FLUDARABINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure and Therapeutic Uses
Fludarabine
IUPAC nomenclature
[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-fluoro-purin-9-yl)- 3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxyphosphonic acid
Classification
Fludarabine falls under the category of purine antagonist antimetabolite. It is also an immunosuppressive agent.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 285.23 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | They are produced in the crystalline form |
| 3 | Melting point | 260 °C |
| 4 | Solubility | It is sparingly soluble in water and other organic solvents |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | -2.8 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Purine ring system |
Mechanism of Action
i. Fludarabine phosphate is dephosphorylated to form 2-floro-ara-A.
ii. In the cell, the compound is then phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase, and the active form which is triophosphate , 2-floro-ara-ATP is formed.
iii. This active metabolite inhibits certain enzymes such as DNA polymerase alpha, DNA primase and ribonucleotide reductase enzymes.
iv. This overall, inhibits the synthesis of DNA. [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- The activity of the drug increases with increase in the carbon chain upto 15-16 carbons, after that, it again decreases.
- Substituent at position 6 which can lead to the increase in the resonance at 6th position will lead to increase in the activity of the drug.
- Introduction of the hydrophobic substituent at 6th position will increase the activity of the drug.
- Substitutions at 2nd position may not change the activity of the drug, or it may decrease the activity of the drug depending upon the type of substituent. [2]
Methods of Synthesis
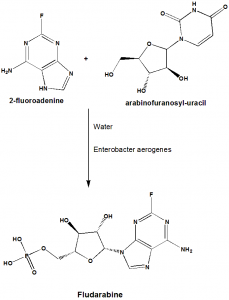
i. 2-Fluoroadenine is reacted with 9-β-D-arabinosyl-uracile, taking water as a solvent. The reaction will take place in the presence of Enterobacter aerogenes.
ii. Fludarabine so formed is then treated with acetic anhydride to form the acetylderivative.
iii. The acetyl derivative is then crystallize to get back the pure Fludarabine.
iv. Through the phosphorylation reaction, Fludarabine phosphate can be obtained from Fludarabine. [3]
Therapeutic Uses
- Chronic lymphocyctic leukemia
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Acute leukemias
- As a conditioning regimens prior to allogenic stem cell transplant.
Side Effects
- Common side effects of this drug includes low blood counts, fever, weakness, nausea, vomiting, cough, infections and loss of appetite.
- Less common side effects include swellings, diarrhea, numbness in hand and foot, sweating, pain, fatigue, chills, skin infections and taste changes.
- Some other side effects can be increased risk of infection, neurotoxicity, hemolytic anemia, infertility and tumor lysis syndrome.
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct IUPAC nomenclatures
| i. (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid. | A. Lomustine |
| ii. 2-(2-Methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl) ethanol | B. Penicillin g |
| iii. 1-(2-chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea
|
C. Fludarabine |
| iv. [(2R,3S,4S,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-fluoro-purin-9-yl)- 3,4-dihydroxy-oxolan-2-yl]methoxyphosphonic acid | D. Metronidazol |
a) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Q.2 How many statements below are true with respect to the SAR of the drug Fludarabine?
- Activity of the drug can be increased with increase in the carbon chain length.
- Substituent at position 6 which can lead to the increase in the resonance at 6th position will lead to increase in the activity of the drug.
- Introduction of the hydrophobic substituent at 6th position will increase the activity of the drug.
- Substitutions at 2nd position may not change the activity of the drug, or it may decrease the activity of the drug depending upon the type of substituent.
a) 4
b) 3
c) 2
d) 1
Q.3 The drug Fludarabine is found in which form at NTP
a) Liquid form
b) Crystalline form
c) Buff powder form
d) Thread like form
Q.4 Which statement is incorrect with respect to the method of synthesis of the drug Fludarabine?
a) The reaction takes place in the organic solvent
b) Reaction takes place in the presence of Enterobacter
c) Reaction takes place in the water medium
d) Final step is phosphorylation of drug
Q.5 Which amongst the following is NOT a therapeutic use of drug Fludarabine?
a) Low blood count
b) Arthritis
c) Loss of appetite
d) Tumor lysis syndrome
Q.6 The correct classification of the drug Fludarabine can be?
a) Antibiotic
b) Epidophyllo toxin
c) Purine antagonist antimetabolite
d) Pyrimidine antagonist antimetabolite
Q.7 How many number of rings are found in the chemical structure of the drug Fludarabine?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
For More Standard and Quality Question Bank you can Join Our Test Series Programme for GPAT, NIPER JEE, Pharmacist Recruitment Exam, Drug Inspector Recruitment Exams, PhD Entrance Exam for Pharmacy: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-d
2-a
3-b
4-a
5-b
6-c
7-d