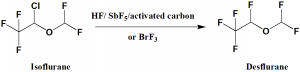DESFLURANE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Desflurane
IUPAC nomenclature
2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane.
Classification
Desflurane is an inhalational anesthetic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 168.04g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Colourless liquid |
| 3 | Boiling point | 23.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Solubility in water is poor |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.9 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Not present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Desflurane decreases the gap junction channel opening times and increases gap junction channel closing time which induces reduction in junctional conductance.
- The drug also increases the fluidity of the lipid membrane and thus, activates calcium dependent ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Desflurane also binds with D subunit of ATP synthase, GABA receptors, glutamate receptors , glycine receptors, the large conductance Calcium ion activated potassium channel and NADH dehydrogenase.
Structure Activity Relationship
The SAR for inhaled anesthetics can be summarized as follows:
- Halogenations of the hydrocarbons and ether increases the anesthetic potency.
- Halogenations of the hydrocarbons tends to induce arrhythmia in the following order F<Cl<Br<I.
- Due to presence of asymmetric halogenated carbon in ether, they are better anesthetics.
- Halogenated methyl ethyl ethers are more stable, more potent and have better clinical profile than halogenated diethyl ether.
- Fluorination increases the stability and decreases the flammability.
- Compete halogenations of the alkane or ether decreases the anesthetic potency and increases the convulsant potency
- Presence of double bond increases chemical reactivity and toxicity.
Method of synthesis
Desflurane can be synthesized from isoflurane using HF and Lewis acid catalysts.
Therapeutic Uses
Desflurane is used for:
- Induction of anesthesia for inpatient and outpatient surgery in adults.
Side Effects
Side effects of Desflurane are:
- Cardiovascular effects
- Priapism
- QT prolongation
- Effects on eyes
- Sudden hearing loss
- Headache
- Flushing
- Nasal congestion
- Dyspepsia
- Dizziness
- Back pain
- Allergic edema
- Angiodema
- Allergic reactions
- Chest pain
- Tinnitus
- Vertigo
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Muscle cramping
- Somnolence
- Insomnia
- Amnesia
- Seizure
MCQs
Q.1 “2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Desflurane
b) Letrozole
c) Triptorelin
d) Etoposide
Q.2 Correct melting point of the drug desflurane is?
a) 23.5°C
b) 233°C
c) 10.6°C
d) 237.5°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Desflurane | A. Vinca alkaloids cytotoxic drug |
| ii. Vinblastin | B. Epipodophyllo toxin |
| iii. Etoposide | C. Inhalational anesthetics |
| iv. Aspirin | D. Anti-inflammatory agent |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
Q.4 Mechanism of action of drug Desflurane includes?
I. Decreases the gap junction channel closing time.
II. Increases the gap junction channel opening time
III. Decreases the fluidity of the lipid membrane.
IV. Activates calcium dependent ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum.
a) II, III, IV
b) I, II, IV
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of Inhaled anesthetics drugs?
- Halogenated methyl ethyl ethers are more stable, more potent and have better clinical profile than halogenated diethyl ether.
- Fluorination decreases the stability and decreases the flammability.
- Compete halogenations of the alkane or ether increases the anesthetic potency and decreases the convulsant potency
- Presence of double bond decreases chemical reactivity and toxicity
a) FFTT
b) TFTF
c) TFFF
d) TTTT
Q.6 Reaction of isoflurane with HF and Lewis acid catalyst produces which drug?
a) Antipyrine
b) Acetaminophen
c) Desflurane
d) Sevoflurane
Q.7 The drug Desflurane is used for?
a) Induction of anesthesia
b) Control of seizures
c) Treatment of panic attacks
d) Prevention of seizures
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-b
4-b
5-c
6-c
7-a