MEPERIDINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ, Structure, Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
MEPERIDINE
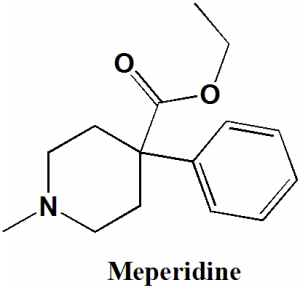
IUPAC nomenclature
Ethyl 1-methyl-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
Classification
- Opiate (narcotic) analgesics
- Pethidine also known as Meperidine
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 247.33g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 270°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 0.01M |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.72 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Piperidine, phenyl |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Meperidine is a kappa-opiate receptor agonist.
- It binds with G-protein receptor and produces positive and negative synaptic transmissions via G-protein which activates the effector proteins.
- Binding of drug also stimulates exchange of GTP for GDP on the G-protein complex.
- Drug also decreases the intracellular cAMP by inhibiting adenylate cyclase enzyme.
- The release of neurotransmitters like substance P, noradrenaline, acetylcholine, dopamine, GABA is inhibited by the drug.
- There is also decrease in the release of vasopressin, somatostatin, insulin and glucagon.
- Neuronal excitability is reduced by closing of the N-type voltage-operated calcium channels and opening of the calcium-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channels, which results in hyperpolarization.
Structure Activity Relationship
SAR for Opiates can be summarized as follows:
- Replacement of phenolic hydroxyl into –OCH3/-OC2H5 will make the morphine less analgesic and cough suppression will also takes place.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound 5 times more active.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with -OC2H5 makes the compound 2.4 times more active than morphine.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCOCH3 will also activates the compound by 4.2 times.
- Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with ketone group inactivates the compound and makes it lesser active.
- By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage, activity increases by 1.2 times.
- On replacement of the methyl group from tertiary nitrogen by hydrogen atom, activity decreases.
- On replacement of N-CH3 by NCH2CH2Ph, activity increases by 14 times.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N-allyl/methallyl/propyl, the compound so formed acts like the Morphine antagonist.
- When the methyl group of tertiary nitrogen replaced by N(CH3)2 Cl– , compound have curare action and it do not possesses any analgesic activity.
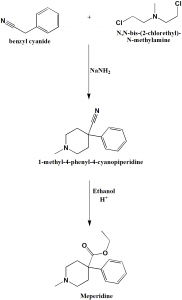
Method of synthesis
i. Alkylation of benzyl cyanide using N,N-bis-(2-chlorethyl)-N-methylamine in presence of sodium amide to form 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-cyanopiperidine.
ii. On subsequent acidic ethanolysis, meperidine is formed. [1]
Therapeutic Uses
Meperidine is used for:
- Relief from moderate to severe pain
- Before and during surgery
Side Effects
Side effects of meperidine are:
- Respiratory depression
- Circulatory depression
- Respiratory arrest
- Shock
- Cardiac arrest
- Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Sweating
- Sedation
- Shortness of breath
- Sedation
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Euphoria
- Hypotension
- Palpitations
- Syncope
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Anxiety
- Headache
- Somnolence
- Weakness
- Visual problems
- Tremors
- Severe convulsions
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the Opiates.
| i. Replacement of alcoholic hydroxyl with –OCH3 makes the compound | A. Activity increases |
| ii. By hydrogenation of alicyclic unsaturated linkage | B. Activity decreases |
| C. Activity increases | |
| D. Activity decreases |
a) i-A, ii-C
b) i-A, ii-D
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-B, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
I. Meperidine: Ethyl 1-methyl-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
II. Lorazepam: 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one.
III. Homatropin: (N-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
IV. Ephedrine: (1R,2S)-2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpropan-1-ol
a) TFFF
b) FTFT
c) TTTT
d) FTTF
Q.3 Correct statement related with the solubility of the drug Meperidine from the following is?
a) Solubility in water is approx. 0.01M
b) Solubility in water is approx. 0.1M
c) Solubility in water is approx. 1M
d) Solubility in water is approx. 10M
Q.4 Meperidine inhibits?
a) Release of parathormone
b) Excretion of glucose in urine
c) Adenylate cyclase enzyme
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug meperidine?
a) As an anesthetic agent
b) Relief from moderate to severe pain
c) Treatment of migraine headaches
d) Treatment of Parkinson diseases
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Meperidine: Inhalational anesthetics
II. Diclofenac: Anti-inflammatory drug
III. Bethanechol: Choline ester cholinergic agonist
IV. Acetylcholine: Alkaloid cholinergic agonist
a) I
b) II, IV
c) II, III
d) , I, IV
Q.7 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-cyanopiperidine can be converted into meperidine by?
a) Methanolysis
b) Ethanolysis
c) Phosphorylation
d) Chlorination
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-a
4-c
5-b
6-c
7-b