CARBINOXAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
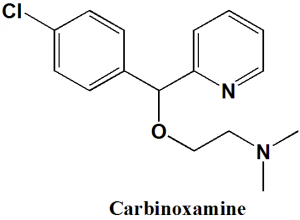
Carbinoxamine
IUPAC nomenclature
2-[(4-Chlorophenyl)-pyridin-2-yl-methoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-ethanamine
Classification
- H1-receptor antihistamine
- Ethanolamine ether antihistamine
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 290.79 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | <25oC |
| 4 | Solubility | 2.28e-01 g/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.6 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl , pyridine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. The drug binds with Histamine H1 receptor and produces antagonistic effects.
ii. This results in blockage of action of endogenous histamine
iii. Temporary relief of negative symptoms produced due to histamine
iv. Antiemetic effect is due to antagonistic effects on muscarinic receptors.
Structure Activity Relationship
Structure activity of ethanolamine ethers can be summarized as:
- 8-chlorotheophyllinate salt of diphenhydramine is used for treatment of motion sickness
- Compounds with p-Cl-Ph and 2-pyridyl aryl groups are carboxamine, which is a potent anti-histamine drug.
- Substitution of the methyl group at the carbon alpha to he ether function gives a related compound known as doxylamine.
- An additional carbon atom between oxygen and nitrogen produces clemastine which has lower sedative properties.
- In setastine, alkyl amine substituent is incorporated into seven-membered hexahydroazepine ring, having lower sedative properties.
- With increase in alkyl group size at C-2’, there is decrease in antihistaminic activity and increases in anticholinergic activity..
- Introduction of alkyl substituents at C-4’results in decrease in anticholinergic activity and increase in antihistaminic activity.[1]
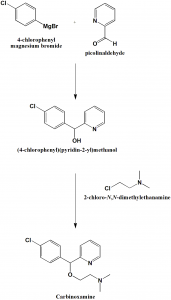
Method of synthesis
i. 4-chloropenyl magnesiumbromide is reacted with picolinaldehyde to give (4-chlorophenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methanol.
ii. (4-chlorophenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methanol is reacted with 2-chloro-N,N-dimethylethanamine to give carbinoxamine
Medicinal Uses
Carbinoxamine is used for treatment of:
- Allergies
- Hay fever
- Common cold
- Rash
- Watery eyes
- Itchy
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
Side Effects
Side effects of carbinoxamine are:
- Drowsiness
- Blurred vision
- Restlessness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Stomach upset
- Constipation
- Dry mouth, nose and throat
- Difficulty in breathing
- Mental or mood changes
- Hallucinations
- Allergic reactions
- Seizures
MCQs
Q.1 “2-[(4-Chlorophenyl)-pyridin-2-yl-methoxy]-N,N-dimethyl-ethanamine” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Carbinoxamine
b) Edrophonium
c) Auranofin
d) Tenoxicam
Q.2 Molecular weight of Carbinoxamine is?
a) 199.3 gm/mol
b) 234.2 gm/mo
c) 290.79 gm/mol
d) 134.32 gm/mol
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Carbinoxamine | A. Ethanolamine ether antihistamine drug |
| ii. Propranolol | B. Benzodiazepine anticonvulsants |
| iii. Secobarbital | C.Barbiturates |
| iv. Clonazepam | D. Beta-adrenergic blockers |
a. i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
b. i-C, ii-D, iii-A, iv-B
c. i-D, ii-,B iii-A, iv-C
d. i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
Q.4 Which of the following mechanisms are involved for the action of Carbinoxamine drug?
I. Produces antagonistic effects on muscarinic receptors
II. Produces antagonistic effects on H1 receptors
III. There is blockage of action of endogenous histamine
IV. Drug also produces beta blocking actions.
a) I, IV
b) II, III
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II, III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of class ethanolamine ethers antihistamines can be?
- An additional carbon atom between oxygen and nitrogen produces clemastine which has lower sedative properties.
- In setastine, alkyl amine substituent is incorporated into seven-membered hexahydroazepine ring, having higher sedative properties.
- With decrease in alkyl group size at C-2’, there is decrease in antihistaminic activity and increases in anticholinergic activity..
- Introduction of alkyl substituents at C-4’results in decrease in anticholinergic activity and increase in antihistaminic activity.
a) TFFT
b) TFTF
c) TTTT
d) FTFF
Q.6 (4-chlorophenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methanol is reacted with 2-chloro-N,N-dimethylethanamine to give which drug?
a) Dimenhydrinate
b) Carbinoxamine
c) Diphenhydramine
d) Chlordiphenhydramine
Q.7 The drug carbinoxamine is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of sneezing
b) Treatment of watery eyes
c) Treatment of runny nose
d) All of the above
List of Successful GPATINDIAN Candidates
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-d
4-b
5-a
6-b
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.