LOPINAVIR Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
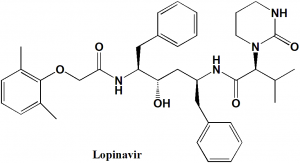
Lopinavir
IUPAC nomenclature
(2S)-N-[(2S,4S,5S)-5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide
Classification
Lopinavir is an HIV protease inhibitor.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 628.8g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to light tan powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 124-127°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in methanol. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | log Kow = 5.94 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrimidine, benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 4 |
Mechanism of Action
- Gag polyprotien is very crucial for the lifecycle of the HIV. HIV-1 protease enzyme is responsible for the cleaving of Gag polyprotien.
- Lopinavir inhibits the HIV-1 protease enzyme.
- Proteolysis of GAG polyprotien is thus inhibited due to prevention of HIV-1- protease activity.
- Due to this, immature and non-infectious viral particles are produced.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the side chain with the conformationally constrained hexahydrofurofuranyloxy P(2) ligand in combination with a dimethylphenoxyacetate on the other end of the drug core diamine yielded highly potent HIV protease inhibitors.
- Substituted groups on the P1 aromatic rings have influence on their biological activity.
- Compounds having an alkyl or fluorine atom at the meta or para position on their P1 benzene ring are good inhibitors.
- Substitutions on the P2 ring is also important for good antiviral property [1]
Method of synthesis
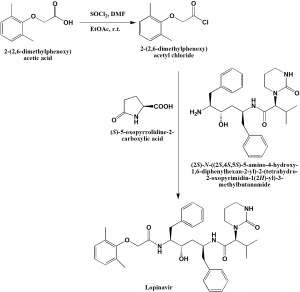
i. Reaction of 2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetic acid with thionyl chloride in EtOAc at room temperature to get the acyl chloride product.
ii. Reaction of the acyl chloride compound formed with pyroglutamate salt in ethyl acetate under Schotten-Baumann reaction conditions in presence of water solution of sodium bicarbonate for the liberation of free amine, produces lopinavir. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
- Lopinavir and Ritonavir are given in combination for the treatment ad prevention of HIV infection.
- Lopinavir and Ritonavir are given in combination for the treatment ad prevention of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19/Novel Corona Virus Infection
Side Effects
Side effects of Lopinavir are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Stomach upset
- Trouble sleeping
MCQs
Q.1 ‘Kaletra’ is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Chloroquine
b) Lopinavir
c) Triptorelin
d) Albuterol
Q.2 Correct statement related to the solubility of the drug lopinavir is?
a) Freely soluble in water
b) Soluble in water
c) Slightly soluble in water
d) Practically insoluble in water
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Lopinavir | A. Neuraminidase inhibitor |
| ii. Acyclovir | B. Acyclic nucleoside analogue |
| iii. Peramivir | C. HIV protease inhibitor |
| iv. Raltegravir | D. HIV integrase inhibitor |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Lopinavir?
I. Inhibition of HIV-1 protease enzyme
II. Production of immature and non-inective viral particles
III. Proteolysis of Gag polyprotien is inhibited
a) II – I – III
b) I –III – II
c) III – II – I
d) II – III – I
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug lopinavir?
- Replacement of the side chain with the conformationally constrained hexahydrofurofuranyloxy P(2) ligand in combination with a dimethylphenoxyacetate on the other end of the ritonavir core diamine yielded highly potent HIV protease inhibitors.
- Substituted groups on the P1 aromatic rings have influence on their biological activity.
- Compounds having an alkyl or fluorine atom at the meta or para positionon their P1 benzene ring are good inhibitors.
- Substitutions on the P2 ring is also inmportantfor good antiviral property.
a) FFTF
b) FTFT
c) TTTT
d) TFFT
Q.6 Type of ring present in the structure of lopinavir?
a) Triazole
b) Pyrimidine
c) Purine
d) None of the above
Q.7 The drug lopinavir is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of Parkinson
b) Treatment of HIV
c) Treatment of malaria
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-b
2-d
3-c
4-b
5-c
6-b
7-b