ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
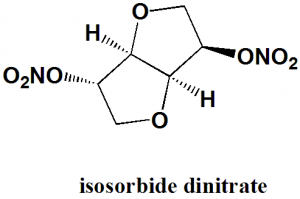
Isosorbide dinitrate
IUPAC nomenclature
1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-nitro-D-glucitol.
Classification
- Organic nitrate antianginal drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 236.14 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Ivory white crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 70oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in acetone |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.31 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | furan |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 4 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Isosorbide dinitrate gets convert into Nitric oxide.
ii. Activation of enzyme gunanylate cyclase
iii. Increase in concentration of cGMP within vascular smooth muscles
iv. Vasodilation occurs due to cGMP-dependent protein kinase.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of organic nitrate antianginal drugs can be summarized as:
- The number of nitrate groups determines the potency of organic nitrate for guanylate cyclase activation.
- Increase in nitric group increases the potency.
- Increase in lipophillicity doesn’t have major effect over activation of drug.
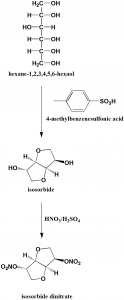
Method of synthesis
i. Intermolecular dehydration of D-sorbite to give isosorbide using paratoluenesulfonic acid.
ii. Nitration of isosorbide by nitric acid to give isosorbide dinitrate. [1]
Medicinal Uses
Isosorbide dinitrate is used for treatment and prevention of:
- Angina pectoris
Side Effects
Side effects of Isosorbide dinitrate are:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Flushing
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weakness
- Restlessness
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Isosorbide dinitrate?
a) 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-nitro-D-glucitol.
b) 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-nitro-D-propanol.
c) 1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]-4-methylpiperazine
d) 1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]-4-ethyliperazine
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are correct related to the SAR of organic nitrate antianginal drugs?
I. The number of nitrate groups determines the potency of organic nitrate for guanylate cyclase activation.
II. Decreasing nitric group increases the potency.
III. Increase in lipophillicity doesn’t have major effect over activation of drug
a) I, III
b) II, III
c) I, II
d) I, II, III
Q.3 The correct order for the synthesis of drug Isosorbide dinitrate from D-sorbite can be?
I. Intermolecular dehydration
II. Nitration
III. Sulfonation
IV. Sulfonylation
a) I – IV
b) I – II
c) III – II
d) II – IV
Q.4 Side effects of drug isosorbide dinitrate is/are?
a) Headache
b) Allergic reactions
c) Weakness
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct Octanol water partition coefficient-
| i. Isosorbide dinitrate | A. 1.31 |
| ii. Esomeprazol | B. 5.8 |
| iii. Azatadine | C. 3.59 |
| iv. Meclizine | D. 0.6 |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
Q.6 An example of drug from class Organic nitrate antianginal drug?
a) Procyclizine
b) Meperidine
c) Alprazolam
d) Isosorbide dinitrate
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of drug isosorbide dinitrate is
a) Dihydroopyridine
b) Furan
c) Phenyl
d) Pyrimidine
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-b
4-d
5-c
6-d
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.