LOPERAMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
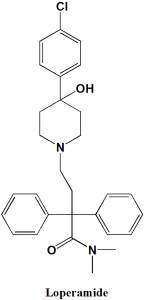
Loperamide
IUPAC nomenclature
4-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-N,N-dimethyl-2,2-diphenylbutanamide
Classification
- Loperamide falls under category of antidiarrheal agents.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 477 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 222.1°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 405 mg/L in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 5.5 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl, piperidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Loperamide is a non-selective calcium channel blocker.
- Loperamide slows the intestinal motility and affects water and electrolyte movement through the bowel.
- Peristaltic activity is inhibited by direct acting of the drug on the circular and longitudinal muscles of the intestinal wall.
- At higher concentrations, loperamide binds with calmodulin.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for Opiates can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the drug less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than morphine.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activates the compound by 4.2 times.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group inactivates the compound and makes it lesser active.
- By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage, activity increases by 1.2 times.
- On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom, activity decreases.
- On replacement of N-CH3 by NCH2CH2Ph, activity increases by 14 times.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N-allyl/methallyl/propyl, the compound so formed acts like the Morphine antagonist.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N(CH3)2 Cl– , compound have curare action and it do not possesses any analgesic activity.
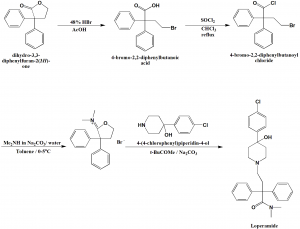
Method of synthesis
i. Ring opening of compound 2,2-diohenyl-4-hydroxubutyric acid y lactone with 48% HBr in acetic acid to get 4-bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyric acid.
ii. Reaction of last with thionyl chloride in chloroform produces 4-bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyroyl chloride.
iii. Compound formed in ii. Step is dissolved in toluene and dimetylamine and sodium carbonate in water are carefully added to it at low temperature to get tetrahydro-3,3-diphenyl-2-furylidene ammonium salt.
iv. Coupling of dimethyl(tetrahydro-3,3-diphenyl-2-furylidene)ammonium bromide with 4-(4-chlorophenyl)piperidin-4-ol on refluxing reagents in isobutyl methyl ketone in presence of excess sodium carbonate produces the Loperamide drug. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Loperamide is used for:
- Treatment of sudden diarrhea
- To reduce the amount of discharge in patients who have undergone ileostomy
- Treatment of on-going diarrhea in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Side Effects
Side effects Loperamide are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Irregular heartbeats
- Fainting
- Allergic reactions
- Rash
- Trouble breathing
MCQs
Q.1 “4-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-N,N-dimethyl-2,2-diphenylbutanamide” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Chlorpromazine
b) Sevoflurane
c) Loperamide
d) Thioridazine
Q.2 Correct melting point of the drug Loperamide is?
a) 154°C
b) 782°C
c) 222°C
d) 157°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Loperamide | A. Antidiarrheal agent |
| ii. Diazepam | B. ß-blockers |
| iii. Halothane | C. Sedative hypnotic |
| iv. Betazolol | D. Anticonvulsant drug |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
Q.4 Mechanism of action of drug Loperamide includes?
I. It is a selective α-blocker.
II. It increases the intestinal motility.
III. Peristaltic activity is inhibited by the drug.
IV. Drug can also bind with calmodulin at higher concentrations.
a) III, IV
b) II, IV
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of opiate drugs?
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the morphine less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than morphine.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activates the compound by 4.2 times.
a) FFTT
b) TFTF
c) TFFT
d) TTTT
Q.6 Type of ring present in the structure of Loperamide is?
a) Piperidine
b) Pyridine
c) Pyrimidine
d) Pyrrole
Q.7 The drug loperamide is used for?
a) Treatment of diarrhea
b) Treatment of pain
c) As an anti-inflammatory agent
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-a
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-a