BUTABARBITAL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
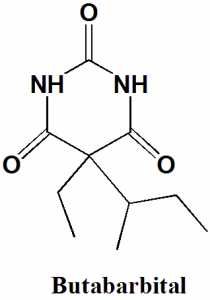
Butabarbital
IUPAC nomenclature
5-butan-2-yl-5-ethyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione.
Classification
Butabarbital is a barbiturate sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 212.25 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Fine white crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 166.5°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.65 |
| 5 | Solubility | 294 mg/L in water |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrimidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Butabarbital increases the duration of time for which the chloride ionopore is open through binding with GABAA
- The post-synaptic inhibitory effect of thalamus prolongs.
- There is decreases in GABA sensitive neuronal calcium conductance.
- The overall result is acute potentiation of inhibitory GABAnergic tone.
- Drug also inhibits excitory AMPA-type glutamate receptors which results in profound suppression of glutamatergic neurotransmission.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Tri-keto form is most stable in aqueous solution.
- 4,6-dialcoholic tautomeric forms are least stable in aqueous solution.
- 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid is the prime requirement for the barbituares to be sedative hypnotics.
- Esterification of either of the 1,3-diazine nitrogens decreases hypnotic activity.
- Substitution of either of the 1,3-diazine nitrogens with aliphatic carbons retains the anticonvulsive properties.
- Esterification of the 5th-position substituents yields agents with analgesic activity but with weak hypnotic properties.
- Introduction of the polar functional group at the 5th– position yields compounds which are fully devoid of sedative-hypnotic or anticonvulsive activity.
- As the number of carbons at R2 carbon increases, the lipophillicity of the drug increases.
- Modification of the 2nd-position oxygen of the barbiturate backbone with sulfur atom yields thiobarbiturate derivatives with increased lipophillicity, shorter duration of action, faster time of onset compared to oxy-derivative. [1]
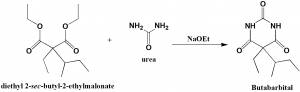
Method of synthesis
Diethyl 2-sec-butyl-2-ethylmalonate reacts with urea in presence of sodium ethoxide to give butabarbital.
Therapeutic Uses
Butabarbital is used for:
- Treatment of insomnia
- Sedative before surgery
Side Effects
Side effects of Butabarbital are:
- Allergic reactions
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Suicidal thoughts
- Memory problems
- Depression
- Trouble breathing
- Tissue damage
- Feeling sleepy
- Somnolence
- Nervousness
- Hallucinations
- Nightmares
- Psychiatric disturbance
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Bradycardia
- Hypotension
- Angiodema
- Hypersensitivity
- Liver damage
- Anemia
- Fever
MCQ
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug butabarbital-
| i. Triketoform | A. Increased lipophillicity |
| ii. 4,6-dialcoholic form | B. Most stable in aqueous form |
| iii. Esterifiation of either of diazine nitrogen atom | C. Decreased hypnotic activity |
| iv. Modification of the 2nd-position oxygen of the barbiturate backbone withv sulfur atom | D. Least stable in aqueous form |
a) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
c) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
d) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Butabarbital: 5-butan-2-yl-5-ethyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione
- Xylometazoline: 2-[(4-tert-butyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)methyl]- 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole
- Epinephrine: (R)-4-(2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl)benzene-1,2-diol
- Norepinephrine: (R)-4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FTTF
d) FFFF
Q.3 Physical appearance of butabarbital is?
a) Red-brown crystalline powder
b) Fine white crystalline powder
c) Green granular form
d) None of these
Q.4 Butabarbital shows its mechanism of action through biding with which receptor?
a) GABAA
b) Acetylcholine muscarinic receptor
c) Acetylcholine nicotinic receptor
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Butabarbital?
a) Sedative before surgery
b) Treatment of anxiety
c) Treatment of cancer
d) All of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Butabarbital: Barbiturate sedative-hypnotic
II. Diazepam: Benzazepenes
III. Thiothixene: Benzodiazepenes
IV. Haloperidole: Benzisothiazole
a) I
b) I, III
c) II, IV
d) II, III
Q.7 Butabarbital can be synthesized from reaction of?
a) Diethyl 2-sec-butyl-2-ethylmalonate with Urea
b) Diethyl 2-sec-butyl-2-ethylmalonate with Hydrazine
c) Diethyl 2-sec-butyl-2-ethylmalonate with Thiourea
d) Diethyl 2-sec-butyl-2-ethylmalonate with Methylhalide
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-b
3-b
4-a
5-a
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 473-474.