Hypertrophy: Definition, Causes, Physiologic Hypertrophy, Pathologic Hypertrophy, Morphological Features, Symptoms and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF
“Hypertrophy refers to increase in the size of cells and, with such changes, an increase in the size of the organs.”
1.] Basically, in hypertrophy the increased size of the cell is not due to the increased intake of fluid, called as cellular swelling or edema, but due to the synthesis of more structural components.
2.] Hypertrophy is an adaptive response.
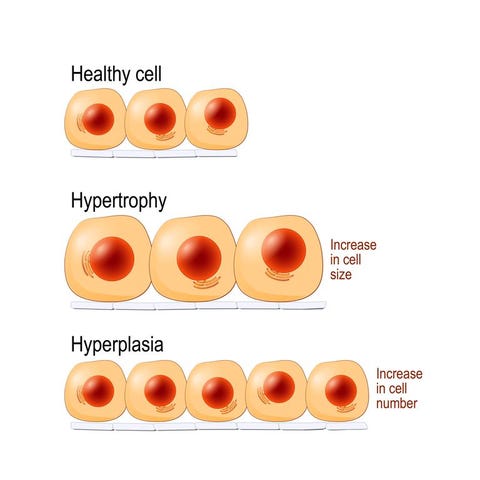
This image is taken for educational purpose from menshealth.com
CAUSES OF HYPERTROPHY: –
Following are the causes of hypertrophy:
- Hypertension
- Lack of exercise
- Lifestyle
- Valve disease
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Congestive heart failure
PHYSIOLOGIC HYPERTROPHY: –
Hypertrophy can be physiological i.e.; the physiological growth of the uterus during pregnancy involves hypertrophy and hyperplasia both.
The cellular hypertrophy is stimulated by estrogenic hormones through smooth muscle estrogen receptor, which allow for interaction of the hormone with unclear DNA, eventually resulting in increased synthesis of smooth muscle protein and an increase in cell size.
This is then the physiologic hypertrophy effected by hormonal stimulation. Hypertrophy is basically an adaptive response which can be exemplified by muscular enlargement.
PATHOLOGIC HYPERTROPHY: –
Following are the disease associated with Pathologic Hypertrophy:
1.] In number of cardiovascular disease hypertrophy of cardiac muscle may occur. Following are the reasons which may cause hypertrophy in cardiovascular muscle:
- Systemic Hypertension
- Mitral insufficiency
- Aortic valve disease
2.] Cardiac achalasia (occurs in esophagus), Pyloric stenosis (occurs in stomach), Intestinal strictures, Muscular arteries in hypertension are the examples of hypertrophy in smooth muscle.
3.] Compensatory Hypertrophy may occur in an organ when the contralateral organ is removed. For example, in Adrenal hyperplasia following removal of one adrenal gland.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPERTROPHY: –
Following are the symptoms of hypertrophy:
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in ankle, feet etc.
- Fainting
- Fatigue
MORPHOLICAL FEATURES: –
In hypertrophy organ become heavy and enlarged. For example, in a patient having hypertrophied heart with systemic hypertension may weigh 700 – 800 gm as compared to normal adult weigh of 350gm.
There is also enlargement in the muscle fiber as well as of nuclei. Also, due to increased protein synthesis an increased number of organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils.
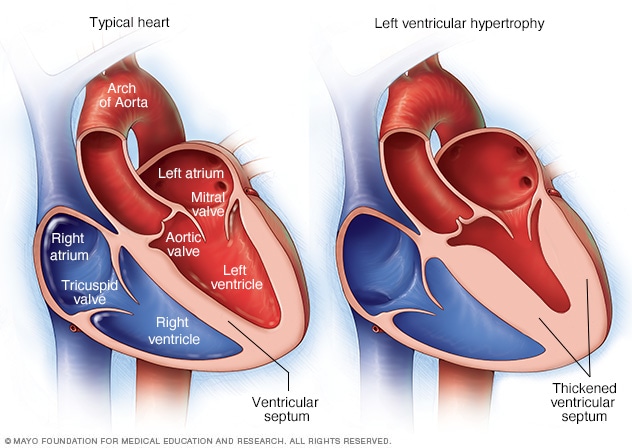
This image is taken for education purpose from myoclinic.org
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: –
1.] Hypertrophy refers to?
a. Increase in cell size
b. Increase in organ size
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
2.] In hypertrophy increase in the cell size is due to cell swelling?
a. True
b. False
3.] Hypertrophy is?
a. Adaptive response
b. Non – Adaptive response
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
4.] Following are the causes of hypertrophy?
a. Hypertension
b. Athletic Hypertrophy
c. Lifestyle
d. All of the above
5.] Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy refers to?
a. Heart muscle become abnormally thick
b. Heart muscle become abnormally thin
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
6.] The cellular hypertrophy is stimulated by which hormone through smooth muscle estrogen receptor?
a. Adrenal hormones
b. Estrogenic hormones
c. Thyroid hormone
d. All of the above
7.] Which of the following are the example of hypertrophy of smooth muscle?
a. Cardiac achalasia
b. Pyloric stenosis
c. Intestinal strictures
d. All of the above
8.] Which of the following are the symptoms of hypertrophy?
a. Dizziness
b. Fatigue
c. Shortness of breath
d. All of the above
9.] Cardiac achalasia occurs in which organ of the body?
a. Stomach
b. Esophagus
c. Lung
d. All of the above
10.] Pyloric stenosis occurs in which body organ?
a. Heart
b. Stomach
c. Large intestine
d. None of the above
SOLUTIONS: –
1.] (c)
2.] (b)
3.] (a) Adaptive response
4.] (d)
5.] (a) Heart muscle become abnormally thick
6.] (b) Estrogenic hormone
7.] (d)
8.] (d)
9.] (b) Oesophagus
10.] (b) Stomach
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
REFERENCES: –
1.] Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no.38 – 39.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no.45 – 46.