness of eyes
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Drowsiness
Some uncommon side effects are:
- Lightheadedness
- Pounding heartbeats
- Restlessness
- Speech problems
- Trouble in swallowing
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
- Weakness
- Imbalance
- Dry skin
- Skin rashes
MCQ
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Atropine?
a) (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
b) [8-methyl-8-(1-methylethyl)- 8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1] oct-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenyl-propanoate
c) (RS)-(8-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
d) 2-[(Aminocarbonyl)oxy]-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride.
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Atropine?
I. X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
II. The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
III. Minimum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
a) III
b) I
c) II, I
d) II, III
Q.3 The interaction of Tropine and tropic acid produces?
a) Atropin
b) Carbachol
c) Procyclidine
d) Doxacurium
Q.4 Side effects of drug Atropine is/are?
a) Pounding heart beats
b) Blurred vision
c) Dryness in mouth
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with correct number of chiral carbons they are having.
| i. Propranolol | A. 1 |
| ii. Carbachol | B. 4 |
| iii. Ipratropium bromide | C. 0 |
| iv. Atropine | D. 5 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-,B iii-A, iv-C
c) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class Acetylcholine Antagonist (muscarinic antagonist) is?
a) Donepezil
b) Carbachol
c) Atropin
d) Paraoxin
Q.7 The type of ring system found in Atropin?
a) Benzene
b) Napthalene
c) Imidazole
d) None of the above
FREE GPAT online Test: Participate: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-a
4-d
5-d
6-c
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] BERNHEIM F. RELATION BETWEEN THE ACTION OF HISTAMIN, ATROPIN, ADRENALIN, AND HEAVY METALS ON THE INTESTINE. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1931 Aug 1;42(4):441-54.