HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses in COVID 19 and Malaria
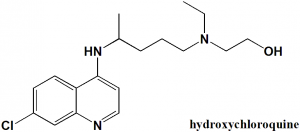
Hydroxychloroquine
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-2-[{4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino]ethanol.
Classification
Hydroxychloroquine is an aminoquininoline like chloroquine.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 335.9 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 90°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 5 mg/ml in PBS |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Quinioline |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- The drug accumulates in the lysosomes of malarial parasite and raises the pH of the vacuole. The ability of the parasite to proteolyse the hemoglobin is disturbed due to this. Thus, the normal growth and replication of the parasite is inhibited.
- Hydroxychloroquine also disturbs the parasite heme polymerase, which leads to the accumulation of the toxic product ß-hematin.
- The drug also accumulates in the human blood and raises its pH. This inhibits the antigen processing, preventing the MHC (major histacompatibility complex) class II from dimerizing, inhibiting the antigen presentation and reducing the inflammatory response.
- Raise in pH of the vesicles alters the recycling of MHC complexes and thus, only high affinity complexes are presented on the cell’s surface
- Self-peptide bids with MHC complexes with low affinity and so they will be less likely to be presented to autoimmune T cells.
- The drug also reduces the cytokine release and release of tumor necrosis factor.
- Viruses cannot utilize their activity fr fusion and entering into the cell due to the elevated pH.
- It also inhibits the terminal glycosylation of ACE2, the receptors that SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 target for entering into cells.
- The entry of the virus is further inhibited due to lesser interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and ACE2, which is not in the glycosylated state.
Structure Activity.
- Chloroquine is crucial for heme binding.
- Nitrogen of the amine attached with the chloroquine entity is responsible for the basic nature of the drug.
- There is no major role of having the secondary alkyl group attached with the carbon next to the amino group near the chloroquine entity.
- Tertiary amine at the terminal is very important for the activity of the drug.
- The length of spacer between the terminal nitrogen and 4-amino group is sensitive towards the parasite resistance. Compounds having shorter chains or longer chains retains the activity against the resistant species of the parasite.
- Small electron withdrawing group at 7th position of the quinoline ring is important for the inhibition of hemozoin formation. [1]
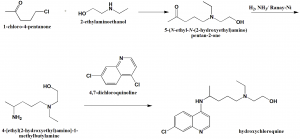
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 1-chloro-4-pentanone qith 2-ethylamino ethanol to give corresponding amino ketone.
ii. The amino ketine will undergo reductive amination to produce –[ethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-1-methylbutylamine.
iii. Reacting the above formed compund with 4,7-dichloroquinoline gives hydroxychloroquinine. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Hydroxychloroquine is used for:
- Prevention and treatment of malaria.
- Currently useful in treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Treatment with Azithromycin
Side Effects
Side effects of Hydroxychloroquine are:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
Serious side effects includes:
- Bradycardia
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling of ankles and feet
- Tiredness
- Weight gain
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Hallucinations
- Liver diseases
- Muscle weakness
- Change in skin and hair color
MCQs
Q.1 ‘(RS)-2-[{4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino]ethanol’ is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Hydroxychloroquine
b) Phenobarbital
c) Methysergide
d) Methotrexate
Q.2 Melting point of hydroxychloroquine is?
a) 90 K
b) 90o F
c) 90o C
d) None of the above
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Raltegravir | A. HIV integrase inhibitor |
| ii. Maraviroc | B. Antimuscarinic |
| iii. Hydroxychloroquine | C. Fusion inhibitor |
| iv. Ipratropium | D. Antimalarial drug |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Hydroxychloroquine?
I. Accumulation of ß-hematin in parasite.
II. Inhibition of the parasite heme polymerase.
III. Destruction of parasite
a) II – I – III
b) I – II – III
c) III – II – I
d) II – III – I
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug hydroxychloroquine
- Chloroquine is not important for heme binding.
- Nitrogen of the amine attached with the chloroquine entity is responsible for the basic nature of the drug.
- There is no major role of having the secondary alkyl group attached with the carbon next to the amino group near the chloroquine entity.
- Tertiary amine at the terminal is very important for the activity of the drug.
a) FFTF
b) FTFT
c) FTTT
d) TFFT
Q.6 Number of chiral centers present in the structure of hydroxychloroquine?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d)3
Q.7 The drug hydroxychloroquine is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of anxeity
b) treatment of HIV
c) Treatment of malaria
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-b
4-a
5-c
6-b
7-c