Concept of dissolution: Dissolution test parameters, Intrinsic dissolution, Compendial dissolution methods and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Dissolution Test Parameters:
- Eccentricity of the stirring device – The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) specifies that the stirring shaft must rotate smoothly without significant wobble. Eccentricity can be measured in terms of total indicator reading(TIR) with the help of machinist’s indicator, which determines the sum of the distance on both sides (180°C) of the axis of rotation.
- Alignment of the stirring element – According to the USP, the axis of the stirring element should not deviate more than 0.2 cm from the axis of the dissolution vessel, which defines centring of the stirring shaft to within ±2 mm. Tilt in excess of 1.5° may increase dissolution rates from 2 to 25%.
- Vibration – Unwanted vibrations can introduce unwanted energy to the dynamic system and could also change the flow patterns of the liquid. Both these effects may result in significant changes in the dissolution rates. For most drugs, the speed of the rotational device as described in the official compendium is generally 50 or 100 rpm. Precise speed control is best obtained with a synchronous motor that locks into the line frequency.
- Agitation intensity- The thickness of the hydrodynamic boundary layer is inversely proportional to agitation speed, and therefore agitation conditions can markedly affect dissolution. The foregoing discussion shows that the physical chemical properties of a compound have a strong influence on its dissolution in the gastrointestinal tract, and hence on whether the dissolution will be the rate-limiting step to its absorption. The poor match between physiological conditions and those used in vitro dissolution test systems is the primary reason for the inability to predict in vivo dissolution from in vitro data.
INTRINSIC DISSOLUTION:
Intrinsic dissolution measures the inherent solubility of the drug in the dissolution medium while temperature, pH, agitation and ionic strength of the dissolution medium are constant. Intrinsic dissolution provides an insight into the dissolution behaviour of a drug at physiological conditions and is a prime indicator of the bioavailability of a drug candidate. Intrinsic dissolution is also used to characterize bulk drug substances. The value of intrinsic dissolution <0.1 mg/min–1/cm2 suggests that dissolution is a rate-limiting step to absorption, whereas the value >1.0 mg/min–1/cm2 suggests that permeation, not dissolution, is a rate limiting step to absorption.
Stationary disk apparatus and rotating disk apparatus (Wood Apparatus) are used to conduct intrinsic dissolution studies. The compacted pellet of a pure drug is mounted in a die, such that only one face of the pellet is exposed to the dissolution medium. In the stationary disk apparatus, the die containing drug pellet is placed face up into a flat bottomed dissolution vessel previously filled with the dissolution medium. The medium is stirred by means of a rotating paddle positioned 6 mm above the pellet surface. In the rotating disk apparatus, the die containing the pellet is inverted and screwed onto a shaft, which is then lowered into the dissolution medium until the face pellet is 3.8 cm from the bottom of the vessel. The intrinsic dissolution rate is calculated by plotting the cumulative amount of drug substance dissolved per unit area of the exposed pellet surface against time until 10% of the drug pellet has dissolved.
COMPENDIAL DISSOLUTION METHODS:
Dissolution studies are designed to demonstrate how efficiently an active drug substance is released from a solid oral dosage form.
According to USP 30, the official dissolution apparatus are classified into seven types.
USP Apparatus 1: the basket method; USP Apparatus 2: the paddle method; USP Apparatus 3: a reciprocating cylinder; USP Apparatus 4: a flow-through cell; USP Apparatus 5: a paddle-over-disk; USP Apparatus 6: a cylinder; and USP Apparatus 7: a reciprocating holder. In the EP, Apparatus 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are official. In the BP and JP, Apparatus 1, 2 and 4 are official, whereas in the IP, only two Apparatus are official: IP Apparatus 1: the paddle method and IP Apparatus 2: the basket method.
Selection of the dissolution apparatus depends on the dosage form, which is to be evaluated, and the intention of dissolution. While selecting the apparatus for dissolution testing, the ideal features of dissolution apparatus must be considered.
Table no. 1 – USP-approved dissolution apparatus
| USP Dissolution Apparatus | Important characteristic | Dosage form evaluated | Diagram |
| Apparatus 1 Basket apparatus | A rotating mesh (40 mesh standard) stainless steel basket in a hemispherical vessel | Immediate-release product Extended-release product Floating dosage forms Nutritional supplements |
 |
| Apparatus 2 Paddle apparatus | A rotating stainless steel metallic blade attached to shaft in a hemispherical vessel | Immediate-release product Extended-release product Chewable, sublingual tablet Powder, granules Suppositories Nutritional supplements |
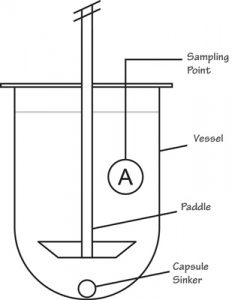 |
| Apparatus 3 Reciprocating cylinder (Bio-Dissolution apparatus) |
A set of glass reciprocating cylinders in cylindrical Ńat-bottomed glass vessels and screens to łt the tops and bottoms of the reciprocating cylinders | Extended-release product |
 |
| Apparatus 4 Flow-through cell | A low-volume (often <30 ml) dissolution cell and a reservoir to continually provide fresh solvent to maintain sink conditions. |
Extended-release product Implants Suppositories Soft gelatine capsules |
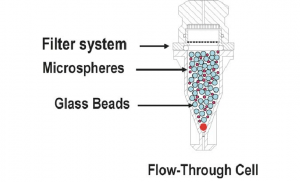 |
| Apparatus 5 Paddle-over-disk | A rotating paddle over a disk in a hemispherical vessel | Transdermal patch | 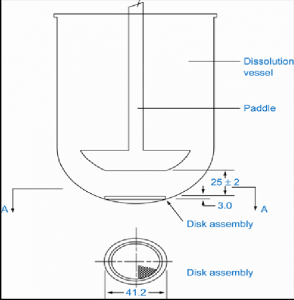 |
| Apparatus 6 Cylinder apparatus | A rotating stainless steel cylinder in a hemispherical vessel. Presence of 4 holes improves circulation of dissolution media | Transdermal patch | 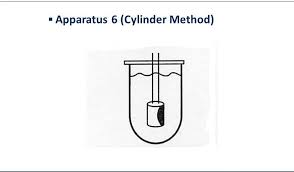 |
| Apparatus 7 Reciprocating holder | A holder (disk, cylinder, spring, or pointed rod) that oscillates up and down in a cylindrical vessel |
Transdermal patch Osmotic pump devices Extended release tablets Coated delivery systems |
 |
Multiple choice questions:
1.Which of the following are dissolution test parameters?
a)Eccentricity of the stirring device
b)Alignment of the stirring element
c)Vibration
d)all of these
2.Eccentricity can be measured in terms of
a)total indicator reading
b)total detector reading
c)indicator reading
d)total reading
3.According to the USP, the axis of the stirring element should not deviate more than
a)0.1 cm
b)0.2 cm
c)0.3 cm
d)0.5 cm
4.Unwanted vibrations can introduce unwanted energy to the dynamic system and could also change the flow patterns of the liquid. Both these effects may result in significant changes in the dissolution rates.
a)true
b)false
5.For most drugs, the speed of the rotational device as described in the official compendium is
a)1 or 10 rpm
b)10 or 30 rpm
c)50 or 100 rpm
d)110 rpm
6.The thickness of the hydrodynamic boundary layer is _______ to agitation speed, and therefore agitation conditions can markedly affect dissolution.
a)directly proportional
b)inversely proportional
c)not proportional
d)none of these
7.Intrinsic dissolution provides an insight into the dissolution behaviour of a drug at physiological conditions and is a prime indicator of the _____ of a drug candidate.
a)solubility
b)dissolution
c)bioavailability
d)disintegration
8.Which of the following is/are used to conduct intrinsic dissolution studies?
a)Stationary disk apparatus
b)rotating disk apparatus
c)Wood Apparatus
d)all of these
9.Dissolution studies are designed to demonstrate how efficiently an active drug substance is released from a solid oral dosage form.
a)true
b)false
10.According to USP 30, the official dissolution apparatus are classified into _____ types.
a)5
b)7
c)9
d)3
11.USP Apparatus 1 is
a)Basket apparatus
b)Reciprocating cylinder
c)Reciprocating holder
d)Paddle apparatus
12.Apparatus 2 Paddle apparatus is used for
a)Immediate-release product
b)Extended-releaseproduct
c)Chewable, sublingualtablet
d)all of these
13.Apparatus 5 Paddle-over-disk is used for
a)Immediate-release product
b)Extended-releaseproduct
c)Chewable, sublingualtablet
d)Transdermal patch
14.In IP how many apparatus are official?
a)2
b)3
c)5
d)7
15.IP Apparatus 1 is
a)Basket apparatus
b)Reciprocating cylinder
c)Reciprocating holder
d)Paddle apparatus
Solutions:
- d)all of these
- a)total indicator reading
- b)0.2 cm
- a)true
- c)50 or 100 rpm
- b)inversely proportional
- c)bioavailability
- d)all of these
- a)true
- b)7
- a)Basket apparatus
- d)all of these
- d)Transdermal patch
- a)2
- d)Paddle apparatus
References:
- Gaurav K. Jain Theory and practice of Physical Pharmacy, 1st edition 2012 Elsevier, page no. 288-292.
- Martins Physical Pharmacy, 6th edition 2011, page no. 572-583.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test