FENOPROFEN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Fenoprofen
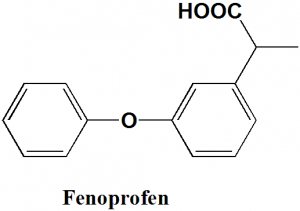
IUPAC nomenclature
2-(3-phenoxyphenyl)propanoic acid
Classification
- NSAID
- Propionic acid derivative
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 242.27 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Viscous oil |
| 3 | Melting point | 168-171°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.1 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
Fenoprofen mechanism of action involves inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR of fenoprofen can be summarized as follows:
- Activity decreases on placing the phenoxy group in the ortho or para position of the arylpropionic acid.
- Replacing oxygen bridge between two aromatic rings with carbonyl group produces another marketed analogue known as ketoprofen. [1]
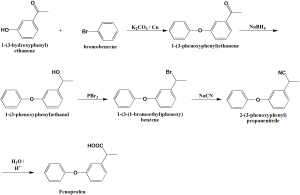
Method of synthesis
i. 3-hydroxyacetophenone is esterified by bromobenzene in presence of potassium carbonate and copper fillings to give 3-phenoxyacetophenone.
ii. Carbonyl group of the above formed compound is reduced by sodium borohydride.
iii. Resulting alcohol is brominated by phosphorus tribromide.
iv. Bromo derivative so formed is reacted with sodium cyanide to give 2-(3-phenoxyphenyl)propionitrile.
v. On hydrolysis, fenoprofen is produced. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Fenoprofen is used for:
- Relieving mild to severe pain due to arthritis
Side Effects
Side effects of fenoprofen are:
- Allergic reactions
- Skin reactions
- Shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Vision changes
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- No urination
- Anemia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Nervousness
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Ringing sounds in ears
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Fenoprofen?
a) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
b) 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-Carboxylic acid
c) 2-(3-phenoxyphenyl)propanoic acid
d) 2-(3-phenoxyphenyl)pentanoic acid
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of propionic acid derivatives?
I. Activity Increases on placing the phenoxy group in the ortho or para position of the arylpropionic acid.
II. Replacing oxygen bridge between two aromatic rigs with carbonyl group produces another marketed analogue known as ketoprofen
a) I
b) II
c) I, II
d) None of the above
Q.3 Correct sequence of steps required for the synthesis of drug fenoprofen from 3-hydroxyacetophenone can be?
I. Bromination by phosphorus tribromide
II. Reduction of carbonyl group by sodium borohydride
III. Esterification by bromobenzene
IV. Hydrolysis
V. Reaction with sodium cyanide
a) III – II – I – V – IV
b) II – I – III – IV – V
c) I – IV – V – III – II
d) IV – III – II – I – V
Q.4 Side effects of drug Fenoprofen is/are?
a) Allergic reactions
b) Shortness of breath
c) Pale skin
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with the correct number of the chiral carbons they have in their structure:
| i. Fenoprofen | A. 5 |
| ii. Ipratropium | B. 2 |
| iii. Atropine | C. 4 |
| iv. Metaraminol | D. 1 |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class NSAIDs?
a) Fenoprofen
b) Cetrizin
c) Norepinephrin
d) Atropine
Q.7 The type of ring system found in fenoprofen?
a) Furan
b) Benzothiazine
c) Both a) and b)
d) None of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-a
3-a
4-d
5-b
6-a
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito SW. FOYE. S Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Seventh Edition Copyright. 2013. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.