ESOMEPRAZOLE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
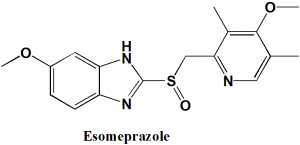
Esomeprazole
IUPAC nomenclature
(S)-(−)-5-Methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-3H-benzoimidazole
Classification
- Proton pump inhibitors
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 345.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 155 oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.6 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Imidazole, pyridine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Esomeprazole covalently binds with cystien residues via disulfide bridges on the α subunit of H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system.
- Thereby it inhibits the H+/K+ ATPase pump which in turn inhibits the gastric acid secretion or formation of hydrochloric acid in parietal cells
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivatives acting as acid pump antagonists can be summarized as:
- The inhibitory property of drugs depends on hydrophobic group substituted at the left side ortho-position of the phenyl ring.
- Increase in hydrophobic value increases the activity.
- Increasing the GTCI value decreases the activity.
- Small molecule substitutions may participate in hydrophobic interaction as well as steric interactions. [1]
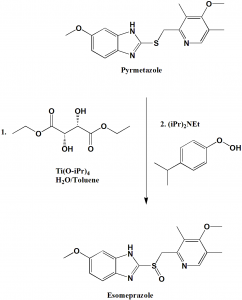
Method of synthesis
Large scale asymmetric synthesis of esomeprazole can be done by following method:
i. The suspension of pyrmeprazole in toluene is added to water solution of (S, S)-diethyl tartrate and titanium tetraisopropoide.
ii. N, N-diisopropylehylamine and cumene hydroperoxide are added.
iii. Sodium salt is obtained using sodium hydroxide and acetonitrile.[2]
Medicinal Uses
Esomeprazole is used for treatment of:
- Active duodenal ulcers
- To reduce the risk of duodenal ulcers by eradicating Helicobacter
- Active benign gastric ulcer
- GERD
- Erosive esophagitis
- Zollinger-Errison syndrome
- Reduce heart burn symptoms
Side Effects
Side effects of Esomeprazole are:
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Low magnesium blood level
- Irregular heartbeat
- Muscle spasms
- Seizures
- Lupus
- Diarrhea
- Blood in stool
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the Heteroaryl- and heterocyclyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]Pyridine derivative acid-pump antagonists:
| i. Increasing the hydrophobic value | A. Increases the activity |
| ii. Increasing the GTCI value | B. Decreases the activity |
| C. Increases the activity | |
| D. Decreases the activity |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Esomeprazole: 4-(5H-Dibenzo)-1-methylpiperidine
- Dacarbazine: 4-(diphenylmethoxy)-N,N-dimethylethanamine
- Loperamide: 2-{2-[(1R)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethoxy]ethyl}-1-methylpyrrolidine
- Zolpidem: 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine
a) TFFT
b)TFFF
c) TTTT
d) FFFF
Q.3 Molecular weight of Esomeprazole is?
a) 453 gm/mol
b) 432.0 gm/mol
c) 187.4 gm/mol
d) 345.4 gm/mol
Q.4 Esomeprazole acts on which system?
a) Sodium potassium pump
b) The respiratory system
c) H+/K+ ATPase pump
d) All of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Esomeprazole?
a) GERD
b) Erosive esophagitis
c) Itching
d) Heart burn symptoms
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Esomeprazole: Proton pump inhibitor
II. Meprilcaine: Local anesthetics
III. Rabeprazole: Diuretics
III. Quinidine: Anti-arrhythmic drug
a) I, III
b) II, III, IV
c) III, IV
d) I, II, IV
Q.7 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of Esomeprazole?
a) 0
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-d
4-c
5-c
6-d
7-a