HYDROFLUMETHIAZIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
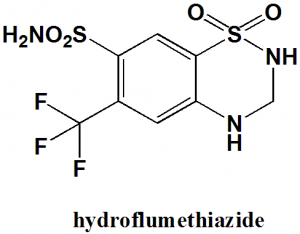
Hydroflumethiazide
IUPAC nomenclature
1,1-Dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
Classification
- Thiazide diuretic
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 331.3 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to cream colored crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 272-273oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in acetone; soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.36 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Benzothiazine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Hydroflumethiazide inhibits the sodium-chloride symportor in the DCT which further inhibits the reabsorption of water.
- Sodium-chloride transportor facilitates the entrance of sodium into the epithelial cells in the DCT. The influx of sodium establishes an osmotic gradient which is necessary for water reabsorption.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of thiazide diuretics can be summarized as:
- Chlorothiazide is the simplest member of the series.
- Hydrogen atom at the 2-N is most acidic due to presence of electron-withdrawing group.
- Sulfonamide group at C-7 position provides additional acidity to the drug.
- Electron withdrawing group is essential at position 6 for diuretic activity of the drug.
- Substitution on hydrogen at 6 position gives little diuretic activity, whereas, substitution with chloro and trifluoromethyl groups gives highly active compounds.
- Substitution of electron donating group at position 6 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Replacement or removal of sulfonamide groups from position 7 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Saturation of the double bond to give 2,4-dihydro derivative are 10-folds more active than the unsaturated compounds.
- Substitution of a lipophillic group at 3 position increases the potency.
- Substitution with the entities such as haloalkyl, aralkyl or thioether gives compounds with longer duration of action due to increased lipid solubility.
- Alkyl substitution at the 2-N position can increase the action duration. [1]
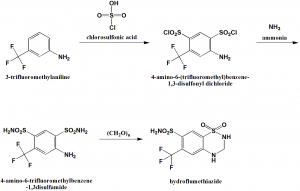
Method of synthesis
i. Chlorosulfonylation of 3-trifluoromethylamiline using chlorosulfonic acid to get 4-amino-6-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1,3-disulfonyl dichloride.
ii. The last is reacted with ammonia to get the compound 4-amino-6-trifluoromethylbenzene-1,3disulfamide.
iii. Cyclization of the above formed compound using paraformaldehyde to get hydroflumethiazide drug.
Medicinal Uses
Hydroflumethiazide is used for:
- Management of hypertension
- Management of edema related to CHF, chronic renal failure, glomerulonephritis, nephritic syndrome and hepatic cirrhosis.
Side Effects
Side effects of hydroflumethiazide are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Low blood sodium and potassium levels
- Loss of appetits
- Stomach cramps
- Sexual problems
- High blood sugar level
- Low blood pressure
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of thiazide diuretics-
| i. Substitution of electron withdrawing groups at position 6th | A. Increases the diuretic activity |
| ii. Removal of sulfonamide group from position 7 | B. Decreased the diuretic activity |
| C. Increases the diuretic activity | |
| D. Decreases the diuretic activity |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Hydroflumethiazide: 2-[2-[bis(2-nitrooxyethyl)amino]ethyl-(2-nitrooxyethyl)amino]ethyl nitrate
- Acetazolamide: 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide.
- Tolterodine: 3-O-ethyl 5-O-methyl 2-(2-aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
- Cocaine: 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine
a) FFTF
b) FFFF
c) TFFT
d) TTTT
Q.3 Molecular weight of drug hydroflumethiazide is?
a) 475 gm/mol
b) 452.3 gm/mol
c) 331.3 gm/mol
d) 978.1 gm/mol
Q.4 Mechanism of action of hydroflumethiazide includes?
a) Alkylation of genetic material
b) Inhibition of Sodium-Chloride symportor in the DCT
c) Inhibition of hydrogen-potassium pump
d) All of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug hydroflumethiazide?
a) Management of hypertension
b) Treatment of peptic ulcers
c) As an antipsychotic
d) As an anesthetic
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Hydroflumethiazide: Diuretics
II. Nifedipine: Diuretics
III. Disopyramide: Calcium channel Blocker
IV. Verapamil: α-adrenergic agonist
a) I
b) II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) I, III
Q.7 Type of ring present in the structure of Hydroflumethiazide?
a) Benzothiazine
b) Pyridine
c) Pyrimidine
d) Pyridine
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-c
4-b
5-a
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] Holdrege, C.T. et al.: J. Am. Chem. Soc. (JACSAT) 81, 4807 (1959).