FUROSEMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
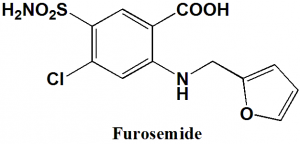
Furosemide
IUPAC nomenclature
4-Chloro-2-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)amino]-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid
Classification
- Anthranilic acid derivative
- Diuretics
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 330.74 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to slightly yellow crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 206oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, chloroform, ether; soluble in DMF, methanol, acetone. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.03 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Furan, phenyl |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Furosemide blocks the tubular reabsorpion of Na and Cl in the PCT and DCT, as well as in the thick ascending loop of Henle.
- It competitively binds inhibits sodium-potassium-chloride cotransportors which are expressed along these tubules in the nephrons. This prevents the transport of Na ions from luminal side into basolateral side for reabsorption.
- Due to this inhibition, there is increase in the excretion of water along with Na, Cl, Mg, Ca, H and K ions. There is decrease in the excretion of uric acid.
- Furesimide also causes vasodilation which helps in treatment of acute pulmonary edema. Due to vasodilatory effects, it causes reduced responsiveness to vasoconstrictors such as angiotensin II and noradrenaline and there is decreased production of natriuretic hormones.
- Drug also causes increased production of prostaglandins with vasodilating properties.
- The MOA of the drug does not depend on inhibitory effects on carbonic anhydrase and aldosterone.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity relationship of furosemide can be summarized as:.
- It is derivative of anthranilic acid.
- It is most active amongst other derivatives.
- It is stronger acid than thiazide due to presence of free carboxyl group.
- There is small change in furan ring, otherwise, the drug excreted out unchanged. [1]
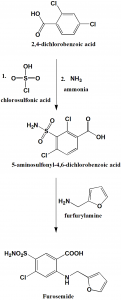
Method of synthesis
i. 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid is converted into 5-aminosulfonyl-4,6-dichlorobenzoic acid by reaction with chlorosulfonic acid followed by reaction with ammonia.
ii. Reaction of the above formed compound with furfurylamine produces furosemide.
Medicinal Uses
Furosemide is used for:
- Treatment of edema related with CHF, liver cirrhosis, renal diseases.
- Management of mild to severe hypertension
- As an adjunct therapy in acute pulmonary edema
Side Effects
Side effects of furosemide are:
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Low blood sodium and potassium levels
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach cramps
- Photosensitivity
- Muscle cramps
- Dry mouth
- Dehydration
- Allergic reactions
- Fainting
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the dihydropyridines calcium channel blockers –
| i. Furosemide is derivative of | A. Benzodiazepine derivative |
| ii. Compare with other thiazide, furosemide is | B. Anthranilic acid derivative |
| C. More acidic | |
| D. More basic |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Furosemide: 3-(2-Methoxyethyl) 5-propan-2-yl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- Ibuprofen: [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid
- Timolol: allylmorphinan-3-ol
- Sodium thiomalate: Sodium;2-hydroxybenzoate
a) FFTF
b) FFFF
c) TFFT
d) TTTT
Q.3 Molecular weight of drug furosemide is?
a) 330.74 gm/mol
b) 652.36 gm/mol
c) 142.45 gm/mol
d) 418.4 gm/mol
Q.4 Mechanism of action of furosemide includes?
a) Inhibition of sodium-potassium-chloride cotransportors
b) Conversion into nitric oxide
c) Inhibition of hydrogen-potassium pump
d) All of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug furosemide?
a) Treatment of edema related with CHF
b) Management of hypertension
c) As an adjunct therapy in acute pulmonary edema
d) As an anesthetic
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Furosemide: Diuretics
II. Levorphanol: Cholinestrase inhibitor
III. Codeine: Antineoplastic drug
IV. Phenytoin: Anticonvulsants
a) I ,II, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) I, III
Q.7 Type of ring present in the structure of furosemide?
a) Furan
b) Pyridine
c) Pyrimidine
d) Pyridine
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-c
2-b
3-a
4-a
5-d
6-d
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.