MELOXICAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
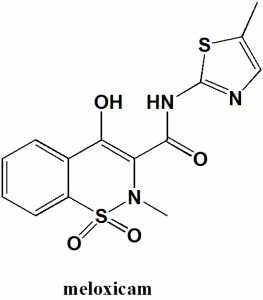
Meloxicam
IUPAC nomenclature
4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
Classification
- NSAID
- Oxicames
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 351.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Pastel yellow solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 254oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in methanol; Freely soluble in strong acid and bases; practically insoluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.9 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzothiazine, thiazole |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Meloxicam selectively inhibits COX-2 enzyme which decreases the synthesis of prostaglandins and thus, acts as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug.
- It also exerts very small effects on COX-1 which is the cause of the GI irritation and other side effects.
Structure Activity Relationship
General SAR for Oxicams can be summarized as follows:
- Substitution on the nitrogen atom of the thiazine ring gives optimum activity.
- Substitution on the caboxamide with aryl group gives compounds with greater activity than when substituents are alkyl groups.
- N-heterocyclic compounds are more acidic than N-aryl carboxamides.
- Primary carboxamides are more potent than secondary carboxamides.
- m-substituted derivatives are more potent than p-substituted derivatives.
- Maximum activity is found with m-Cl substituent in the aryl series.
- Substitution on the carboxamide Nitrogen with heteroaryl group gives compound with seven fold greater anti-inflammatory activity than the aryl group substitution. [1]
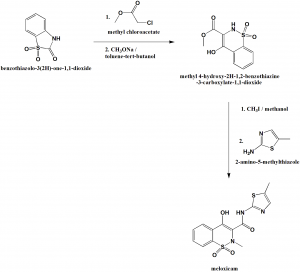
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of benzothiazolo-3-(2H)-one-1,1-dioxide with methyl chloroacetate to produce methyl-2(3H)-acetate derivative.
ii. Isomerization with sodium methoxide in toluene-tert-butanol to give methyl-4-hydroxy-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide.
iii. Methylation with methyl iodide in methanol to produce 2-methylcompound.
iv. Treatment with 2-amino-5-methylthiazole in xylene to get meloxicam.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Meloxicam is used for:
- Treatment of pain and swelling due to rheumatoid arthritis
Side Effects
Side effects of meloxicam are:
- Skin rash
- Shortness of breath
- Stomach bleeding
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Itching
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Dark colored urine
- Jaundice
- Painful urination
- Anemia
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Swelling of face
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Flu like symptoms
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the class Oxicams NSAIDs-
| i. Substitution on the nitrogen atom of the thiazine ring gives optimum activity | A. gives optimum activity |
| ii. Lipophillic group which is noncoplanar with the aromatic or heteroaromatic ring | B. gives minimum activity |
| C. greater activity than when substituents are alkyl groups | |
| D. lesser activity than when substituents are alkyl groups |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Meloxicam: 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-1,1-dioxo-1λ6,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide
- Bitolterol: [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid
- Aspirin: 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid
- 5-FU: {(1Z)-5-fluoro-2-methyl-1-[4-(methylsulfinyl)benzylidene]-1H-indene-3-yl}acetic acid
a) TFTF
b) FFFT
c) TTTT
d) TFFT
Q.3 Molecular weight of drug Meloxicam is?
a) 462.25 gm/mol
b) 254.0 gm/mol
c) 426.21 gm/mol
d) 62.1 gm/mol
Q.4 Meloxicam mechanism of action includes?
a) It exerts effect only on COX-2
b) It exerts effect only on COX-1
c) It exerts effect on COX-1 and on COX-2
d) It do not produce any effect on COX
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Meloxicam?
a) Treatment of Cardiac arrest
b) Reducing pain due to arthritis
c) Controlling vomiting
d) All of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Flutamide: Ethylinimine
II. Meloxicam: DMARDs
III. Zomepirac: NSAIDs
IV. Atenolol: ß-blocker
a) III, IV
b) II, III
c) I, II, III, IV
d) II
Q.7 Treatment of 2-amino-5-methylthiazole in xylene produces which drug?
a) Ibuprofen
b) Diclofenac
c) Halothane
d) Meloxicam
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-a
3-b
4-c
5-b
6-a
7-d