Lymphatic Organs and Tissues; Question answer for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse Exam
The lymphatic organs and tissues are broadly classified into two groups- first is the primary lymphatic organs where the stem cells divide, these include red bone marrow and thymus. The second group is known as secondary lymphatic organs which are involved in immune responses and these include spleen, lymph nodes and lymphatic nodules. Lymphatic nodes, spleen, thymus are lymphatic organs because they are surrounded by a connective tissue capsule; on the other hand lymphatic nodules are not considered as organs because they lack capsule.
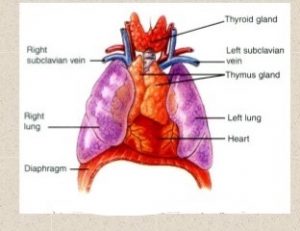
1. THYMUS:-
the thymus gland lies in the upper part of the mediastinum and extends upward till the neck. It weighs around 10-15g and weight increases till puberty when the maximum weight is 30-40g. Anteriorly associated with thymus is the sternum and four coastal cartilage, posteriorly is the aortic arch and inferiorly is the heart.
the thymus consist of two lobes which are joined together by the areolar tissue and these lobes are enclosed by fibrous capsule, and divides the lobes into lobules which consist of lymphocytes and irregularly arranges epithelial cells.
lymphocytes originate from red bone marrow and those who migrate to thymus develops into T- lymphocytes. the T-lymphocytes can distinguish the self(body) tissues from foriegn tissues, also it has the ability to react on only one specific antigen out of millions.
2. LYMPH NODES:-
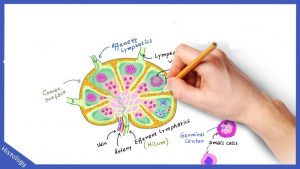
Lymph nodes are the oval bean-shaped organs which are mostly found in groups inside the lymph vessels. the lymph has to compulsory pass through 8-10 modes before it enters into the blood. It has an outer fibrous capsule that comes down to the lymph substance and divides them in partitions known as trabeculae. The main substance of lymph node is the reticular and lymphatic tissue which contains lymphocytes and macrophages. Nods also consist of afferent and efferent vessels, afferent vessels from where lymph enters the nodes and efferent from where the lymph exits. the large no. of lymph nodes are present in groups In different parts of the body.
functions of lymph nodes include
- filtration:-lymph is filtered as it passes through the reticular and lymphatic tissue where it destroys the unwanted substances and worn out cells(dead cells).
- Phagocytosis:- some of the organic particles which are inhaled can be removed by phagocytosis.
- proliferation of lymphocytes:- both the T and B-lymphocytes increases in number within the nodes. antibodies are produced by B-lymphocyte which enters into the blood.
3.SPLEEN:-
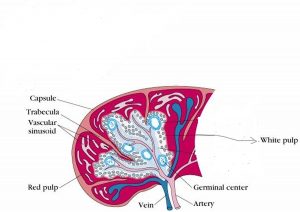
it is the largest lymphatic organ which also contains reticular and lymphatic tissue. it is oval in shape and lies in the abdominal cavity between the fundus of the stomach and the diaphragm. it is purple in color and is about 12cm long, 7cm wide and weighs about 200g. It is surrounded by a capsule made of fibrous and elastic tissue which further on dividing forms trabeculae. Between the trabeculae is the cellular material known as splenic pulp which contains lymphocytes and macrophages.
functions of spleen are
- phagocytosis
- storage of blood- spleen stores about 350ml of blood and during sympathetic stimulation, it returns the blood for circulation.
- immune responses through lymphocytes and macrophages
4. LYMPHATIC NODULES:-
these are the egg shaped mass of lymphatic tissue and not surrounded by a capsule. the lymphatic nodules mostly occur in multiple numbers in specific areas, like tonsils which are found in the pharyngeal regions likewise some occur in ileum of small intestine, some forms the ring at the junction of oral cavity and oropharynx. some of the nodules are scattered by the lamia propria of mucous membrane that lines GIT, urinary, respiratory systems etc, so the lymphatic nodules of these regions are also known as mucous-associated lymphatic tissue(MALT).
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. Where is the thymus gland located?
A. lower part of mediastinum B. upper part of mediastinum
C. behind the mediastinum D. in front of mediastinum
2. Where is the spleen situated?
A. abdominal cavity B. pelvic cavity
C. in the neck D. GIT
3. what is the function of lymphatic system
A. Immunity B. transports lipids from GIT to the blood
C. drains excess interstitial fluid D. all of the above
4. Why lymphatic nodules are not known as a lymphatic organ?
A. because they are less in no. B. due to their small size
C. lacks the surrounding capsule D. both B and c
5. Match the following-
1. responsible for the development of a. spleen
T-lymphocytes
2. works as blood reservoir b. lymphatic nodules
3. MALT c. thymus
4. filtration d. lymph nodes
6. What is the main function of T-lymphocytes?
A. detect self tissue from foreign tissue b. filtration
c. blood reservoir d. forms antibodies
7. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. lymphatic system filters both lymph as well as blood
B. lymph transports proteins from GIT into the blood
c. the capsule that surrounds the spleen is a fibroelastic capsule
D. B-lymphocytes produces antibodies
8. Where are the tonsils situated?
A. ileum f small intestine B. pharyngeal region
C. urinary bladder D. at the junction of oral cavity
9. How much is the length of a spleen?
A. 12cm B. 5cm
C. 8cm D. 14cm
10. In which region, the lymphatic nodules are known as MALT?
A. heart chambers B. brain
C. shoulders D. none of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. upper part of mediastinum
2. abdominal cavity
3. all of the above
4. lacks surrounding capsule
5. 1 – c 2 – a 3 – b 4 – d
6. detect self tissue from foreign tissue
7 lymph transports proteins from GIT into the blood
8. pharyngeal region
9. 12cm
10. none of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:
1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-:136-139 .
2. Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 836-841.