Basic’s and Principle of the IR spectroscopy and MCQ
Basic’s and Principal of the IR spectroscopy :-
In, IR spectroscopy infrared radiation are used. Infrared radiation are classified into three types Accordingly to they wave length.
- Near IR :- 0.78 – 2.6μ
- Mild IR :– 2.5 – 50 μ
- Far IR :– 50- 200μ
Mild IR are widely used in pharmaceutical industry.
Main used of IR spectroscopy is to determine functional group of compound and study of structure of nee compound.
Principal
IR spectroscopy are work on principal of absorption. In IR spectroscopy when ir radiation we give any compound it is excited and show vibration.
Applied IR frequency should be equal to the natural frequency of radiation. Otherwise compound do not give IR peak.
Compound have must be required dipole movement for perfomaning IR spectroscopy.
In any IR spectra there are two important region :-
1. Finger print region
2. Functional group region
• Type of vibration
When we applied IR radiation any compound are absorbed it is saw a vibration.
Compound to compound it is different.
There are mainly two types of vibration
1. Stretching
2. Bending
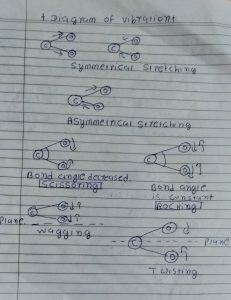
1. Stretching vibration :– It is type of vibration in which bond angle is constant But bond length is increase or decrease.
It has sub division into two types
i. Symmetrical stretching :-
Bond length is increase or decrease.
But bond angle is constant.
Here’s both bond length is increase or decrease.
ii. Asymmetrical stretching
In this Types of stretching in compound one bond length is increase and other must be decrease.
2 Bending vibration
In this Types bond length is constant but bond angle will be change. Also seen plane movement will be change.
It is sub division into four types
1. Scissoring:– In this type of bond angle is decrease.
2. Rocking :- In this type of vibration bond angle is constant.
3. Wagging :- In this type of Bond angle is constant. But movement will be one plane to another plane.
4. Twisting :– In this type of vibration one bond is one plane and other bond is another plane. In this type bond angle is decrease.
Vibration movement you are seeing in this diagram for better understanding:-
MCQ
1. What is the frequency of the mild IR ?
A. 0.7 – 2.5μ
B. 2.5 -50μ
C. 50-200μ
D. All of the above
Ans. B
2. Which is not use of IR spectroscopy ?
A. Functional group
B. Structure identify
C. A and B both
D. Metal detecting
Ans.D
3. Which is principal of the IR spectroscopy ?
A. Absorption
B. Emissions
C. Adsorption
D. Nome of this
Ans. A
4. which is important region in IR spectra ?
A. Finger print region
B. Functional group region
C. A and B both
D. None of this
Ans .C
5. Which movement is required for the IR spectroscopy ?
A. Dipole movement
B. Spin movement
C. Round movement
D. All of the above
Ans. A
6. Which type of vibration bond angle is decrease ?
A symmetrical
B. Asymmetrical
C. Rocking
D. Scissoring
Ans. D
7 . In which vibration bond length is increase or decrease ?
A. Rocking
B. wagging
C. Twisting
D. Symmetrical
Ans. D
8. In which vibration one bond is one plane and other bond is another plane?
A. Rocking
B. Wagging
C. Scissoring
D. Twisting
Ans .D
9. In which bending type of vibration bond angle is constant ?
A. Scissoring
B. Twisting
C. Rocking
D. All of the above
Ans. C
10. Which IR frequency are absorbed by compound ?
A. Applied frequency of the IR is equal to the natural frequency of the compound
B.Applied frequency of the IR is low to the natural frequency of the compound
C.Applied frequency of the IR is greater to the natural frequency of the compound
D. None of this.
Ans. A
Take reference for the analysis text book of third edition of the DR. S. Ravi sankar.
Participate in Free GPAT MOCK Test